Contents:
Medical Video: Coping with Anxiety and Depression During Pregnancy
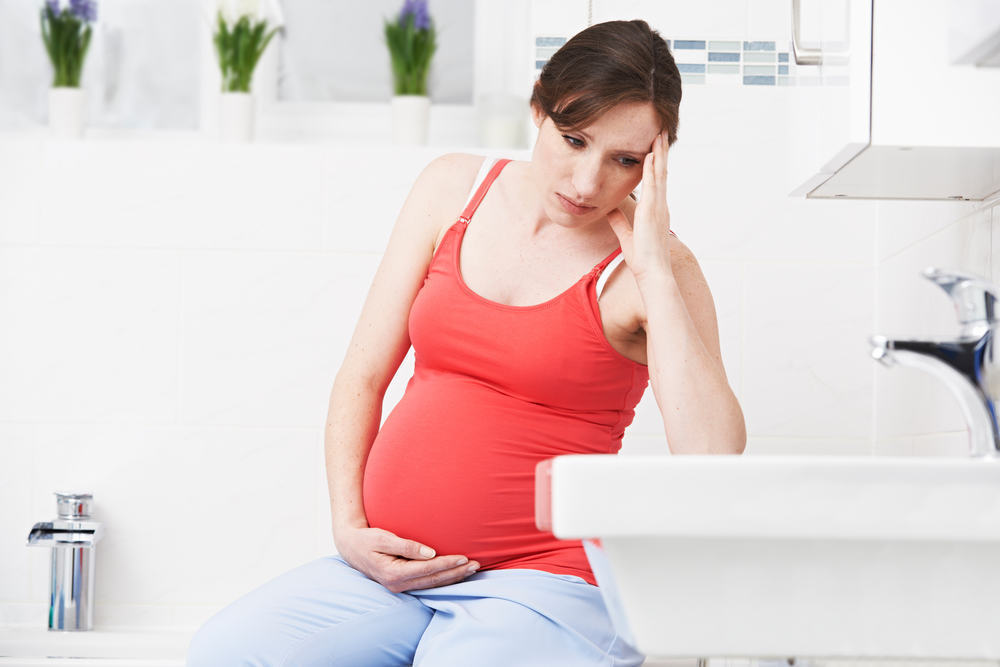
Pregnancy should be one of the happiest moments in a woman's life, but for many women, pregnancy is a confusing, frightening, stressful and even depressing time.
Depression is a mood disorder that affects 1 in 4 women at one point in their lives, so it's not surprising that this disease can also affect pregnant women.
Postpartum depression - a depression that afflicts the mother after giving birth - or the baby blues may be much better known, but mood disorders during pregnancy itself are more common in pregnant women than previously thought.
Depression in pregnant women is often not detected
Depression during pregnancy is often not properly diagnosed because people think that the symptoms shown are just another form of hormonal change - which is normal during pregnancy. Therefore, health care providers may be less responsive to investigating the psychological condition of pregnant women, and a pregnant woman may feel embarrassed to discuss the conditions she is experiencing. As many as 33 percent of pregnant women show symptoms of depression and anxiety disorders, but only 20 percent of those who seek help, reported from Parents.
Inadequate treatment of depression in pregnant women will be dangerous for the mother and the baby in the womb. Depression is a clinical disease that can be treated and managed; However, it is important to seek help and support first.
What are the signs and symptoms of depression in pregnant women?
It may be difficult to diagnose depression during pregnancy because some depressive symptoms can overlap with classic symptoms of pregnancy, such as changes in appetite, energy levels, concentration, or sleep patterns.
It's normal to worry about some changes in yourself for the sake of pregnancy safety, but if you experience persistent symptoms of depression and / or anxiety disorders for two weeks or more, especially until you can't function normally, immediately seek help.
Signs and symptoms of depression during pregnancy, including:
- Stuck in a depressive mood every time
- Sadness that never ends
- Too much or little sleep
- Drastically lose interest in things you usually enjoy
- Guilty feeling
- Withdrew from the surrounding world, including family and close relatives
- Taste is not valuable
- No energy, prolonged weakness
- Poor concentration, or difficulty making decisions
- Changes in appetite (too much or little)
- Feeling desperate
- No motivation
- Have memory problems
- Crying continuously
- Having headaches, aches and pains, or indigestion that doesn't heal
And it may be followed by symptoms of other psychiatric disorders, including:
General anxiety disorders:
- Excessive anxiety that is difficult to control
- Easy to get angry and offended
- Muscle pain / pain
- Feeling restless
- Fatigue
Obsessive-Compulsive disorder:
- Repeated and ongoing thoughts about death, suicide, or despair
- The tendency to take repetitive actions or behaviors to alleviate these destructive thoughts
Panic attack:
- Repeated panic attacks
- A constant fear of the possibility of a subsequent panic attack
Your doctor can find out if your symptoms are caused by depression or something else.
What triggers depression in pregnant women?
Although the accurate incidence of depression in pregnant women in Indonesia is not yet known, it was reported from Healthline, depression in pregnant women, also known as antenatal depression, affects 10-15 percent of women in general. In the United States, quoted from American Pregnancy, according to data from The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), around 14-23 percent of women struggle with some signs and symptoms of depression during pregnancy.
Women with the following risk factors have the opportunity to be prone to depression:
- Personal or family medical history of mood disorders, such as depression or anxiety disorders
- History of premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
- Become a young mother (under the age of 20)
- Lack of social support (from family and friends) owned
- Living alone
- Having a husband and wife relationship problem
- Divorced, widowed, or separated
- Have experienced several traumatic or stressful events in the past year
- Complications of pregnancy
- Have low financial income
- Has more than three children
- Have had a miscarriage
- History of domestic violence
- Drug abuse
- Anxiety or negative feelings about the pregnancy
Anyone can experience depression, but there is no single cause.
Women who experience depression during pregnancy have a greater risk of postpartum depression.
What are the consequences for babies if you experience depression during pregnancy?
The risk to infants in the fetus from mothers who experience depression or anxiety during pregnancy, including low birth weight, preterm birth (before 37 weeks), low APGAR score, and respiratory problems and anxiety. However, it does not rule out the possibility that depression that afflicts pregnant women will also fall to the fetus.
Reporting from Compass, the study in the journal JAMA Psychiatry shows that women who experience depression during pregnancy will reduce the risk of developing lesions in their children as adults.
Rebecca M. Pearson, PhD, from the University of Bristol in the UK, and her research team used data from more than 4,500 patients and their children in a community study. The researchers concluded that children born to mothers who experienced depression during pregnancy, on average, were 1.5 times more prone to depression when they were 18 years old.
While the risk of genetic offspring can be a potential explanation, Pearson, reported from Healthline, said that the physiological consequences of depression experienced by the mother can enter the placenta and affect fetal brain development.
How to treat depression during pregnancy
These findings have an important impact on the nature and timeliness of medical interventions to prevent depression in children in the future. Treating depressive signs and symptoms during pregnancy as soon as possible, regardless of the background of the cause, is the most effective step, according to the study.
Researchers believe that different factors may be involved in depression before and after pregnancy. In postpartum depression, environmental factors such as social support have a great effect on healing.
Treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy - a type of face-to-face speech therapy - have been shown to help pregnant women with depression without the risk of side effects that may arise from psychoactive drugs.
Professional health care providers must be aware and alert to support women. Depression during pregnancy is as important as postpartum depression, and must be addressed as early as possible not just to prevent the pain from continuing after birth.
READ ALSO:
- What Happens In Infants If Mothers Stress When Pregnant?
- Is It Really Excess Folate When Pregnant Can Trigger Autism In Babies?
- The most sound sleep position for pregnant women