Contents:
- Why do you need uterine contractions as soon as the baby is born?
- What are the symptoms of urinary atonia?
- What are the factors that can increase the risk of pregnant women experiencing uterine atony?
- The way doctors diagnose uterine atonia
- What are the complications that may arise from urinary atony?
- How to overcome the failure of uterine contractions due to uterine atony
- How to prevent failure of uterine contractions after childbirth?
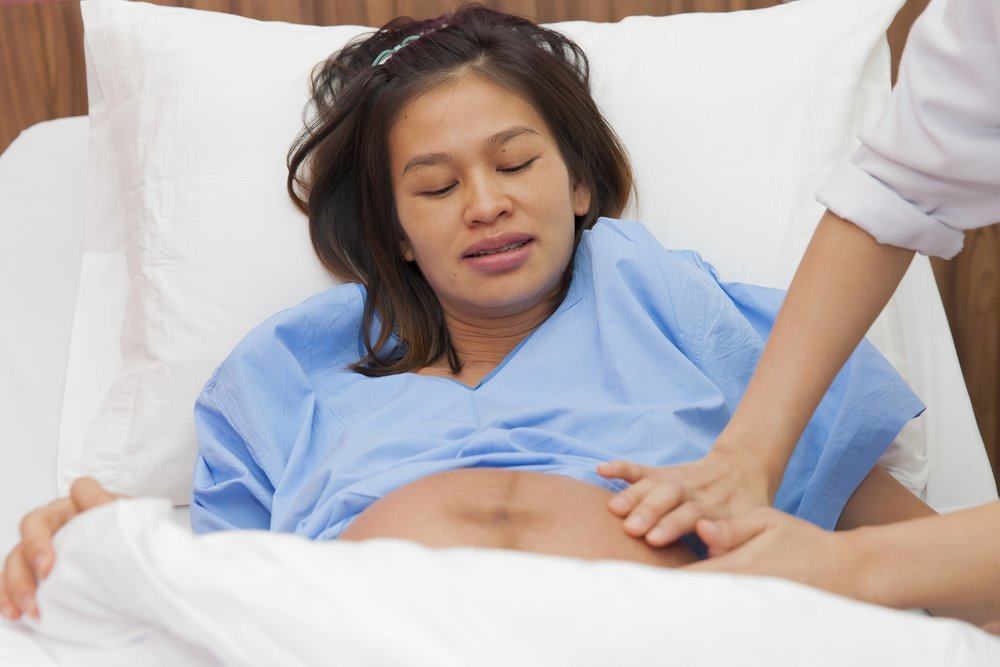
Uterine anemia is a serious condition that can occur after a woman gives birth to a baby. This condition occurs when the uterus or uterus fails to contract after the baby is born. Uterine atonia can cause life-threatening postpartum bleeding.
Why do you need uterine contractions as soon as the baby is born?
After giving birth, the uterine muscles should contract to expel the placenta or placenta which is still in the uterus. This contraction is also useful for suppressing the blood vessels found in the placenta. This emphasis serves to prevent bleeding. If the uterine contractions are not strong enough, then the blood vessels can bleed very much.
Uterine atonia is a condition that requires immediate treatment to stop the bleeding and replace lost blood. This condition can be life threatening, but if detected quickly and dealt with immediately, then this situation can be completely addressed.
What are the symptoms of urinary atonia?
The main symptom of uterine atony is the uterus which relaxes and does not contract after giving birth. Uterine atonia is the most common cause of postpartum bleeding. Postpartum bleeding is defined as blood loss of more than 500ml after the placenta is removed.
Other symptoms that can arise if the mother experiences postpartum bleeding include:
- Very large and uncontrolled blood outflow after the baby is born
- Blood pressure decreases
- Increased heart rate
- Pain
- Back pain
What are the factors that can increase the risk of pregnant women experiencing uterine atony?
There are several factors that can make the uterus unable to contract after giving birth, including:
- Long or too long delivery time
- Too fast delivery time
- The uterus that stretches is too large
- Use of oxytocin or general anesthesia during childbirth
- Labor induction
You may have a higher risk of developing uterine atony if:
- Give birth to twins
- Give birth to a baby that is bigger than most other babies
- More than 35 years old
- Obesity
- Have too much amniotic fluid (polyhidramnios)
- Have a lot of childbirth
The way doctors diagnose uterine atonia
Doctors can usually diagnose uterine atony after feeling that the uterus is not contracting adequately and that you have heavy bleeding after giving birth. The doctor will estimate the amount of bleeding you experience by counting or weighing the gauze used to absorb the blood that comes out. The doctor will also do a physical examination to rule out other possibilities that can cause severe bleeding. The physical examination is usually done by checking whether there is a tear in the cervix or vagina, and making sure there is no residual placenta left in the uterus.
The doctor may also do the following checks:
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Hb
- Freezing factor
What are the complications that may arise from urinary atony?
Uterine atonia causes up to 90% of cases of postpartum bleeding. Bleeding usually occurs after the placenta is born. Some complications of uterine atony include:
- Orthostatic hypotension, with symptoms of dizziness due to low blood pressure
- Anemia
- Fatigue
- Increased risk of postpartum bleeding in subsequent pregnancies
Anemia and fatigue after childbirth can also increase the risk of a mother experiencing postpartum depression.
The most serious complication of uterine atony is the occurrence of shock due to severe bleeding. This condition can even be life threatening.
How to overcome the failure of uterine contractions due to uterine atony
Handling is done to stop bleeding and replace lost blood. If you experience bleeding, you may be given intravenous fluids, or blood as soon as possible. Handling of uterine atony includes:
- massage the uterus or uterus, the doctor will put one hand in the vagina and press it against the uterus, while the other hand presses the uterus through the stomach
- uterotonic drugs like oxytocin and methylergonovine
- blood transfusion
In severe cases, treatment can include:
- surgery to bind blood vessels that are the source of bleeding
- embolization of the uterine or uterine arteries by injecting small particles into the uterine arteries to block the flow of blood to the uterus
- hysterectomy (if other treatments fail)
How to prevent failure of uterine contractions after childbirth?
Uterine atonia cannot always be prevented. Therefore, it is important for your doctor to be able to deal with this condition. If you have a high risk of developing uterine atony, you have to give birth in a hospital, or in a health facility that has adequate equipment to handle bleeding. Intravenous fluids and medicines needed must be prepared, as well as midwives and anesthetists. It is also important to order blood in case there is bleeding.
The doctor will monitor your vital signs continuously and calculate the amount of bleeding that occurs after giving birth to ensure the occurrence of bleeding or not. Massage the uterus immediately after giving birth to the placenta can also reduce the risk of uterine atony.
Taking prenatal vitamins such as iron supplements can also prevent anemia and other complications from failure of uterine contractions (uterine atony) and postpartum bleeding.