Contents:
- Medical Video: Stages of Kidney Disease
- What is diabetes?
- What is kidney failure?
- How to deal with kidney failure?
- If I have kidney failure and diabetes, what is my treatment like?
- Can someone with diabetes get a kidney transplant?
- What about pancreatic kidney transplants?
Medical Video: Stages of Kidney Disease
What is diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your body doesn't make enough insulin or can't use insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone. It controls how much sugar in your blood. A high level of sugar in your blood can cause damage to very small blood vessels in the kidneys. Over time, this can cause kidney disease and kidney failure.
What is kidney failure?
Healthy kidneys do a lot of important work. They filter blood, maintain fluid balance, and make hormones that help control your body's blood pressure, have healthy bones, and make red blood cells. If you have kidney failure, that means the kidneys have stopped working well enough to do this important work and make you live. As a result:
- Hazardous waste accumulates in your body.
- Your blood pressure will rise.
- Your body can contain too much liquid.
- Your body cannot make enough red blood cells.
When this happens, you need treatment to replace a failed kidney job. There is no cure for kidney failure. Someone with kidney failure needs care for life.
How to deal with kidney failure?
Three types of treatment can be used if the kidney fails, namely:
- hemodialysis
- peritoneal dialysis
- kidney transplant
Your team of doctors will discuss the differences in care with you and answer all your questions. They will help you choose the best treatment for you, based on your health, lifestyle, and general care preferences. Your decision does not need to be a final decision. Many people have used each of these treatments at different times in their lives.
If I have kidney failure and diabetes, what is my treatment like?
A kidney doctor (called nephrologist) will plan your treatment with you, your family, and your dietitian. Besides dialysis or transplantation, you will need:
- Keep your blood sugar under control. This is usually done with diet, exercise, and, if needed, insulin injections or hypoglycemic pills. The insulin dose must change when people do dialysis or get a new kidney transplant.
- Test for A1C regularly. Your A1C test will tell you your average blood sugar over the past 2-3 months. This also helps the doctor find out if your diabetes is under control. Ask your health team what the A1C results are good for you. Keeping your A1C at goal value will help protect your heart, blood vessels, eyes, legs and nerves.
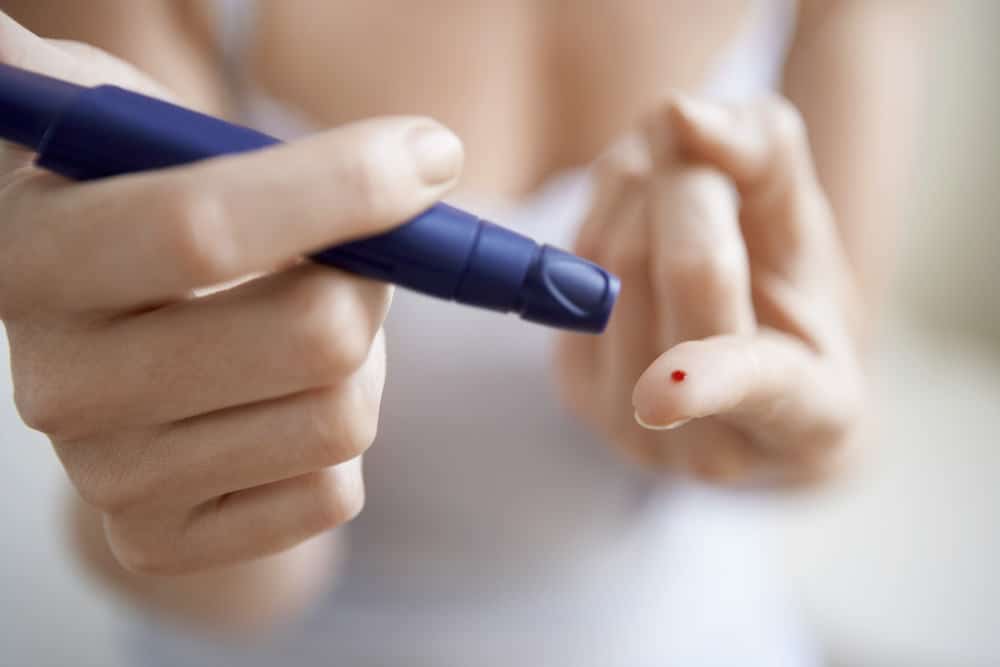
- Use a blood glucose meter. You also have to check your blood sugar levels every day. You can do this test at home with a blood glucose meter. This test is usually done several times a day. This method will tell you how much blood sugar you have at any time.
- Protect yourself against low blood sugar. Most people know that high blood sugar is dangerous. But low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can be dangerous too. The risk of low blood sugar is higher if you are on dialysis, especially if you have difficulty eating, frequent stomachaches, or have other digestive problems. Tell your doctor if you have these symptoms.
- Tested regularly for heart and blood vessel disease. Heart and blood vessel problems are a common problem in people with diabetes and kidney failure.
- Manage your diet carefully. There are special food needs for diabetics who also undergo dialysis. A dietitian who specializes in kidney disease can help you with this.
- Control high blood pressure. You should check your blood pressure as often as your health care provider recommends. You may also need to use drugs to control your blood pressure.
- Manage blood cholesterol and lipids. If your cholesterol and lipids are too high, you might need medication to help lower them.
- Manage anemia (low red blood cell count), if needed. People on dialysis often experience anemia. Treatment involves the use of a special drug called ESA (erythropoiesis agent) and iron supplements to help make red blood cells.
- Manage mineral imbalances and bone disorders, if needed. Many people with kidney failure have mineral disorders and bone disorders. You may need special medication for this condition.
- Follow your diabetes treatment plan, diet and exercise. You must continue to follow your diabetes, diet and exercise treatment plan. This will help protect your entire body, including your heart, blood vessels, eyes, nerves and feet.
Can someone with diabetes get a kidney transplant?
Yes. If you get a new kidney, you may need higher doses of insulin or hypoglycemic pills (for lower blood sugar levels). This is because:
- You will eat more.
- Your new kidney will break down insulin better than your old kidney.
- You will use drugs to keep your body from rejecting new kidneys, these drugs can react poorly to insulin.
- If your transplant kidney loses its function, dialysis treatment can begin and you can wait for a new kidney.
What about pancreatic kidney transplants?
If you have type 1 diabetes, it is also possible to do a pancreatic transplant. This can be done at the same time as a kidney transplant or soon after. The pancreas is an organ in the body that helps produce insulin. Pancreatic transplantation gives you the opportunity to stop using insulin injections. Your doctor can tell you about this procedure.