Contents:
- Medical Video: Cerebral cortex | Organ Systems | MCAT | Khan Academy
- What is the cerebral cortex?
- Parts of the cerebral cortex
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Temporal lobe
Medical Video: Cerebral cortex | Organ Systems | MCAT | Khan Academy
Every human movement and behavior is regulated by the brain. However, the brain does not work alone. There are many parts of the brain that are responsible for carrying out various bodily functions. One of them is the cerebral cortex.
What is the cerebral cortex?
The cortex is the outermost layer of a body tissue. That is why, all human organs have a cortex, such as the kidneys, adrenal glands, thymus, lymph nodes, and brain.
The cerebral cortex is a thin layer (1.5 mm to 5 mm) that wraps the brain. The cerebral cortex is composed of a creased fold that is called a gyri and a gap called sulci. The cerebral cortex is lined with meninges that are composed of hundreds of thousands of nerve cells which are attached together. The brain cortex is often also referred to as gray matter.
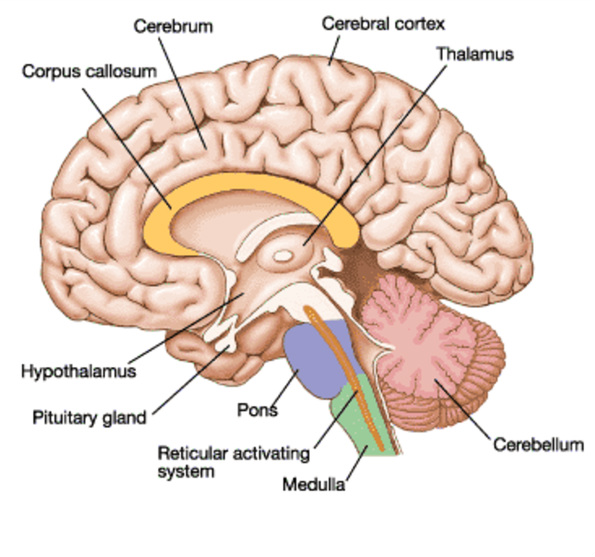
Most of the sensory information processing of the five senses occurs in the cerebral cortex. This part of the brain is the most developed of the human brain and is responsible for thinking, understanding, speaking, producing and understanding language, memory, attention / alertness, caring, awareness, organization and planning, problem solving, social ability, advanced motor function, and taking decision.
Over time, the human cortex undergoes a process of shrinkage. This process occurs because the brain continues to collect and store all information obtained from time to time. Therefore, the more wrinkles your brain has, the higher your intelligence level. These folds increase the surface area of the brain, and therefore increase the amount of gray matter and the amount of information that can be processed.
Parts of the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes, each of which has a specific function. These lobes include the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Here's the full review:
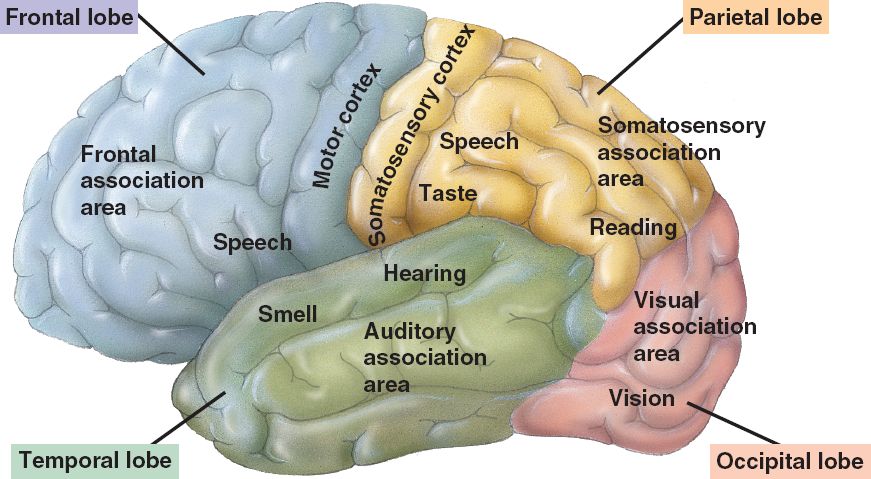
Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe (blue in the upper image) is the frontal part of the brain located just behind the forehead. The frontal lobe is responsible for regulating movement, judgment, decision making, problem solving, spontaneity and planning (impulse control), memory, language, and social and sexual behavior.
The right frontal lobe regulates the left body activity, and vice versa, the right frontal lobe regulates the left body activity.
Parietal lobe
The parietal lobe (yellow in the image) is the main place for processing sensory information, such as taste, temperature, smell, hearing, sight, and touch. The more sensory information the body receives, the more gyri and sulci are present in the lobe. Humans will not be able to feel the sensation of touch, if the parietal lobe is damaged.
Parietal lobes also function as spatial reasoning (space and dimensions) and direction navigators, which include reading and understanding maps, preventing themselves from bumping or bumping into an object, and coordinating limbs without visual stimulation - such as bribing food to the mouth without having to look at the spoon.
Occipital lobe
The occipital lobe (pink in the image) lies below the parietal lobe. The occipital lobe plays a role for us to understand what your eyes see. The lobe works very fast for processing fast information sent by the eye, for example understanding text in books or pictures on banners.
If the occipital lobe is damaged or injured, we will not be able to process the visual signal correctly, so that it can experience visual impairment.
Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe (green in the image) is located below the frontal lobe and parietal lobe. The temporal lobe is involved in the perception of hearing and language, to process the sound signal information from the ear into the words and words we hear. This lobe is also the key to being able to process and understand the meaning of a speech.
The temporal lobe helps us recognize and distinguish all types of sounds and high and low tones that are sent from the sensory receptors of the ear. We will not be able to understand someone speaking to us, if not for the temporal lobe.
In addition, the temporal lobe also acts to process memory and emotions.
The structures of the limbic system such as the olfactory cortex, amygdala and hippocampus are located in this lobe.
Hello Health Group does not provide advice, diagnosis or medical treatment.












