Contents:
- Medical Video: Type 1 Diabetes | Nucleus Health
- What is diabetes?
- Why can you get diabetes?
- Sugar digestion and absorption
- What are the symptoms?
- Other symptoms of diabetes that you should be aware of
- 1. Feet hurt and numb
- 2. Blurred vision
- 3. Changes in the state of the skin
- 4. Susceptible to infection or disease
- 5. Red and swollen gums
- 6. Slow healing of wounds
- 7. Hungry fast
- 8. Sudden weight loss
- When should I go to the doctor?
- What is diabetes medicine?
- Medication for type 1 diabetes
- Medication for type 2 diabetes
- What are some lifestyle changes to help overcome this condition?
- 1. Maintain diet and nutritional intake
- 2. Regular exercise
- 3. Diligently check your blood sugar every day
- 4. Make sure you always take medication or inject insulin
Medical Video: Type 1 Diabetes | Nucleus Health
Diabetes is nicknamed the "mother of all diseases", because of this condition can affect many organs in the body. High blood sugar levels in diabetics can cause many complications. Some of the organs that can be affected are the heart, kidneys, eyes, blood vessels, and nervous system. Let's see more about this disease.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus or commonly called diabetes is a chronic disease. This condition is characterized by a disruption of the regulation of blood sugar in the body due to various things such as:
- Lack of insulin production by the pancreas
- Lack of body response to insulin
- The influence of other hormones that inhibit insulin performance
Therefore, diabetes is divided into several types, namely:
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disorder that causes the endurance system to attack and damage the cells that produce the hormone insulin, so that the pancreas cannot produce these hormones. This will cause the body to lack insulin and increase blood glucose levels.
This condition generally affects patients under the age of 40 years, especially in adolescence. Usually the symptoms of this disease are detected more quickly at a younger age, especially in childhood or adolescence.
The cause of this condition is unclear. Experts suspect that the cause of this disease may be due to genetic and environmental factors. However, you may have a higher risk of developing this condition if:
- your parents or siblings who suffer from this condition
- in a state of exposure to viral diseases
- appearance of autoantibodies
- vitamin D deficiency, consuming cow's milk or formula milk, and cereal before 4 months of age. Although it does not directly cause this condition to occur, it is still risky.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common type of sugar disease, because it occurs in 90-95 percent of all cases.
Unlike type 1 diabetes, type 2 sufferers continue to produce insulin. This condition is more common in adults, because it is often called adult-onset diabetes.
Even so, the exact cause of this is actually uncertain. But experts believe that genetic and environmental factors play a role in the causes of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Being overweight is a major trigger for diabetes, but not all type 2 diabetes mellitus patients are overweight.
Other types of diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that only occurs in pregnant women. This disease can cause problems in the mother and her babies if not treated. However, this condition usually resolves after giving birth.
Other types of the disease usually result from genetic syndromes, surgery, drugs, malnutrition, infections and other diseases. Diabetes insipidus is a different condition caused by the inability of the kidneys to store water. This condition is rare and can be treated.
Why can you get diabetes?
Sugar digestion and absorption
Previously please note, that the condition of this disease is closely related to blood sugar levels (glucose). Glucose is very important for the body, because it works as an energy source for the cells and tissues of the body, especially the brain. Glucose actually comes from the food you eat and from being stored as a backup in the liver (liver). The type of glucose stored in the liver is called glycogen.
If you haven't eaten automatically your blood sugar levels will be low, the liver will break down glycogen into glucose and balance your blood sugar levels.But unfortunately, the body's cells cannot use "fuel" directly without the help of the hormone insulin which should be produced by the pancreas gland.
The hormone insulin makes glucose easier to absorb by the body's cells so that it lowers sugar levels in the bloodstream. However, if you experience impaired pancreatic function to the amount of insulin production, the blood sugar levels will continue to increase.
Meanwhile, the cells in the body that ultimately don't get 'fuel' will feel hungry. This then makes the body assume that it is deficient in sugar so that it breaks down glycogen again. In the end, sugar will continue to accumulate in the blood and there will be high blood sugar levels called hyperglycemia.
What are the symptoms?
The main symptoms of diabetes:
- Often feel thirsty
- Frequent urination, sometimes occurs every hour and is called polyuria
- Unclear and sudden weight loss
- Fatigue
Symptoms that are rare:
- Nausea or vomiting
- In women vaginal infections often occur
- Fungal or thrush infections
- Dry mouth
- Wounds are difficult to heal
- Itching of the skin, especially in the groin or vaginal area
Other symptoms of diabetes that you should be aware of
1. Feet hurt and numb
Very high blood sugar levels will cause damage to the body's nerves. Not all people experience these symptoms.
But people who have diabetes will feel numbness, tingling, and pain in the body, especially in the legs. Symptoms like this usually occur in someone who has had diabetes for 5 years or more.
2. Blurred vision
Blurred views on diabetics (designation for diabetics) usually come from lens disorders (cataracts) or eye nerve disorders (diabetic retinopathy).
The condition of blood sugar that is high enough can trigger a buildup of protein in the lens of the eye resulting in cataracts. Uncontrolled blood sugar can also cause the small blood vessels in the eye to be disturbed or even ruptured so that the eye nerve (retina) cannot work properly.
3. Changes in the state of the skin
High levels of insulin encourage pigments that cause black spots on the skin. If there are changes that are felt on the skin, it could be the first sign that you have diabetes or diabetes. Changes can be characterized by skin that becomes dark, scaly, and early wrinkles appear.
4. Susceptible to infection or disease
Someone with early symptoms of diabetes tends to be more susceptible to bacterial and fungal infections because they have a decreased immune system.
These microorganisms need glucose as their energy source. Infection can grow in warm and moist skin folds, such as between the fingers and toes, under the breasts, or in or around the genitals.
5. Red and swollen gums
This sugar disease can weaken your immune system and your ability to fight infection, increasing the risk of infection in your gums and jaw. Your gums can be swollen or may be injured.
6. Slow healing of wounds
High blood sugar can affect blood flow and cause nerve damage in the body area which interferes with your body's natural healing process.
Knowing the symptoms early will make it easier for you to deal with these symptoms and even prevent them. Diabetes or diabetes can also be prevented by doing regular exercise, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and keeping blood sugar levels normal.
To maintain normal blood sugar levels, you must limit sugar consumption, but that does not mean you are anti sugar, all you can do is replace your daily sugar. Use low-calorie and sugar-free sweeteners to prevent sugar disease and control calorie intake.
7. Hungry fast
The lack of insulin to put sugar into cells makes the muscles and organs weaken and the body runs out of energy. The brain will think that lack of energy is due to lack of food, so the body tries to increase food intake by sending hungry signals.
8. Sudden weight loss
Although appetite increases, diabetics can experience weight loss, even very drastically. Be careful if the change is up to 5 percent of body weight.
Because the ability of glucose metabolism is impaired, the body will use anything else as 'fuel', such as muscle and fat so that people will look thin.
When should I go to the doctor?
You should immediately see a doctor to check the condition if you feel the symptoms of diabetes mentioned above. In addition, you need to call an emergency number if you feel:
- feeling nauseous and weak
- feeling excessive thirst and when urinating accompanied by abdominal pain
- breathe fast
What is diabetes medicine?
Diabetes is an incurable disease. But that does not mean you feel hopeless. This diabetes or diabetes can still be overcome and controlled in a certain way. You can take drugs to control this disease. Here is a cure for diabetes or diabetes:
Medication for type 1 diabetes
Diabetics who have type 1, your body attacks cells that produce insulin so that the body's insulin levels are reduced. Thus, in the type 1 diabetes mellitus medication, patients will generally be given diabetes medication in the form of insulin which will be injected into the patient's body every day. Some types of insulin include:
- Insulin with fast action. Insulin will usually be given when you only have a little time to inject insulin, such as when sugar levels exceed the target.
- Insulin with slow action. In contrast to insulin with rapid action, slow-acting insulin is commonly used when you have a longer time to inject insulin. But compared to fast-acting insulin, slow-acting insulin is used less frequently.
- Insulin with intermediate action. Although the length of time this type of insulin is injected is relatively long, intermediate insulin action is usually combined with faster action, so as to maximize the benefits of injecting.
Medication for type 2 diabetes
In this condition, generally what happens is that your body is not able to use insulin, as it should. So, unlike the case with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, a diabetes drug in the form of capsules taken orally every day will generally be given, or even you may only be encouraged to increase the quantity of your exercise.
Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and diet specifically for diabetes are the main choices in dealing with diabetes. If this is not enough, diabetes medication can help you.
It should also be considered, some type 2 diabetes drugs are able to give some side effects, such as type 2 diabetes medication type metformin which causes effects such as bloating to diarrhea. But these side effects do not always appear in everyone. Discuss with your doctor if you experience side effects of the drug.
For type 1 and type 2 diabetes, you need to take a special diet to control blood sugar. You have to eat snacks at the same time every day.
It is also important to always check your blood sugar level with a glucometer and see if there are any signs of your blood sugar level being too low or too high. The doctor will explain to you how to give insulin injections, so you can inject yourself at home, usually 2-3 times a day.
What are some lifestyle changes to help overcome this condition?
1. Maintain diet and nutritional intake
Actually, food for people with diabetes is almost the same as people who are healthy. The difference is that your food is more arranged by them. Healthy eating patterns every day are almost the same as medical nutrition therapy.
Eating healthy foods is intended to always eat nutritious foods, low in fat and calories so you can control blood sugar levels You. What kind of food should be eaten ??
- Foods made from whole grains or complex carbohydrates such as brown rice, baked potatoes, oatmeal, bread and cereals from whole grains.
- Replace your sugar with a low-calorie sweetener and contain chromium to improve insulin function in the body, so that it can help control blood sugar.
- Lean meat steamed, boiled, roasted and burned.
- Vegetables are processed by boiling, steaming, baking or raw consumption. Vegetables that are good for sufferers, such as broccoli and spinach.
- Fresh fruits. If you want to make juice, you shouldn't add sugar.
- Nuts, including soybeans in the form of steamed tofu, are cooked for soup and sauteed.
- Low fat dairy products and eggs.
- Fish such as tuna, salmon, sardines and mackerel.
If you adopt a healthy diet, your body weight remains ideal, your blood sugar levels are stable, and you avoid the risk of heart disease.
Tips for managing your diet if you use insulin
- Inject your insulin.
- Eat the same amount of food every day at almost the same time.
- Don't skip meals, especially if you have received an insulin injection. If you miss it, your blood sugar level will drop.
Tips if you don't use insulin
- Adhere to the diet given.
- Don't skip meals, especially if you are taking oral hypoglycemic drugs (OHO) for this condition. If you miss it, your blood sugar level will drop.
- Skipping time can make you eat too much in the next hour and can cause your blood sugar levels to drop.
2. Regular exercise
The benefits of regular exercise for diabetics is to help keep weight down, insulin can more easily lower blood sugar, help the heart and lungs work better and give you more energy.
You don't need to be too heavy. You can start walking, swimming, cycling near your house, cleaning your house, or starting a hobby of gardening is a good idea so you stay active.
Try exercising at least three times a week for around 30 to 45 minutes. If you are the type of person who rarely sports, try 5 to 10 minutes at the beginning of the sport, from here later you can increase the time.
If your blood sugar level is less than 100-120, eat an apple or a glass of milk before you exercise. When you are exercising, bring snacks so that your blood sugar does not drop.
Tips if you use insulin
- Exercise after eating, not before eating.
- Test your blood sugar before, during, and after exercise. Don't exercise if your blood sugar level is low, less than 70.
- Avoid exercising before bed because it can cause your blood sugar to drop at night.
Tips if you don't use insulin
- See your doctor, if you intend to join a fitness class or exercise training program.
- Your blood sugar test before and after exercise if you take diabetes mellitus medication. Make sure your blood sugar is not lower than 70.
3. Diligently check your blood sugar every day
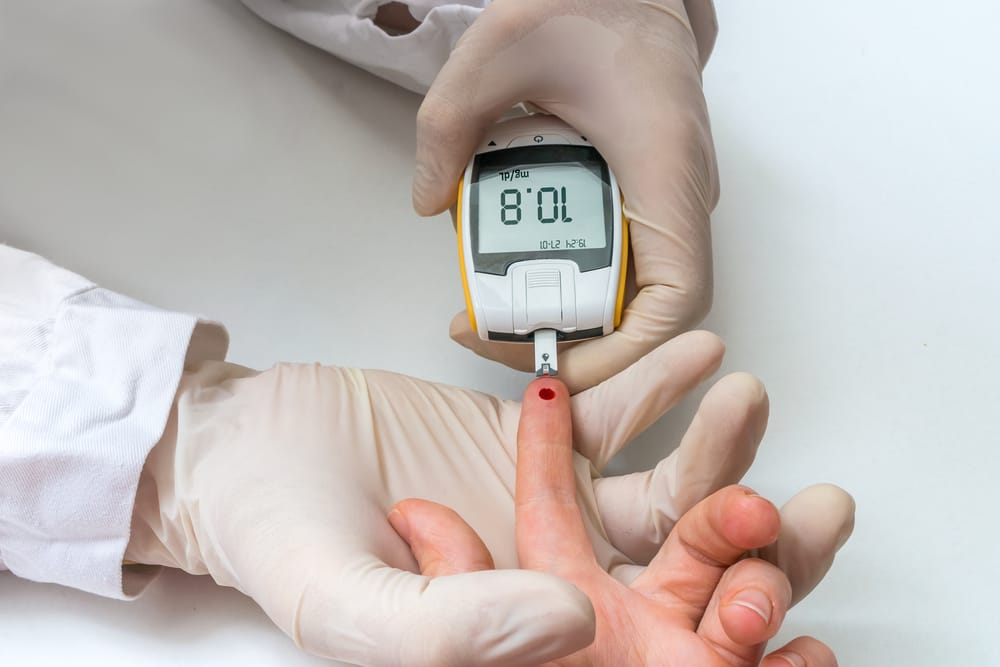
Blood sugar levels must be monitored regularly. This is an important way to deal with and keep your blood sugar levels normal. Blood sugar checks can also provide information about your blood glucose levels at that time. You can use a blood sugar test kit called a glucometer. With usage instructions as follows:
- Make sure your hands have been washed, put the paper in test strip to a blood sugar meter.
- Slowly, prick the fingertips with a sterile needle until the blood comes out
- If the blood comes out a little, slowly massage the finger until the blood comes out enough
- Hold and hold the tip test strip until blood drips on test strip, and wait for the results.
- Your blood glucose level will appear on the device screen
Glucose levels are generally different before and after you eat. For normal blood sugar levels before meals, the levels are around 70-130 mg / dL. Then, blood sugar levels two hours after eating should be less than 180 mg / dL and before bedtime ranges from 100-140 mg / dL.
The amount of blood sugar levels can describe your health condition. High blood sugar levels are considered a sign that your body's condition is not healthy. Record blood sugar levels every time you check blood sugar levels.
4. Make sure you always take medication or inject insulin
Although this condition cannot be cured, an early examination can control the blood sugar levels of people with diabetes. The goal of insulin injection treatment is to maintain a balance of blood sugar levels and minimize the risk of complications.
The right medicines to treat Type 2 Diabetes
The balance of blood sugar levels in diabetics can sometimes not be maintained properly only through the application of a healthy diet and regular exercise. You might also need medication to handle it.
There are several types of drugs (usually in tablet form) that can be used for this condition (oral hypoglycemic drugs). You may also be given a combination of two or more drugs to control your blood sugar levels. The usual medicine is given metformin, sulfonylureas, pioglitazone, gliptin, agonist, acarbose, nateglinide and repaglinide
Insulin therapy as a companion to other medicines
Medicines in tablet form may be less effective for treating diabetes or diabetes, so you need them insulin therapy. Based on the dosage and how to use it, this therapy can be given to replace or be given along with the medicines as mentioned above.