Contents:
- Medical Video: I Thought We Required Animal Protein...
- Various differences in animal protein with vegetable protein
- 1. Have different amino acid contents
- 2. Sources of animal protein have more vitamins and minerals
- 3. Vegetable protein does not contain cholesterol and saturated fatty acids
- 4. Vegetable protein helps reduce weight
Medical Video: I Thought We Required Animal Protein...
Protein is a nutrient that is very important to repair damaged body cells. Especially for children, protein is a nutrient that must be fulfilled to support growth and development. Maybe you already know if there are two sources of protein that are usually consumed, namely animal protein with vegetable protein. Even though it's both protein, what's the difference between the two? Consider the differences in animal protein with vegetable protein as follows.
Various differences in animal protein with vegetable protein
1. Have different amino acid contents
Amino acids are the smallest structures of proteins that will later be absorbed in the body. Basically there are 20 types of amino acids used in the human body.
These types of amino acids are of the essential type, as well as non-essential amino acids. Essential types of amino acids cannot be produced by the body itself, so it is very dependent on the food that enters the body. While this type of non-essential amino acid can be produced by the body itself, so it does not need to be obtained from the outside.
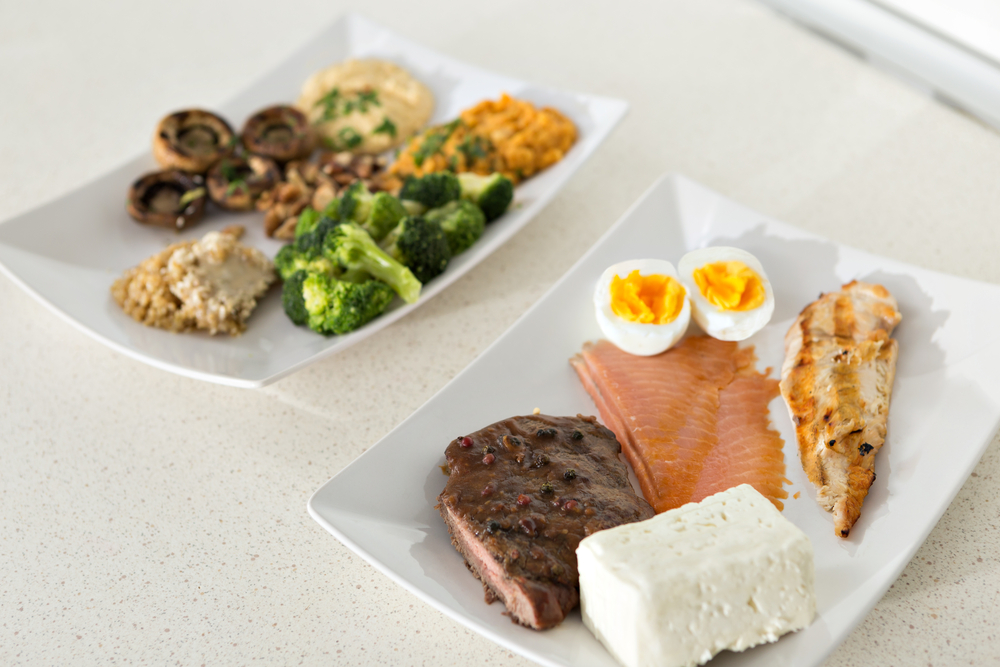
For optimal results, the body needs all types of amino acids. Animal protein such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, milk and its products contain more complete types of essential amino acids than vegetable protein.
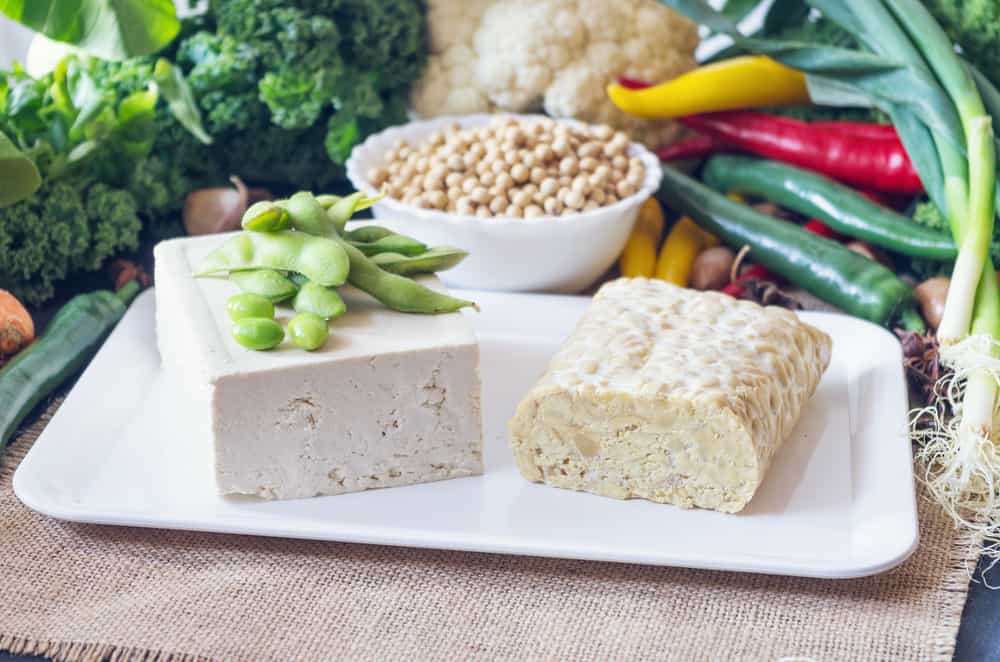
Conversely, vegetable protein foods such as beans including tofu and tempeh do not have the complete type of amino acids such as animal protein, except vegetable protein from soybeans.
Some sources say that protein from soybeans is quite complete. However, there are two types of essential amino acids which are only found in small amounts in soybeans, so that even though the levels are complete they are not comparable to animal protein.
2. Sources of animal protein have more vitamins and minerals
Food sources of animal protein tend to have higher micronutrients compared to food sources of vegetable protein. Nutritional sources include:
- Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is mainly found in fish, meat, poultry and dairy products. People who don't eat animal foods usually tend to lack this nutrient.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is found in fatty fish, eggs and dairy products. Some plants may contain vitamin D, but the type of vitamin D in animals is more easily absorbed by the body making it easier to use.
- DHA (Deocosahexaenoic acid): is an omega 3 fatty acid found in fatty fish. DHA is very important for brain health. Unfortunately, DHA is difficult to obtain from vegetable sources.
- Iron heme type: This type of iron is mostly found in meat, especially red meat. This type of heme iron is more easily absorbed by the body than other types of iron, non-heme iron found in plant foods such as spinach.
- Zinc: Zink is also mostly found in animal proteins such as beef or lamb.
3. Vegetable protein does not contain cholesterol and saturated fatty acids
Even though animal protein sources look more nutritious, you should still be careful about consuming them. Because, most sources of animal protein contain cholesterol and saturated fatty acids.
This is the very opposite of vegetable protein. Vegetable protein does not contain cholesterol or saturated fatty acids. Eating vegetable protein can actually help lower blood cholesterol levels.
High cholesterol in animal protein can pose a risk of heart and blood vessel disease, cancer, obesity, and diabetes mellitus.
Reported on the page of the American Council of Science and Health, it turns out there is a relationship between consumption of red meat, especially in processed forms such as sausages and others with cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks, strokes, and even cancer.
That is why, you must be careful when consuming animal protein, and it's better to replace too much intake with vegetable protein.
Although vegetable protein does not contain cholesterol and saturated fatty acids, you also need to be careful about how to process it. Do not process vegetable sources to make your food filled with saturated fatty acids.
4. Vegetable protein helps reduce weight
Eating foods high in vegetable protein like those done by vegetarians, turns out to provide many benefits. Research shows that groups of vegetarians tend to have lower weight and have lower blood pressure levels.
Another study in JAMA Internal Medicine 2016, showed that from the results of a comparison of each group in the study, the group of people who consumed vegetable protein had a lower body weight compared to a group of people who consumed animal protein.
Vegetable protein foods can help control weight. Because, intake of vegetable protein can cause a feeling of fullness faster which will disappear longer, so this is very good for regulating the amount of food eaten and preventing weight gain.
Although it has advantages and disadvantages, you still have to consume both in the recommended amount. Don't overdo it or not. If indeed you are confused about dividing the portion of food sources of animal protein with vegetable protein, you can consult a nutritionist.