Contents:
- Medical Video: Should You Get Genetic Testing During Your Pregnancy?
- Screening test during pregnancy 1st trimester
- 1. Ultrasound
- 2. Blood test
- 3. Chorionic villus sampling
- Screening test during pregnancy 2nd trimester
- 1. Blood test
- 2. Blood sugar test
- 3. Amniocentesis
- Screening test during pregnancy 3rd trimester
- ScreeningStrepococcus Group B
Medical Video: Should You Get Genetic Testing During Your Pregnancy?
Prenatal screening test or screening tests during pregnancy are a set of procedures performed during pregnancy to determine whether babies tend to have certain abnormalities or birth defects. Most of these tests are not invasive. These tests are usually done during the first and second trimesters, but some are also done in the third trimester.
Screening tests during pregnancy can only tell the risk or the possibility of certain conditions in the fetus. If the results of the screening test are positive, a diagnostic test is needed to get more accurate results. Here are some screening tests that are routine procedures for pregnant women.
Screening test during pregnancy 1st trimester
The first trimester screening test can start from 10 weeks of pregnancy, which is a combination of fetal ultrasonography (USG) and the mother's blood test.
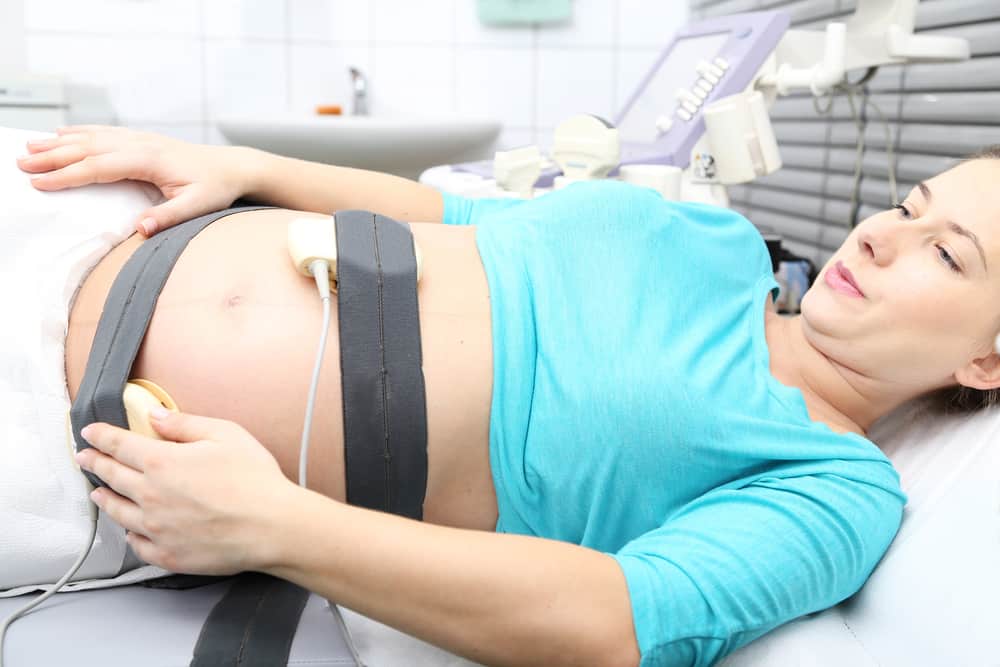
1. Ultrasound
This test is done to determine the size and position of the baby. It also helps determine the risk of the fetus experiencing birth defects, by observing the structure of the bones and organs of the baby.
Nuchal translucency (NT) ultrasound is a measure of the increase or thickness of fluid in the back of the fetal neck at 11-14 weeks of gestation with USG. If there is more fluid than usual, it means there is a risk of Down syndrome in higher infants.
2. Blood test
During the first trimester, two types of maternal blood serum tests are carried out, namely Pregnancy-associated plasma protein (PAPP-A) and the hormone hCG (Human chorionic gonadotropin) This is a protein and hormone produced by the placenta in early pregnancy. If the results are not normal, then there is an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Blood tests are also conducted to determine the presence of infectious diseases in infants, or called the TORCH test. This test is an acronym for five types of infectious infections, namely toxoplasmosis, other diseases (including HIV, syphilis, and measles), rubella (German measles), cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex.
In addition, a blood test will also be used to determine your blood group and Rh (rhesus), which determine your Rh relationship with a growing fetus.
3. Chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling is an invasive screening test that is carried out by taking small pieces of the placenta. This test is usually carried out between the 10th and 12th weeks of pregnancy.
This test is usually a follow-up test of NT ultrasound and abnormal blood tests. This test is done to better ensure the presence of genetic abnormalities in the fetus such as Down syndrome.
Screening test during pregnancy 2nd trimester
1. Blood test
Blood tests during second trimester of pregnancy include several blood tests called multiple markers. This test is done to determine the risk of birth defects or genetic disorders in infants. This test should be carried out at weeks 16 to 18 of pregnancy.
The blood test includes:
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels. This is a protein that is usually produced by the fetus' liver and is present in the fluid surrounding the fetus (amniotic fluid or amniotic fluid), and crosses the placenta into the mother's blood. Abnormal AFP levels may increase risks such as spina bifida, Down syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities, defects in the fetal abdomen, and twins.
- The hormone levels produced by the placenta include hCG, estriol, and inhibun.
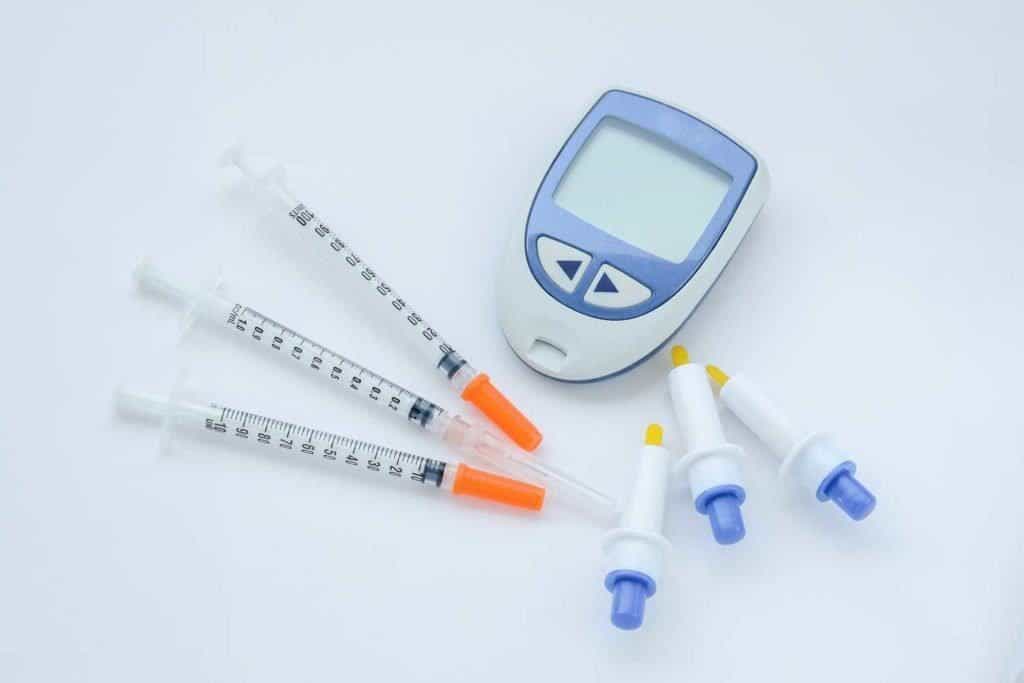
2. Blood sugar test
A blood sugar test is used to diagnose gestational diabetes. This is a condition that can develop during pregnancy. This condition can increase cesarean delivery because babies of mothers with gestational diabetes usually have a larger size.
This test can also be done after pregnancy if a woman has high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Or if you have low blood sugar levels after giving birth.
This is a series of tests that are done after you drink a sweet liquid containing sugar. If you have positive gestational diabetes, you have a higher risk of diabetes in the next 10 years, and you should get another test after pregnancy.
3. Amniocentesis
During amniocentesis, amniotic fluid is removed from the uterus to be tested. It contains fetal cells with the same genetic makeup as babies, as well as various chemicals produced by the baby's body. There are several types of amniocentesis.
Genetic amniocentesis test for genetic disorders, such as spina bifida. This test is usually done after the 15th week of pregnancy. This test is recommended if:
- Test screening during pregnancy shows abnormal results.
- Has a chromosomal abnormality during a previous pregnancy.
- Pregnant women aged 35 years or more.
- Have a family history of certain genetic disorders.
Screening test during pregnancy 3rd trimester
ScreeningStrepococcus Group B
Strepococcus Group B (GBS) is a group of bacteria that can cause serious infections in pregnant women and newborns. GBS in healthy women is often found in the area of the mouth, throat, digestive tract, and vagina.
GBS in the vagina is generally not dangerous for women regardless of whether they are pregnant or not. However, it can be very dangerous for newborns who do not have a strong immune system. GBS can cause serious infections in babies infected at birth. This test is done by rubbing the vagina and rectum of a pregnant woman at 35 to 37 weeks' gestation.
If the results of GBS screening are positive, you will be given antibiotics during labor to reduce the risk of the baby getting GBS infection.