Contents:
- Medical Video: Complications Of What is Gestational Diabetes And Prevention - Manipal Hospitals
- Impact of gestational diabetes on pregnant women
- Impact of gestational diabetes on the fetus
- Babies are born with very large weights (macrosomia)
- Lower blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) at birth
- Premature birth
- Temporary breathing problems
- Jaundice
- What can I do if I have gestational diabetes while pregnant?
- Apply a healthy diet
- Do exercise regularly
- Perform routine antenatal care
- Do your own blood sugar test
Medical Video: Complications Of What is Gestational Diabetes And Prevention - Manipal Hospitals
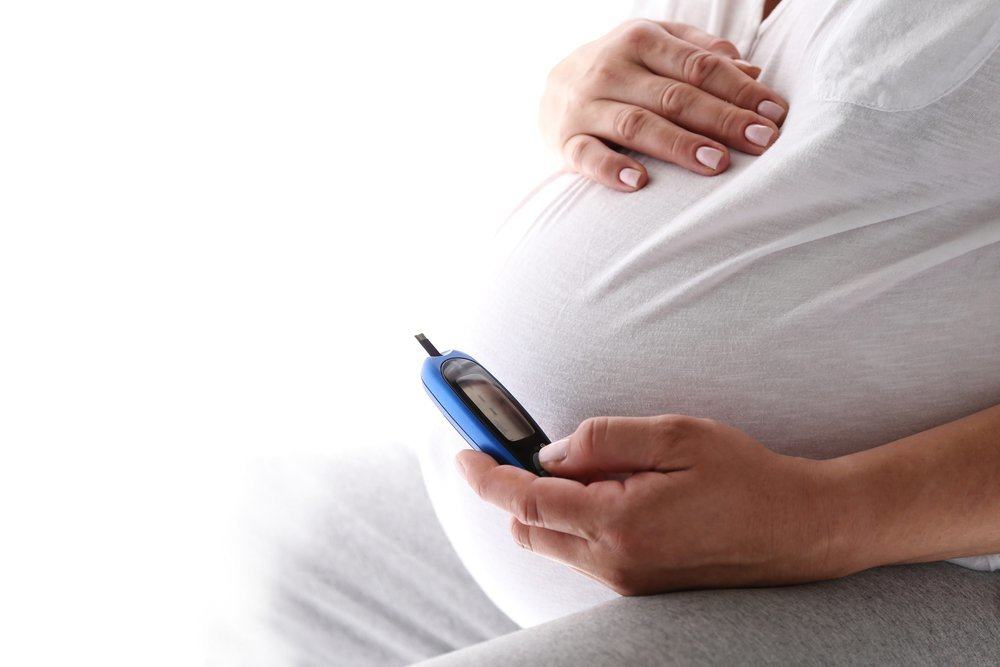
One of the complications that can be experienced by pregnant women is gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes is diabetes that occurs in pregnant women, even though previously pregnant women have never had diabetes. This disease is characterized by high blood sugar levels in pregnant women. Of course, the impact of gestational diabetes is not only experienced by the mother, but also on the fetus in the womb.
Impact of gestational diabetes on pregnant women
Maybe you are confused, why can you have gestational diabetes during pregnancy even though you have never had diabetes before becoming pregnant? Yes, gestational diabetes can appear when you are pregnant because of hormonal changes during pregnancy. Changes in this hormone can make your blood sugar levels increase during pregnancy. However, don't worry because your blood sugar levels will return to normal after you give birth, in many cases.
Even so, gestational diabetes can still endanger your health during pregnancy, increasing your risk for complications during pregnancy. Some of the effects of gestational diabetes that you can experience are:
- The risk is higher for giving birth by caesarean section because usually the size of the baby is greater than normal in women with gestational diabetes
- Miscarriage
- Premature birth, to avoid higher health risks
- High blood pressure (hypertension) or preeclampsia during pregnancy
- Increases the risk of gestational diabetes in the next pregnancy
- Increases the risk of a mother having type 2 diabetes mellitus after giving birth
Impact of gestational diabetes on the fetus
Gestational diabetes also affects your fetus because the fetus gets nutrients from the mother's bloodstream, where gestational diabetes is a disease that affects blood sugar levels. Some of the effects of gestational diabetes on the fetus in the womb are:
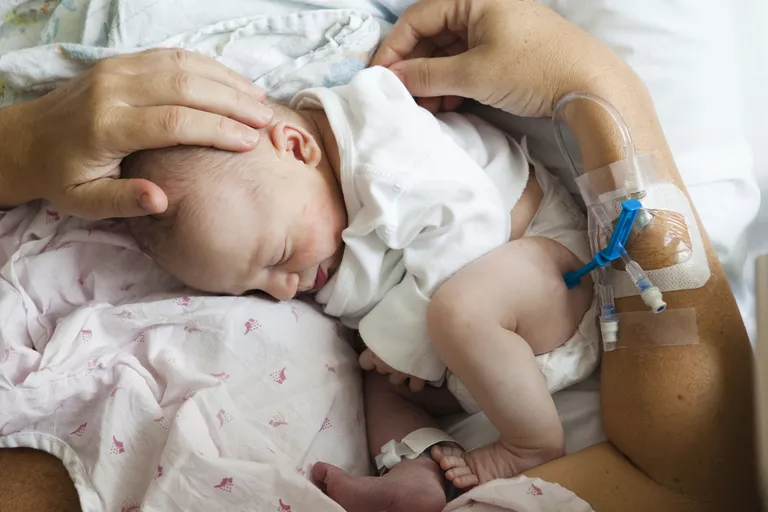
Babies are born with very large weights (macrosomia)
Mothers who have gestational diabetes during pregnancy usually have a larger size fetus. Infants in the womb keep the excess sugar they receive from the mother's bloodstream as fat, so the womb baby can grow bigger. Babies with very large sizes can increase the risk of injury at birth (especially on the shoulder). Therefore, a caesarean section may be needed in this condition.
Lower blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) at birth
Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes usually experience hypoglycemia shortly after birth because of the high levels of insulin produced by the baby's own body. Very severe hypoglycemia can cause the baby to spasm.
Premature birth
High blood sugar levels in pregnant women increase the risk of preterm birth. Your doctor may recommend premature labor because of the large size of the baby. If it continues to be maintained, then the size of the baby can be even bigger and can cause higher complications.
Temporary breathing problems
Babies born prematurely may have temporary respiratory problems. Babies may need breathing assistance until the baby's lungs are mature enough and stronger. Even though babies are not born early, babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes are more at risk of experiencing temporary breathing problems after birth.
Jaundice
Babies from mothers with gestational diabetes are also more likely to experience jaundice after birth. Babies with jaundice must be treated with special treatment after birth, usually babies are placed under special lights. Jaundice can not only be experienced by babies of mothers with gestational diabetes, but also commonly experienced by all newborns.
In addition, babies of mothers who have gestational diabetes during pregnancy also have a higher risk of obesity and diabetes in the later stages of life.
What can I do if I have gestational diabetes while pregnant?
Gestational diabetes is a complication that is often experienced by pregnant women. This complication only appears when you are pregnant and can then disappear after giving birth. If you have gestational diabetes, all you can do is control it so that it doesn't cause too much impact on you and your fetus.
Some things you can do to control gestational diabetes are:
Apply a healthy diet
A healthy diet can help you to maintain normal blood sugar levels in the body. You need to limit your intake of foods and drinks that contain carbohydrates or high sugar, such as sweet cakes and soft drinks. Also, limit consumption of fatty foods, such as fried foods.
Do exercise regularly
Exercise can also help you control blood sugar levels and maintain weight. At least do light exercise for 30 minutes every day, you can walk, relax, swim, and other sports that do not harm your fetus.
Perform routine antenatal care
Keep an appointment with your doctor, so you and your doctor can monitor the development of the baby in the womb and your health condition. Don't forget to take medication according to your doctor's prescription. This is to help maintain your blood sugar levels.
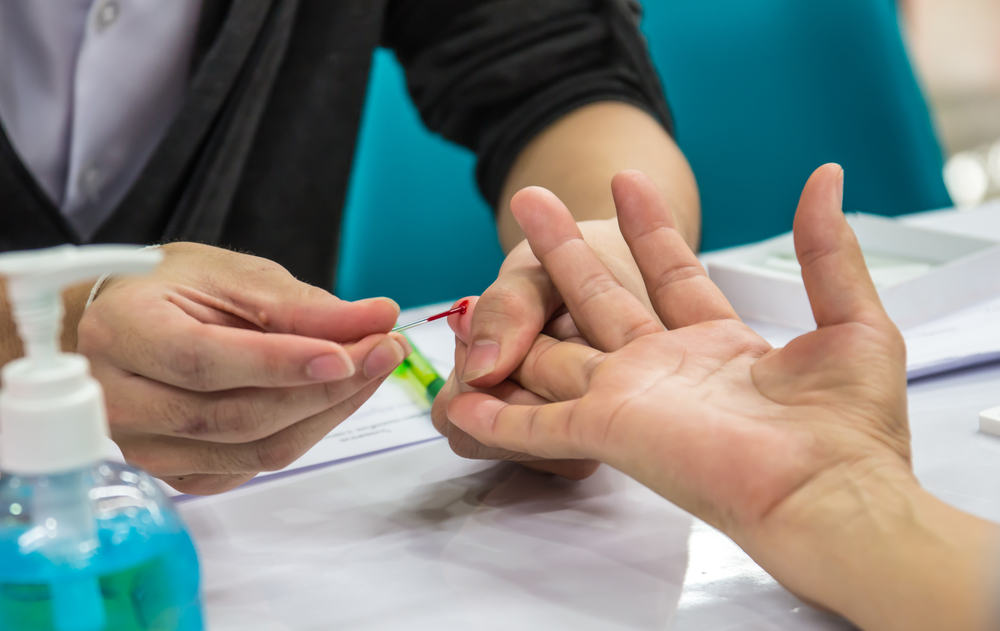
Do your own blood sugar test
To monitor your blood sugar levels every day, you need to do your own blood sugar test at home. Your doctor may ask you to do a blood sugar test several times a day at certain times. Consult with your doctor what you should do if you get the results of a very changing blood sugar level (too high or too low).
READ ALSO
- All You Need to Know About Gestational Diabetes
- Not Only In Mothers, Preeclampsia Also Affects Infants
- What Causes Yellow Disease in Newborns?