Contents:
- Medical Video: New Test for Liver Disease-Mayo Clinic
- Examination of physical history
- Blood test
- Imaging test
- Network analysis
Medical Video: New Test for Liver Disease-Mayo Clinic
It might feel a little scary to see a doctor to find out if you have liver disease. Nurses and doctors may take your blood and inject you without telling you what the test uses. We can help you reduce anxiety by explaining diagnostic tests.
Examination of physical history
One of the first things a doctor will do is to do a physical examination and review your medical history. Your doctor will ask a series of questions and evaluate general signs and symptoms. Including:
- Yellowish skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Swelling of the legs and ankles
- Itchy skin
- Dark urine
- Pale or bloody stool
- Chronic fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- The tendency to easily bruise.
After reviewing your symptoms, your doctor may want you to talk about your medical history. This means you need to tell your doctor if there is a history of liver disease in your family, if you currently use herbal medicines or supplements, or if you have other health conditions.
Your doctor may also ask about your recent activities, such as unprotected sexual intercourse, taking drugs or alcohol, or sharing contaminated needles, to determine possible causes of symptoms. It's important to always tell your doctor everything; no matter how embarrassing or simple it is. This can be a clue to the causes of your liver disease. Next, the doctor will examine the physical signs for liver disease. By pressing on the heart area, they will look for:
- Enlargement of the liver (hepatomegaly): Enlarged liver may be a sign of hepatitis, obstruction, liver fat, or cancer.
- There is a lump: If you have a lump that you can feel, the doctor will check it too. This should be examined further to see if it is cancer.
- Irregular heart shape: Density of the heart, irregular shape, blunt edge, and if there is scarring in the liver caused by cirrhosis.
- Pain in the liver: Pain and pain in the liver can cause bleeding, hepatitis or cancer.
In addition to examining the liver, your doctor may examine other parts of your body. The following are signs that your doctor might check:
- Accumulation of fluid in the stomach (ascites) which causes swelling of the stomach
- Abnormal enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly)
- Sleepy and confused
- Nausea and vomiting
- Yellowing on the skin or eyes
- Itchy skin
- Swelling of the legs and ankles
- Bruises without cause.
The doctor will not confirm your diagnosis until further tests are carried out. There are three main types of tests performed in the diagnosis of liver disease: blood tests, imaging tests, and tissue analysis.
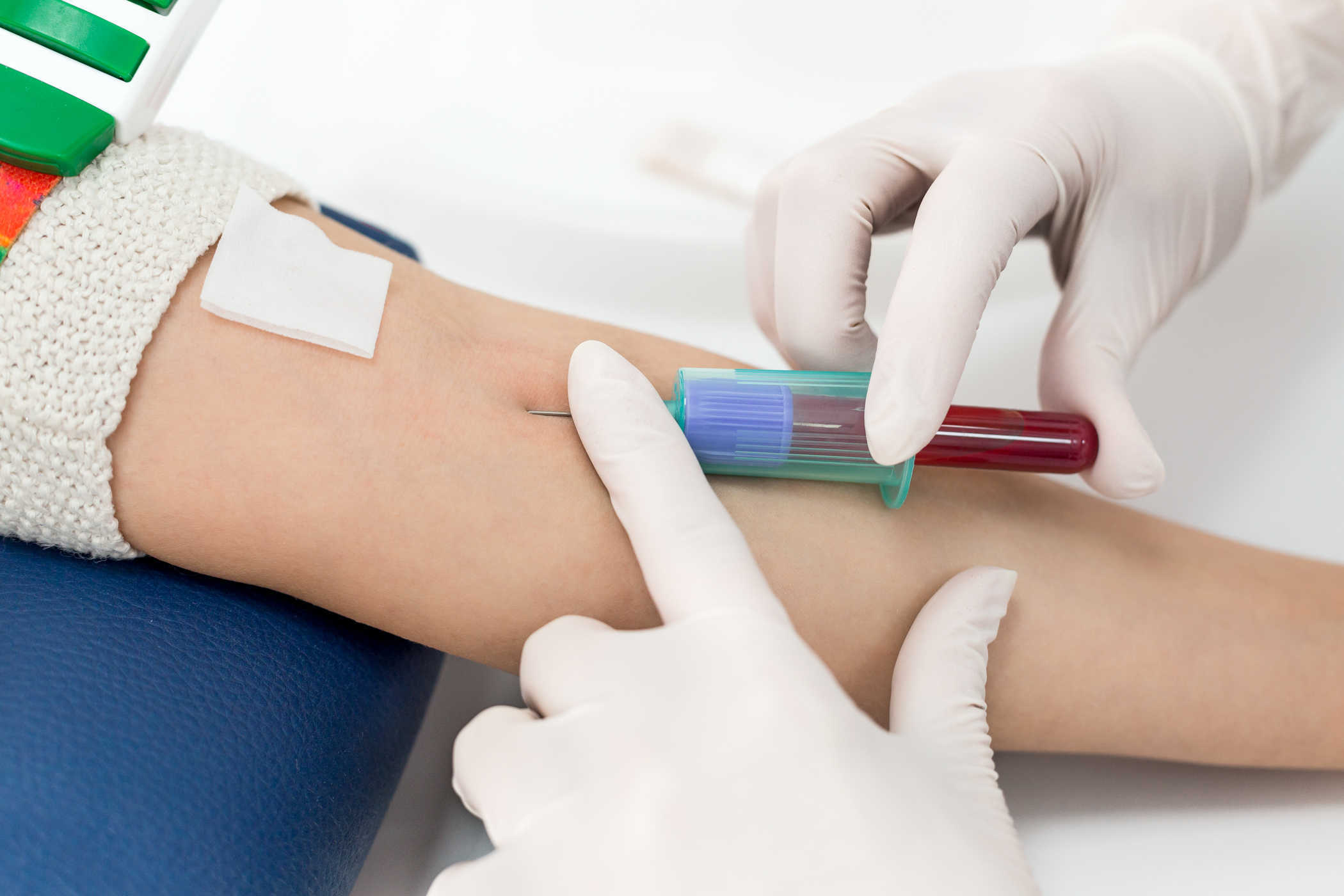
Blood test
The most common type of laboratory test for liver disease is a blood test and will be one of the first tests recommended by your doctor. This test can reveal the following:
- Amount of blood. Your blood count may show a decrease in red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. This confirms that there is an advanced liver disease that suppresses blood cell production.
- Increase liver enzymes. Serum AST (aspartate amionotransferase) and ALT (Alanine aminotransferase) enzymes. This is an enzyme produced by the liver. Too much of this enzyme means there is a problem with the liver. This can be caused by injury or inflammation of the liver. Liver enzymes can increase due to alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Increased GGT (Gamma glutamyl transferase) and ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase): these are also enzymes that increase during liver disease. Usually removed from the bile duct.
- Increased bilirubin: Levels of increase in bilirubin in liver disease. Bilirubin reaches the heart where they will be extracted. Higher bilirubin levels mean increasing clotting factors and the risk of bleeding and easy bruising.
- Low albumin level: Albumin is a protein made by the liver. If you have liver disease, your liver cannot produce enough albumin to be used on your body.
Your blood test along with a physical and medical examination can reveal the following types of liver disease:
- Acute alcoholic hepatitis
- Hepatitis virus (hepatitis A, B, C)
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Imaging test
Imaging tests are another diagnostic test used to confirm liver disease. This method is used primarily to check the size of the tumor or scar tissue in the liver. This includes:
- X-rays of the stomach. X-ray imaging creates images of the inside of your body in shades of black and white
- Computed tomography (CT) scan. Use special x-ray equipment to make cross-sections of your body.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses large waves of magnets and radios to see the organs and structures in your body. This results in more detailed photos of x-rays and CT scans.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). A small camera attached to a thin tube called an endoscope, or space for short, which allows the doctor to see if there are problems with the biliary or system pancreatic duct.
During X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, you will stand or lie on the machine to take photos of your heart. You will not feel sick from this procedure and need a little preparation for this test.
For endoscopy, you will listen to the risks of this procedure and the preparation from your doctor. Generally, you will be given instructions to fast before the test. This means not eating or drinking 8 hours before ERCP. Smoking and chewing gum are also prohibited during this time.
During ERCP, you may need to lie on your back or face sideways on the x-ray table. Infusion needles are inserted into the blood vessels in the arm with tranquilizers, drugs to help you relax and not feel sick, if needed. The doctor inserts the endoscope into the esophagus, through the stomach, and to duodenum to examine tumors.
Network analysis
Tissue analysis, also known as liver biopsy, will examine tissue samples of your liver. You may need general anesthesia to help you not feel pain during the procedure. The doctor will slash a little on your skin and use a long thin needle to aim it towards your heart to lift the sample of liver cells. After taking the sample, the incision is sewn back. This will heal with a little scar.
The sample is then examined under a microscope to examine cancer cells, bacteria or fat in the liver. This will help the doctor to determine the cause of your liver disease.
There may be other tests not mentioned above. If you have a problem, please discuss with your doctor. Complete understanding is very important for you to make the best health decisions.