Contents:
- Medical Video: Healing Global Warming
- The effect of global warming on the health of the population of Indonesia
- 1. Air pollution
- 2. Disease spread
- 3. Decreased nutrition of food
Medical Video: Healing Global Warming
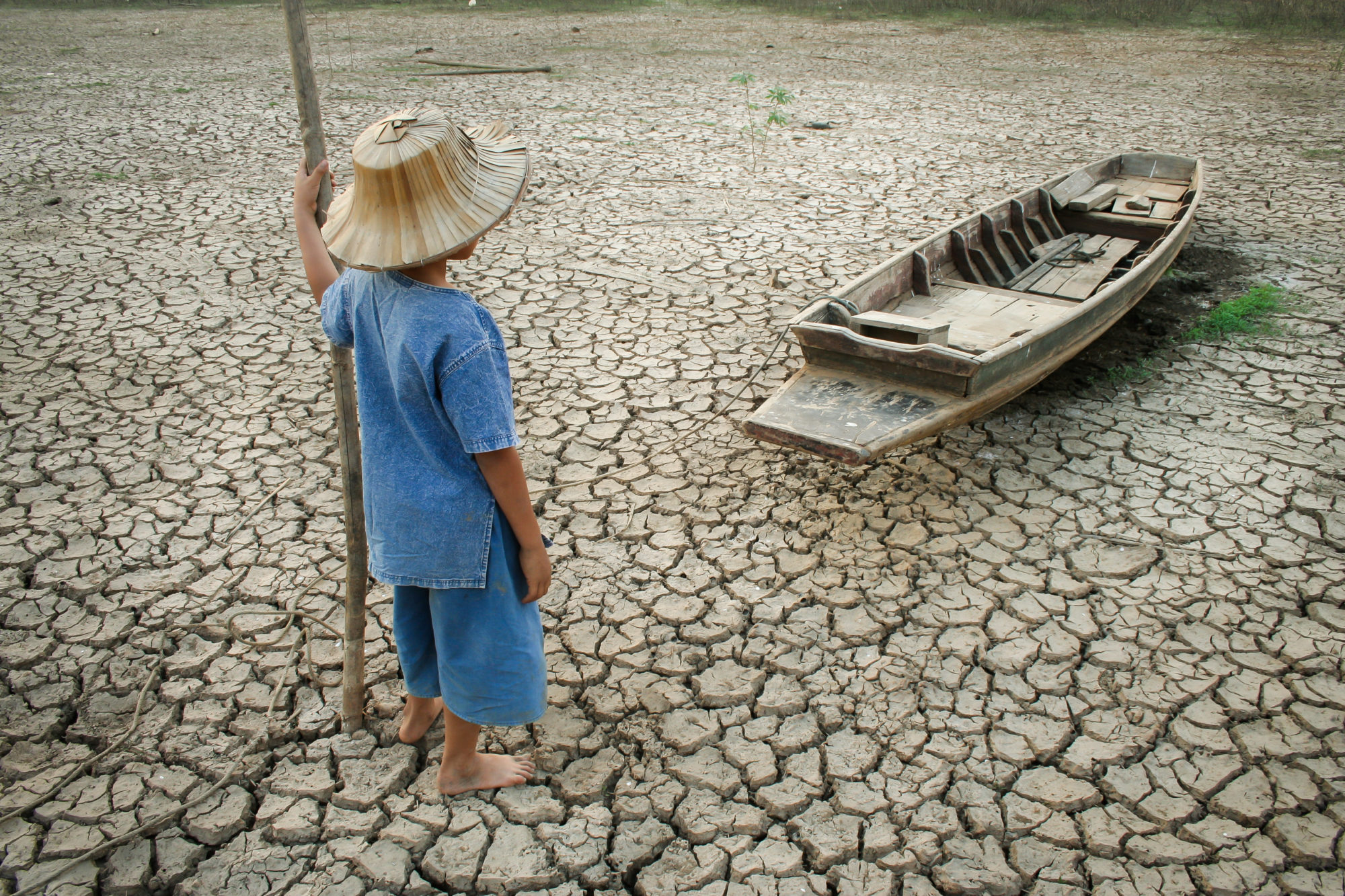
We have known for a long time that climate change has occurred on earth, or which is often generalized under the name 'global warming'. Climate change is a change in the world weather system caused by humans and results in rising sea water, rising earth temperatures, decreasing agricultural yields, deforestation or deforestation, and so on.
In the end, climate change impacts on the air we breathe, the water we drink, the food we eat, and the land we occupy. And without you realizing it, climate change can affect your health. But how can it be?
The effect of global warming on the health of the population of Indonesia
Unlike the country which has four seasons, as a tropical country, Indonesia only has two seasons, namely the rainy season and the dry season. Here's how climate change affects health, especially in countries with two seasons like Indonesia:
1. Air pollution
Climate change increases temperature; high temperatures increase the occurrence of forest fires which further increases smoke and air pollution. Poor air quality will increase asthma and allergies.
People with a history of asthma and allergies will also be more susceptible to recurrence. Even air pollution can affect those who have no history of asthma and allergies.
2. Disease spread
Global warming can increase the risk of extreme events, such as heat waves, floods, and large storms that can trigger the spread of infectious diseases through pathogens, hosts and transmissions. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported that an increase in earth temperature and changes in precipitation caused climate change. This makes the spread of infectious diseases faster.
Here are some ways climate change can trigger the spread of infectious diseases:
- The increase in temperature and high rainfall will benefit certain disease vectors such as insects to spread dengue fever, malaria, and so on. Several studies have found a link between increased rainfall and the spread of epidemics, especially waterborne diseases.
- Studies in West Africa state that absolute CD4 + T-lymphocyte counts, and CD4 + / CD8 + ratios are significantly lower during the wet season compared to the dry season; while the CD8 + percentage is higher in the rainy season than in the dry season. CD4 + cells are the body's first defense during infection, and CD8 + cells are a defense aid.
- Heavy rain can trigger sediment in water, which causes a buildup of fecal microorganisms, so the rainy season is often associated with increased fecal pathogens that trigger diarrhea. No wonder if in the rainy season, tropical diarrheal diseases such as Indonesia usually peak. The main causes of diarrhea associated with high rainfall and contaminated water supplies are cholera, cryptosporidium, E. coli, giardia, shigella, typhoid, and viruses such as hepatitis A. In addition, unusual rainfall after a long drought can cause an increase pathogens, which cause disease outbreaks.
- Temperature and humidity during the rainy season can also support the spread of dengue virus to mosquitoes, which contributes to an outbreak of dengue fever. Mosquitoes need access to stagnant water to breed, and adults need moist conditions for viability.
3. Decreased nutrition of food
Global warming is also characterized by an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) on earth. Although CO2 is an important element that allows plants to harness energy from the sun, a study found that increasing the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere threatens human nutrition throughout the world with a reduction in the amount of important nutrients, zinc, iron and protein in seeds such as rice, wheat and soybeans.