Contents:
- Medical Video: What Is Role of Homocysteine In Cardiovascular Disease?
- Why is high homocysteine levels dangerous?
- What causes high levels of homocysteine?
- How do you measure homocysteine levels?
- How do you reduce high homocysteine levels?
- What happens next?
Medical Video: What Is Role of Homocysteine In Cardiovascular Disease?
Homocysteine is an amino acid (a protein composed of several blocks) produced in the human body.
Why is high homocysteine levels dangerous?
High levels of homocysteine in the blood can damage the arterial lining. In addition, high levels of homocysteine can facilitate the formation of blood clots. This condition can increase the risk of blood vessel blockage. Clots inside the blood vessels are called thrombus. This thrombus can participate in the bloodstream and stagnate in the lungs (called pulmonary embolism), in the brain (which can cause strokes) or inside the heart (which can cause heart attacks). People who have very high levels of homocysteine in their blood have an increased risk of coronary artery disease.
What causes high levels of homocysteine?
Homocysteine is usually converted into other amino acids for use by the body. If the level of homocysteine is too high, chances are the body is deficient in B vitamins used to treat homocysteine.
Most people who have high homocysteine levels lack folate (also called folic acid), vitamin B6 or vitamin B12 in their dietary patterns. Usually, keeping this vitamin intake will help restore homocysteine levels to normal. Other causes are low levels of thyroid hormone, kidney disease, psoriasis, some drugs or when such conditions occur in the family.
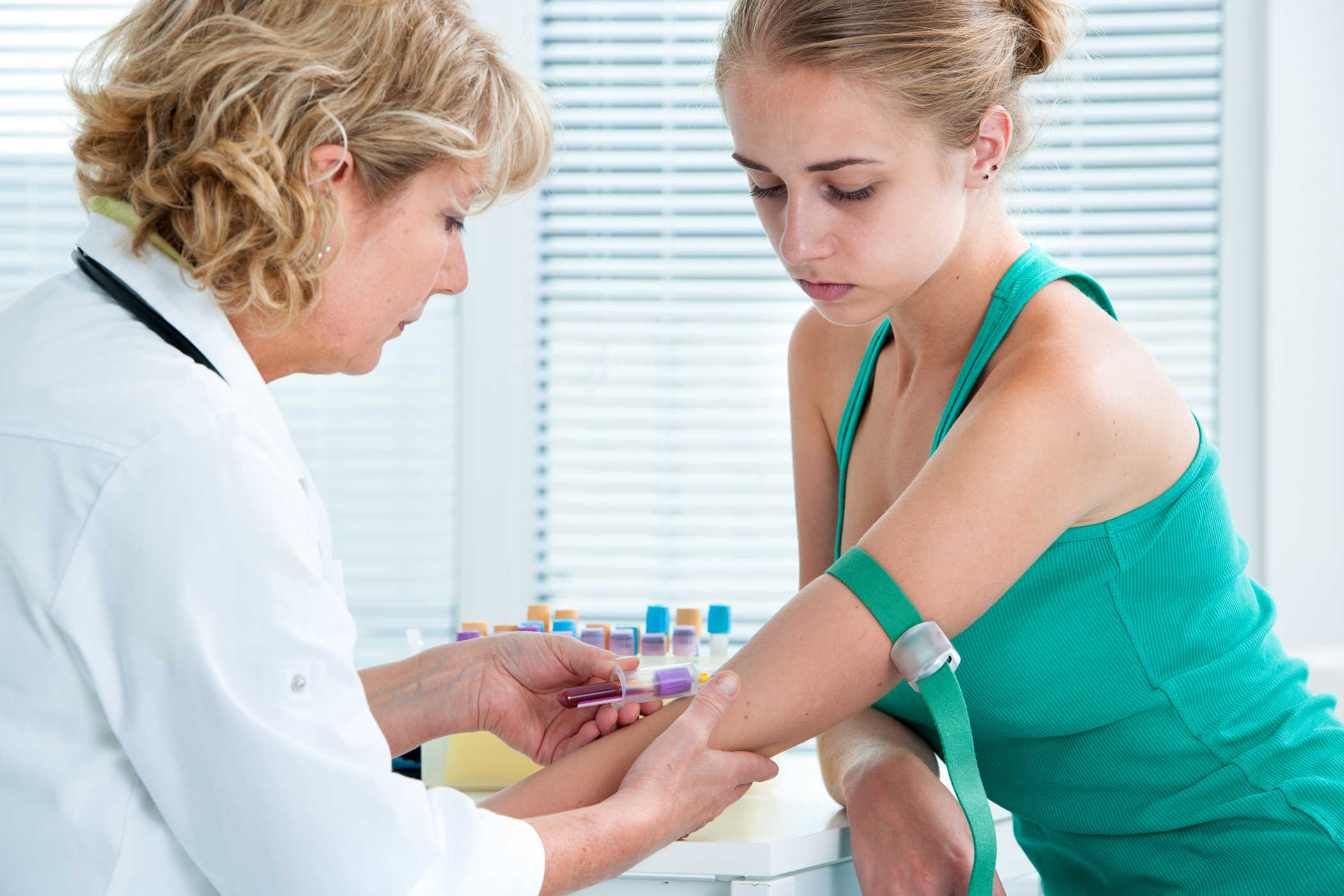
How do you measure homocysteine levels?
Homocysteine is measured using a simple blood test. You do not have to prepare a special method to undergo a blood test.
If the level of homocysteine is too high, you need to reduce it, especially if you have a blockage in the blood vessels. If you don't have the main risk factors for cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in the arteries), your doctor will monitor your condition. If your homocysteine level continues to increase, you need to reduce it.
Although no studies have shown that lowering homocysteine levels can help reduce the risk of strokes, heart attacks and other cardiovascular diseases, it is still a good idea to reduce the risk of heart disease.
How do you reduce high homocysteine levels?
Eating more fruits and vegetables (especially green leafy vegetables) can help reduce homocysteine levels by the percentage of how much folate is obtained in your diet. Good sources of folate include cereals, processed grain products, lentils, asparagus, spinach and almost all types of beans.
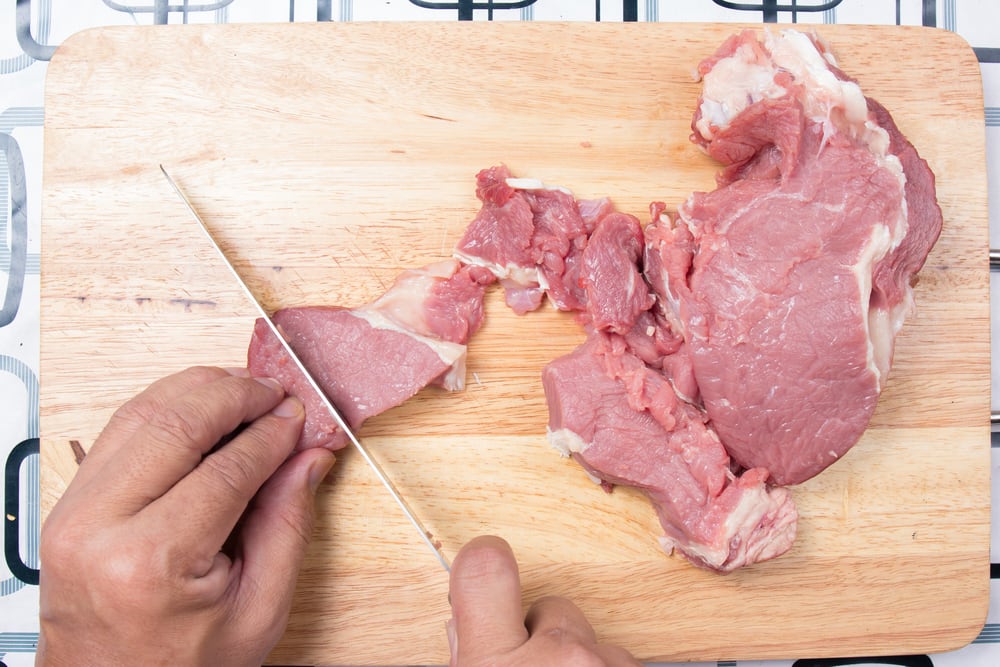
If you don't get enough vitamin B-6 in your diet, foods like cereals, potatoes, bananas, garbanzo beans and chicken are good sources. Dairy products, meat-containing organs (such as the liver), beef meat and some types of fish are good sources of vitamin B-12.
If adjusting your diet has not been enough to reduce your homocysteine levels, your doctor will recommend using folate supplements. You may also need to take vitamin B-6 supplements and vitamin B-12.
What happens next?
If you start taking folate or vitamin B supplements, you should double-check homocysteine levels in the body after 8 weeks. If it's still high, your doctor may recommend using a higher dose. You may have to undergo several tests to find out if you have other health problems that cause an increase in homocysteine levels in the body. If homocysteine levels are high, you need to undergo regular checks (2 or 3 times a year).
Please consult a doctor if you have questions or problems.