Contents:
- Medical Video: The Lymphatic System Overview, Animation
- What are lymph nodes?
- Function of lymph nodes
- 1. Maintain fluid balance in the body
- 2. Maintain body resistance and fight infection
- 3. Absorb fat and fat-soluble nutrients
- Diseases that often attack lymph nodes
Medical Video: The Lymphatic System Overview, Animation
You may have often heard the term lymph nodes or commonly abbreviated as KGB. However, do you know where the KGB is and its function in the human body? It is also important for us to know what diseases can interfere with and attack the system because these glands play a very important role in health. Come on. learn about the KGB in the full review below.
What are lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes are rounded masses surrounded by connective tissue capsules. The task of lymph nodes is to filter lymph fluid (lymph) that circulates throughout the body through lymph vessels, as well as blood circulating in our body through blood vessels.
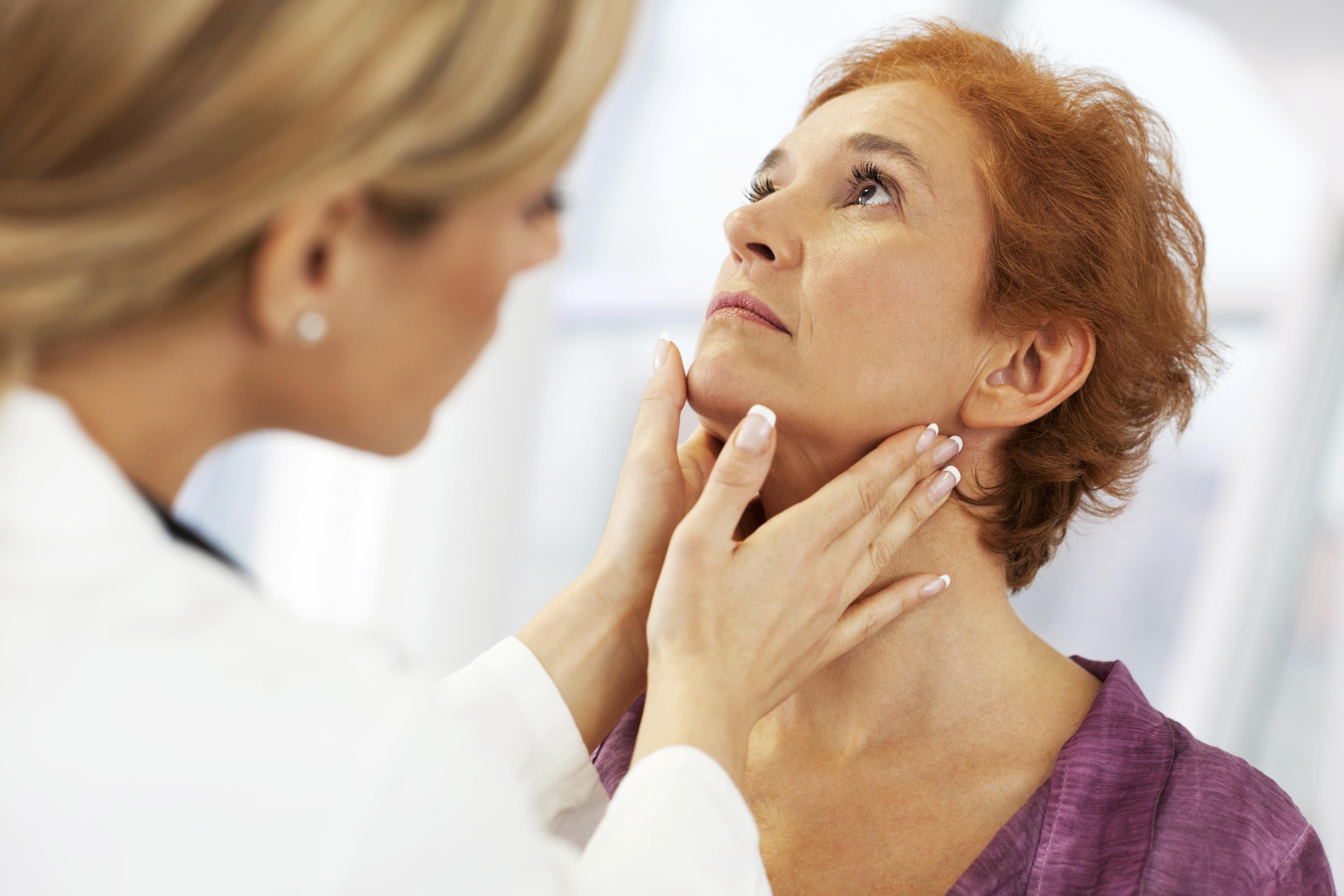
There are around 600 lymph nodes in the body, but only a few can be felt or touched by the hand. Among them are in the lower part of the jaw, neck, armpit, and groin.
The size of the KGB varies, starting from as small as the tip of a needle to a size of one ripe kidney bean.
Function of lymph nodes
KGB is very important to fight disease and maintain endurance. For more details, consider the three main functions of the KGB for your health.
1. Maintain fluid balance in the body
Lymph fluid is obtained from various kinds of fluids that are present in body tissues. After that, the liquid will be filtered by the KGB. If there is excess liquid or liquid containing dangerous organisms, the KGB will return it to the bloodstream to be discharged by the body through the excretion system. That way, the fluid level in your body will always be balanced.
2. Maintain body resistance and fight infection
Inside the KGB, there is one type of white blood cell, namely lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are useful for detecting and attacking harmful organisms that cause infection in the body. For example viruses, bacteria, germs, damaged cells, and cancer cells.
The KGB has a special system for "remembering" and distinguishing which organisms are harmful to the body and which are safe. That's why the KGB is very important to prevent you from being attacked by disease.
3. Absorb fat and fat-soluble nutrients
KGB in the intestine can help your digestive system to absorb fat and other fat-soluble nutrients. Because the fat and nutrients that dissolve in fat can not be directly absorbed by capillary blood vessels such as other nutrients such as sugar and protein
Diseases that often attack lymph nodes
The KGB can experience failure or damage if there is inflammation, swelling, blockage, infection, or the growth of cancer cells in your vessels, glands, or lymph tissue. Here are the types of diseases that often attack the KGB.
- If your lymph system is blocked, you can develop lymphedema (lymphatic obstruction). The characteristics of lymphedema include swelling of certain parts of the body, but usually does not cause pain.
- If the infection occurs in the KGB or is called lymphadenitis, you can experience swollen lymph nodes. Children are usually more susceptible to this, because their immune system is still developing. The causes of KGB swelling include sore throat, viral infections, ear infections, dental infections, bacterial infections, and HIV / AIDS infections.
- You can get lymph node cancer if there are cancer cells in your body which are then transported by the KGB. Your KGB may also be the forerunner of the cancer itself, but this case called lymphoma cancer is rare.