Contents:
- Medical Video: Meningitis - What You Need To Know
- What is meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain)?
- What causes this disease?
- 1. Virus infection
- 2. Bacterial infections
- 3. Fungal infections
- 4. Other causes
- How does this disease infect the body?
- What are the symptoms of meningitis?
- What are the complications that might occur from meningitis?
- How to diagnose this disease?
- How to treat this disease?
- Meningitis injections, the best way to prevent the transmission of inflammation of the lining of the brain
- Understand side effects after injecting meningitis
- Another way that can be done to prevent transmission of this infection
Medical Video: Meningitis - What You Need To Know
Inflammation of the lining of the brain, also called meningitis, is an infectious disease that can be fatal. But if it is quickly treated, this infection can be cured. Therefore, it is important for you to be aware of the symptoms of this disease early to reduce the risk of complications. Check out all the basic information about this disease from starting symptoms, causes, and ways to prevent and treat it below.
What is meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain)?
Meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain) is an infection that attacks the meninges, the protective membranes covering the brain, and the spinal cord. This infection is most often caused by a virus. But in some cases it can also be caused by bacteria and fungi.
Inflammation of the lining of the brain caused by viruses generally can heal without treatment. While inflammation of the lining of the brain caused by bacteria is generally more serious, it requires antibiotic treatment to speed up the recovery of patients.
Delay the treatment of lining caused by bacteria can increase the risk of permanent brain damage and other permanent harmful effects.
Meningitis is a disease that can occur at any age. However, it most often attacks people with weak immune systems such as infants, the elderly, and people with HIV / AIDS. In addition, several factors that cause meningitis are:
- Do not do meningitis vaccine
- People who have just undergone a bone marrow transplant.
- Have a history of diabetes.
- Is pregnant. If you are pregnant, you increase your risk of contracting listeriosis (an infection caused by listeria bacteria, which can also cause this disease).
What causes this disease?
In general, the causes of membrane inflammation are divided into four types, namely:
1. Virus infection
Viral infection is the most common cause of meningitis. The virus that causes this infection also has various types. But nearly 85 percent of cases of meningitis are caused by enteroviruses, followed by coxsackievirus A, coxsackievirus B, and echoviruses.
The herpes simplex virus, HIV, mumps, West Nile virus and others can also cause inflammation of the lining of the brain. This infection is usually mild and can disappear with home care.
2. Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections can also be a cause of inflammation of the lining of the brain. Bacteria that enter the flow and blood develop in the brain and spinal cord can cause inflammation of the lining of the brain.
But in some cases, bacteria can also directly attack the meninges (brain protective membranes) due to ear or sinus infections, skull fractures, or side effects after surgery related to head organs.
Some strains of bacteria that can cause inflammation of the lining of the brain include:
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococci)
This bacterium is the most common cause of inflammation of the lining of the brain in infants, children and adults. These bacteria more often cause pneumonia or ear or sinus infections. Vaccinating meningitis can reduce your risk of infection.
Neisseria meningitidis (meningokoks)
This bacterium is also the most common cause of meningitis in adolescents and adults. In many cases, these bacteria usually cause upper respiratory tract infections but can cause meningococcal meningitis when they enter the bloodstream. Vaccinating meningitis can reduce your risk of infection.
Haemophilus influenzae (haemophilus)
The infection of the haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) bacteria is most common in infants and children. The Hib vaccine can reduce your risk of infection.
Listeria monocytogenes (listeria)
These bacteria can be found in milk or unpasteurized dairy products (cheese) and processed meat products. Pregnant women, newborns, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems are most vulnerable to this bacterial infection.
3. Fungal infections
The inflammation of the lining of the brain caused by fungi is actually relatively rare and is not a contagious infection. Even so, this infection can be life-threatening if not treated with appropriate treatment, such as antifungal drugs.
4. Other causes
Not only that, in some cases, the cause of this disease can also be due to parasitic infections (such as pig meningitis), side effects of certain drugs, or as a complication of physical trauma (such as post surgery or brain surgery, serious head blows) or an illness (eg cancer, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis).
This type of meningitis includes non-infection, so it is not contagious. There is no way to find out what kind of cause of meningitis you or your child without consulting a doctor.
Whether it's caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites, this infection can spread from human to human through the respiratory tract or saliva. For example, someone who is infected with coughing or sneezing does not close his mouth, so that the splash of saliva is inhaled by people around who are healthy.
Or, by touch if they don't wash their hands after sneezing or coughing, then touching other people. A kiss can also be a cause of meningitis because the throat secretions of an infected person, such as sputum and saliva, contain particles of infection.
How does this disease infect the body?
The incubation period of meningitis is 3-4 days (span of 2-10 days) after the microbes that cause meningitis enter the body. In the body, viruses or bacteria infect the brain, spinal cord, or meninges (protective membranes of the brain and spinal cord).
When an infection occurs, the meninges swell and suppress the brain and spinal cord. Pressure on these organs will cause temporary symptoms, such as headaches and nerves, and inhibit blood flow to the brain so that it can cause long-term damage to the nervous system and brain. In many cases, meningitis ends death.
What are the symptoms of meningitis?
One of the most typical symptoms of meningitis from meningitis is that patients often experience severe headaches that don't improve with neck pain. Unfortunately, the symptoms of meningitis are the same as some other diseases. That is why, immediately consult a doctor if you experience severe headaches accompanied by pain.
Actually the symptoms of meningitis will vary depending on the age and cause of the infection. Even so, generally the symptoms of meningitis are:
- Fever and chills
- Severe headaches that don't improve
- Nausea and vomiting
- Feeling weak, tired and not powerful
- Neck stiffness and pain
- Joint and muscle pain
- Feet and hands feel cold
- Breathe fast (fully tired)
- So it is more sensitive to light (photophobia)
- Changes in mental conditions such as confusion, irritability, difficulty concentrating
- Frequent fainting
- Abdominal cramps if a virus or bacteria has infected the blood
- In serious cases, inflammation of the lining of the brain can be indicated by symptoms of seizures or coma
Symptoms of meningitis in infants and children are slightly different from those mentioned above. Some symptoms of meningitis in infants and children include:
- High fever, chills
- Jaundice appears (yellowish to the skin)
- Baby's body and neck are stiff
- Looks confused, weak, and less responsive
- Fussy and even crying with high shouts continuously
- Refuse to eat or suckle
- Lumps appear on the baby's head
- Sleep continuously or it's hard to wake up
- Lumps appear on the baby's head
If you or your child has one of the symptoms of meningitis as mentioned above, consult a doctor immediately. This is done to ascertain the cause of the symptoms of meningitis that are being experienced.
What are the complications that might occur from meningitis?
If symptoms of meningitis are ignored, especially in infants and young children, the possibility of complications increases. Some of the complications that may occur from meningitis are:
- Hearing loss
- Learning disorders
- Seizures
- Brain damage
- Shock (blood circulation disorders)
- Kidney failure
- Dead
How to diagnose this disease?
If the doctor suspects you have this disease, the doctor will check your medical history, carry out a physical examination and certain diagnostic tests. During a physical examination, the doctor will check for signs of infection around the head, ears, throat and skin along the spine.
To find out the specific cause of meningitis experienced by the patient, the doctor will usually perform a series of diagnostic tests. Some tests that doctors may make to diagnose meningitis are:
- Blood test. This examination is done to find out the cause of meningitis that you experience comes from infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms.
- Fitness test. MRI or CT Scan of the head, chest and sinuses can also be done by the doctor to show the possibility of other infections associated with this infection.
- Lumbar puncture test. This test is done to take fluid samples in the spine to check glucose (blood sugar) levels, proteins, and blood cells. This test also helps the doctor to find out the bacteria that causes meningitis.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test.If your doctor is exposed to viral meningitis, he can do this test. PCR is an examination that uses technology real-timeto detect and calculate the viral load that causes meningitis in your body.
How to treat this disease?
Treatment of inflammation of the lining of the brain basically depends on the cause. Meningitis caused by bacterial infections can be treated with intravenous antibiotics or corticosteroid drugs to accelerate recovery and reduce the risk of complications, such as brain swelling and seizures.
Do not use antibiotics arbitrarily without consulting a doctor first. Non-random use of antibiotics can worsen your condition.
If you have brain inflammation caused by a virus, antbiotics cannot treat this type of infection. In many cases, patients affected by this type of lining will improve in a few weeks.
Treatment for this condition is relatively mild and can be done at home such as bed rest (complete rest), consuming lots of fluids, and taking painkillers without a prescription to reduce fever and relieve pain in the body. If your condition does not improve for several weeks, contact your doctor immediately.
Proper treatment can reduce the risk of death to below 15 percent according to the National Institutes of Health.
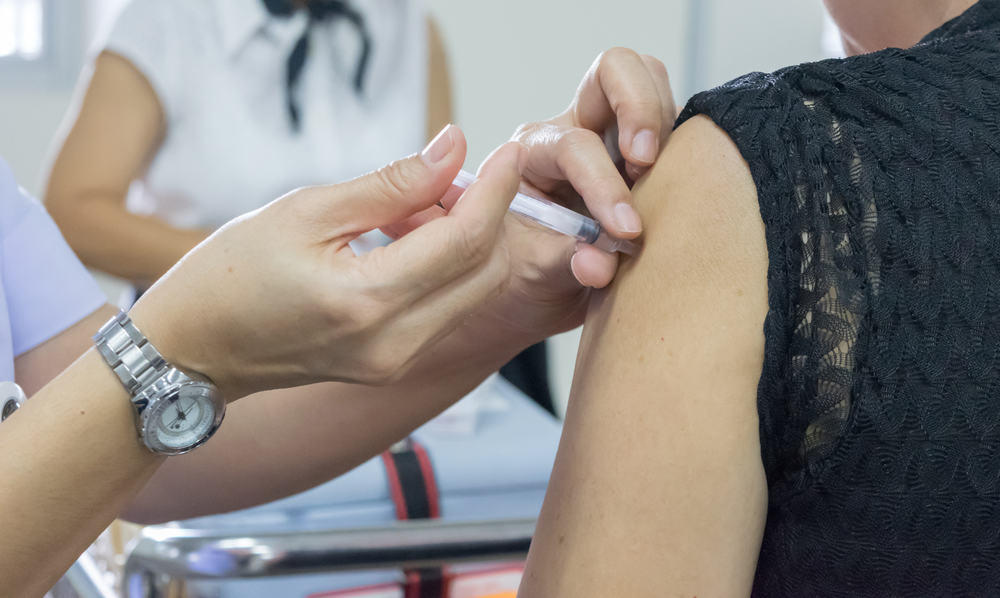
Meningitis injections, the best way to prevent the transmission of inflammation of the lining of the brain
The main way to prevent transmission of this disease is by injecting meningitis. ACWY135 meningitis vaccine can protect you from meningococcal disease, pneumococcal meningitis, and Haemophilus Influenzae Type b.
In addition, the measles and rubella vaccine (MMR) and chickenpox vaccine can protect children from inflammation of the lining of the brain caused by viruses.
Health agencies around the world agree to recommend that all young people and young adults who want to travel far to the regions risk being injected with meningitis. Not everyone can inject meningitis. Some conditions that cause a person not to inject meningitis are:
- Has a severe and life-threatening allergic reaction to the components contained in the meningitis vaccine or in one of the other vaccine components.
- Have experienced Guillain-Barre syndrome.
- women who are pregnant can inject meningitis, but this procedure is only recommended for those who have certain immune problems or those who are at high risk of getting this infection.
While some of the people who are highly recommended for injecting meningitis are:
- People who will travel or live in a country where meningitis is widespread, such as Saudi Arabia and parts of Africa. In Indonesia, the government itself has required prospective Umrah and Hajj participants to inject meningitis before leaving there.
- Having an immune system disorder, such as HIV.
- Have damage to the spleen or no spleen.
- Has certain types of rare disorders (complement component deficiency).
- Take Soliris medicine.
- Have a history of this infection before.
- Work in laboratories that routinely intersect with bacteriaNeisseria meningitidis.
Not all hospitals provide services for meningitis vaccines. That is why, always consult your doctor first before carrying out the meningitis vaccine. Doctors can recommend hospitals or other health care providers that provide meningitis vaccines
Understand side effects after injecting meningitis
Side effects of meningitis vaccine are actually the same as vaccinations in general, such as redness, bruising, itching, swelling, pain, or headache. The side effects of meningitis vaccine are generally mild and can disappear without special treatment.
Serious side effects are rare. If it occurs, symptoms that often appear include high fever, weakness and lethargy, and behavioral changes. In addition, severe allergic reactions can also occur within minutes or hours after the vaccination is complete.
Some people may develop symptoms that are not mentioned above. However, if you experience some of the signs above, you should immediately go to the doctor to get the right treatment.
Another way that can be done to prevent transmission of this infection
Thoughtransmission of this infection by air is not as easy as transmission of fluYour risk will also increase if you experience itprolonged direct contact with infected people, such as sharing eating or drinking and drinking equipment from the same source simultaneously. Therefore, if you live with or are caring for an infected person, avoid direct contact as much as possible. Here are a few examples:
- Don't share food, glasses, water bottles, or eating utensils with an infected person
- Don't share tissues or towels
- Don't share lip gloss or lipstick
- Wash hands with soap and running water after using public facilities
In addition, it is also important for you to keep your immune system healthy so that you can be protected from various viruses and diseases. You can do this by adopting a healthy lifestyle.
You can start by eating healthy and nutritious foods, getting enough rest, actively moving or exercising regularly, and avoiding unhealthy lifestyles such as smoking and consuming alcohol.
If you are pregnant, avoid eating raw foods. Meningitis often occurs because of the habit of eating undercooked or raw food.
Therefore, it is highly recommended that you cook the right way and make sure that your cooking is completely cooked. Also avoid dairy products or unpasteurized milk products because of the risk of bacterial infection.
While to prevent fungal meningitis, you try to avoid exposure to the environment that tends to contain fungal elements (eg bird droppings and dust).
If you have pets at home, make sure to always keep the cage clean by regularly cleaning at least once a week. Wear gloves and boots if you want to clean the cage. Don't forget, make sure you wash your hands with soap and running water every time you finish contact with pets.