Contents:
- Medical Video: WHO: The Two Polio Vaccines
- How can vaccines prevent disease?
- The way injecting vaccines and vaccines work is different
- The side effects are also different
- Various injection vaccines and oral vaccines
- Oral vaccine
- Injection vaccine
Medical Video: WHO: The Two Polio Vaccines
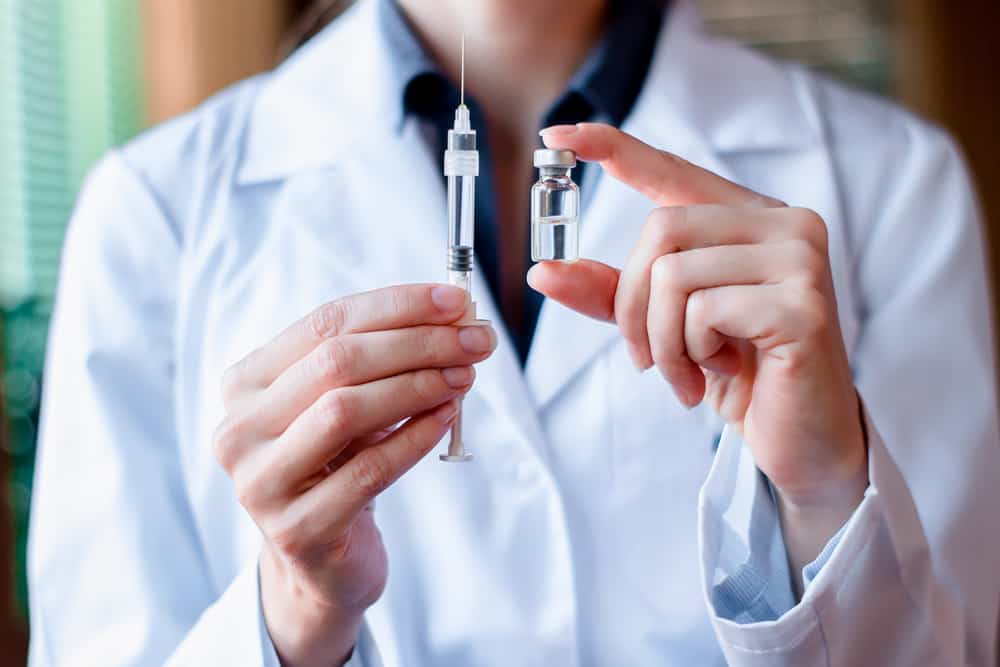
Vaccination or immunization is needed to prevent various types of infectious diseases by building immunity. The vaccine itself consists of two types, namely the injection vaccine and the form of liquid to be dropped directly into the mouth (oral vaccine). So, do you know the difference between injecting vaccines and drop vaccines? Are the benefits different too?
How can vaccines prevent disease?
Vaccines are made from disease-causing microbes (whether viruses, fungi, poisons, or bacteria; depending on the type of disease you want to prevent) that has been weakened or dead.
In the body, the vaccine works to mimic the infection of the disease but does not necessarily cause disease. The disease seeds will move towards the closest lymph nodes to trigger the immune system to build up and train against it.
The immune system will immediately react and study the seeds of the disease to form the memory of the pattern of the attack. This will then make the body always ready for the actual disease attack because it has "remembered" which organisms are dangerous and need to be eradicated.
Vaccines can be given in various ways, which are injected or dripped into the mouth, also called an oral vaccine.
The way injecting vaccines and vaccines work is different
The drip vaccine contains seeds that are still alive but weakened, while injecting vaccines usually contain dead viruses or bacteria.
Different types of viruses provide different immune benefits between injection vaccines and drops vaccines, because the way they work in the body will also be different.
The vaccine drops will enter the digestive tract directly to stimulate the immune system in the intestine. When there is a wild virus that enters the intestine, the virus will be bound and immediately turned off by the body's immune system in the digestive tract so it cannot multiply and does not harm or spread to other people. The vaccine drops also prevents the virus from spreading to the nervous system through the bloodstream.
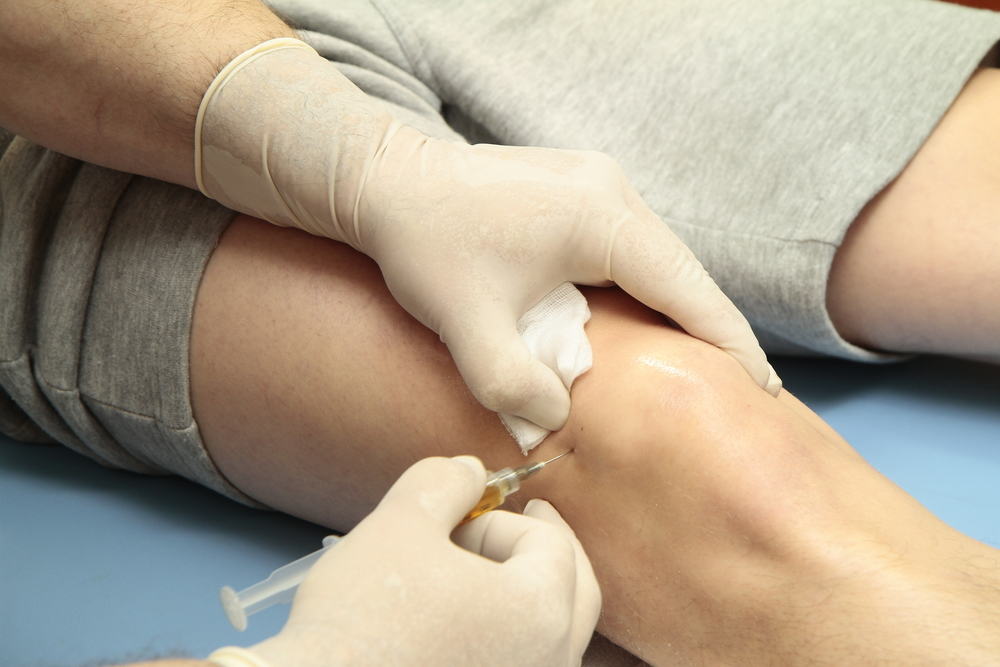
Meanwhile, the injection vaccine will be injected under the skin layer or directly towards the muscle (usually in the arm or thigh). The dead virus content will form immunity directly in the blood. If later there is a wild virus entering the intestine of a child who is injected with a vaccine, the virus can still multiply in the intestine but it will not make the child sick because his blood contains the virus's immune system. This immunity only applies to people who are vaccinated, so the benefits can only be felt for themselves.
The side effects are also different
How to administer a vaccine that is not in accordance with its purpose can reduce the efficacy of the vaccine and risk increasing negative reactions (allergies) to the body.
The injectable vaccine works faster because it directly affects muscle tissue, but can cause redness or swelling in the injected area. Meanwhile, drops of vaccine can cause side effects of diarrhea because vaccines that are dropped on the mouth will flow into the digestive system.
Whichever method is given and whatever side effects the vaccine might cause, immunization is still important to obtain. The benefits of a vaccine will always outweigh the risks. Most of the risks of vaccine side effects are relatively mild and easily overcome.
Various injection vaccines and oral vaccines
Depending on the method of administration, there are many types of vaccines to prevent various infectious diseases - but not all of them are available in Indonesia, so make sure to return with your doctor before getting them.
Oral vaccine
- Drop polio vaccine
- RIT 4237 rotavirus, MMU18006, and others to prevent diarrheal disease caused by rotavirus infection
- 103-HgR CVD vaccine live cholera strain to prevent cholera
- The SC602 vaccine attenuated Shigella flexneri strains to prevent dysentery
Injection vaccine
- BCG vaccine to prevent tuberculosis
- MMR vaccine (Measles, Mumps, Rubella)
- Yellow fever vaccine
- Hepatitis A and B vaccines
- DTaP and Tdap vaccines and Td and Dt to prevent diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (whooping cough).
- Injection polio vaccine
- Flu vaccine (Haemophilus Influenzae type B)
- Pneumoccocus vaccine to prevent pneumonia and meningitis
- Smallpox vaccine (chicken pox and shingles / snake pox)