Contents:
- Medical Video: Blood Clotting Risks During Pregnancy and Delivery - The Balancing Act
- Is blood clotting after childbirth normal?
- Type of blood clot after giving birth
- Symptoms of normal blood clots after childbirth
- Signs and symptoms of dangerous blood clots
- Overcome blood clots that occur after childbirth
- Can you prevent blood clots after giving birth?
Medical Video: Blood Clotting Risks During Pregnancy and Delivery - The Balancing Act
All women who gave birth must have experienced bleeding for approximately 40 days. Often these bleeding times are accompanied by blood clots that are indicated by the presence of clots in the blood released. Many women question whether normal blood clots after childbirth occur. Well, to distinguish between normal and dangerous, following the review.
Is blood clotting after childbirth normal?
About 6 to 8 weeks after giving birth, the body is in a period of healing. At these times, the body usually experiences bleeding which is known as the name lockia. Not all blood is liquid, some blood clots with a size that is large enough which is usually released profusely 24 hours after birth. Blood clots that are shaped like a collection of gelatin are also normal when the uterus contracts and shrinks and releases the lining after giving birth. This blood is usually sourced from damaged tissue in your uterus and birth canal.
Type of blood clot after giving birth
There are two types of blood clots that are commonly experienced by women after childbirth, namely:
- Clots that are released through the vagina during the postpartum period that originate from the lining of the uterus and placenta.
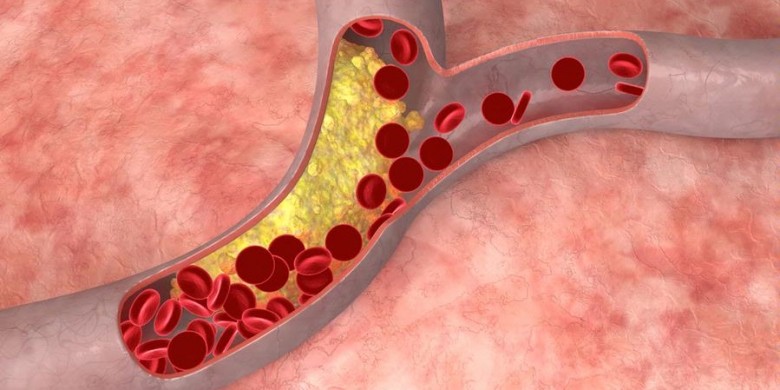
- Clots that occur in the body's blood vessels. This is a rare case but can be life threatening.
Symptoms of normal blood clots after childbirth
Blood clots have a gelatinous appearance that usually contains mucus and certain tissues and can be as large as a golf ball. You may experience this bleeding shortly after birth until 6 weeks afterwards. Following are normal blood clots after childbirth:
- First 24 hours after birth. In this period it is the hardest bleeding period with bright red blood. The size varies, can be about the size of a grape to the size of a golf ball. Usually you need to change the pads every hour because the volume of blood is quite heavy.
- 2-6 days after birth. In this period, blood flow will gradually become lighter, similar to normal blood flow during menstruation. The lumps that are formed even smaller in size compared to the first 24 hours after birth. The color of the blood also becomes brown or pink. If at this time you still have bright red blood, immediately consult a doctor because this indicates bleeding does not slow down as it should.
- 7-10 days after birth. The blood will be brown or pink which starts to fade. The flow also becomes lighter compared to the first week of birth.
- 11-14 days after birth. Blood flow will be lighter and less. In addition, the blood clots will be smaller than the previous days. However, some women state that the blood flow is heavier with bright red color after doing heavy physical activity.
- 2-6 weeks after birth. At this time, some women did not even experience bleeding at all. The blood that was previously pink will turn white or yellow, similar to the vaginal discharge that usually occurs before becoming pregnant.
- 6 weeks after birth. In this period the bleeding will usually stop. However, you will usually find brown, red and yellow blood spots in your underwear and this is normal and nothing to worry about.
Signs and symptoms of dangerous blood clots
Because the risk of blood clots in postnatal women is quite high, try to identify dangerous blood clots, including:
- Pain, redness, swelling, and a feeling of warmth in the legs that can be a symptomdeep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Hard to breathe.
- Chest pain.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- The skin feels cold or moist.
- Heart rate faster than normal and irregular.
Some women are more at risk for this complaint. Risk factors are:
- Have experienced previous blood clots.
- Family history with blood clotting disorders.
- Obesity.
- Aged over 35 years.
- Rarely do physical activity during pregnancy and often sit for long periods of time.
- Contain twins or more.
- Have other health problems related to autoimmune diseases, cancer, or diabetes.
Blood clots that form in blood vessels after birth can sometimes rupture and form clots in the arteries or brain that can lead to heart attacks or strokes.
Overcome blood clots that occur after childbirth
To deal with prolonged bleeding and blood clots, the doctor will perform an ultrasound test to test the remaining placental pieces in the uterus. Then the surgical removal of the placenta and other tissues that are held in the uterus is also likely to be done to stop the bleeding.
In addition, the doctor will also prescribe certain drugs to make the uterus contract and reduce bleeding that can be caused by the uterus that fails to contract so that it compresses the blood vessels attached to the placenta. As a result the uterus is blocked and can cause blood clots.
Can you prevent blood clots after giving birth?
Having blood clots after giving birth is normal and cannot be prevented. However, there are several ways that can be done to prevent complications from blood clots that can be life-threatening, namely:
- Wake up and move regularly throughout the day.
- Consult a doctor from the beginning of pregnancy if you have the risk factors mentioned.
- Make regular visits after giving birth to monitor the condition and bleeding that occurs whether normal or not.
Always consult a doctor if you experience prolonged blood clots after childbirth or if you are worried about any symptoms.