Contents:
Medical Video: Blood Donation at Mayo Clinic
Blood is something we can easily donate because our bodies will continue to refill to replace the amount of blood lost. The average adult has 5 liters of blood that continues to spin in the body. In general, each blood cell will be broken down and then replaced with new blood cells every 120 days. Conversely, this donor blood can only last up to 42 days. This short age means that blood donors are always needed and need to be donated regularly.
Reporting from Datin Info RI Ministry of Health, blood availability for donors is ideally 2.5% of the population. That is, to meet the availability of blood stock in each region, PMI requires approximately 5 million bags of blood each year. However, data from 2013 stated that Indonesia still lacked a blood supply of up to half of the total needed.
Is blood donor safe?
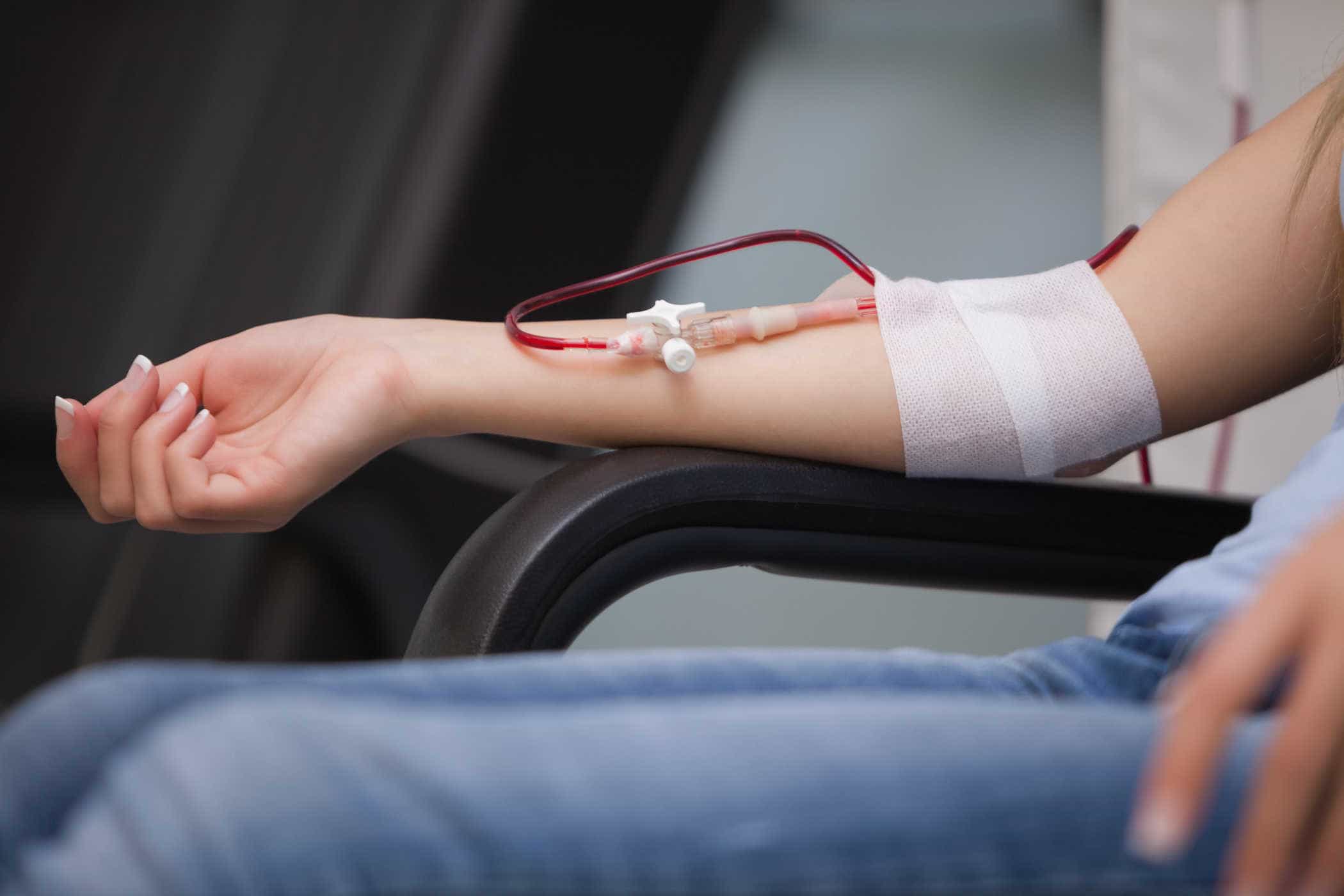
Blood donation is a guaranteed safe process. Blood from each donor will be collected through a single-use sterile needle, then collected in a sterile blood bag.
Blood donors in Indonesia are governed by Government Regulation No. 2/2011 concerning blood donor services regulated by the Indonesian Red Cross (PMI) as a social and humanitarian goal. Blood donors under the supervision of PMI are also guaranteed by Law No. 36/2009 concerning Health, that the government is responsible for implementing blood donor services that are safe, easily accessible, and in accordance with the needs of the community.
Who can donate blood?
All people aged 17-65 years may donate blood. However, new donor candidates are said to be eligible if they pass a medical examination before donating blood.
Donors must weigh no less than 45 kilograms and be healthy, both physically and spiritually. In addition, your blood pressure must be in the numbers 100-170 (systolic) and 70-100 (diastolic). Blood hemoglobin levels at the time of examination should range from 12.5g to 17g%.
If you are on prescription antibiotic treatment, you must complete the prescription completely before donating blood.
For those of you who just got a tattoo, you might be required to wait up to one year to be able to donate blood.
If you have a fever or flu, low blood pressure (below 80/50), or if your blood hemoglobin level is too low, you cannot donate blood. Similarly, donors who have or are at risk of malaria, HIV, hepatitis B and C, heart and lung disease, cancer, hypertension, diabetes, blood disorders or abnormal bleeding, epilepsy or seizures, syphilis, and drug and alcohol dependence.
How is the blood donation process?
The blood donation process from you arrive to completion takes about one hour. Blood donation itself only lasts about 8-10 minutes. The steps in this process are:
Registration: You will be asked to show an identity card (KTP / SIM / Passport) and a donor card (if you have one) and fill out the registration form around your identity, including the donor's identity number (if you are a regular donor).
Medical examination: The service clerk will interview you about your medical history and illness. At this stage, your blood pressure, hemoglobin level, body temperature, and pulse will be measured.
Donation: Blood donation is carried out in a sitting or lying position, and is carried out by a trained health professional. A sterile needle will be inserted into the skin at the inner elbow for 8-10 minutes while one liter of blood and several tubes of blood samples are collected. After that, the clerk will close the injection site area with a bandage.
Break: You will be given time to recover by enjoying food and drinks provided by blood donor organizers to replenish energy after losing a lot of fluid volume.
After blood donation, you will not feel anything - you can go home and continue your daily routine - although a small number of people may feel dizzy, stomach ache, or bruising in the area of the injection site. Very rarely, donors experience loss of consciousness, nerve damage, or arterial damage.
What should be done before blood donation?
Sufficiently supply your body's nutrients and fluids with iron-rich foods and drinks, such as red meat, chicken, fish, dairy products, nuts and seeds, and spinach. Avoid fatty foods, such as fast food or ice cream, which can outwit blood tests. If your blood contains too much fat, your blood cannot be tested for infectious diseases and your blood cannot be used for transfusion. Also avoid alcohol consumption before the blood donor H-day.
On the eve of a blood donor, try to get enough sleep. Drink plenty of water or other non-alcoholic drinks before blood donation.
On blood donor days, wear clothes that are easily rolled up above the elbow, or wear a T-shirt.
What should be done after blood donation?
Increase fluid and food intake. Avoid alcohol for up to 24 hours after blood donation.
You can remove the bandage 5 hours after the donor. If you experience bleeding, raise your arms above your head and apply pressure until the bleeding stops. If you feel sick, compress ice for the first 24 hours. If the pain continues, compress with warm water.
Do not lift heavy items or carry out heavy activity with your arms during the day.
If you feel weak, dizzy, or nauseous after donating blood, stop everything that is doing and sit or lie down for a few moments until you feel better.
Will the donor be notified if he or she has an illness based on the results of a blood test?
Blood test results are private and confidential information. PMI will not divulge positive test results to anyone, except donors and if required by law.
Donors who have tested positive for HIV or other blood-borne infectious diseases will be notified immediately by PMI and have the opportunity to counsel with a professional health counselor from PMI.
PMI keeps records of people who are at risk of spreading transfusions. PMI will be required by law to report any risk information to the Ministry of Health and other government agencies concerned, if needed.
Donation information can also be used confidentially for medical research.
Can you get HIV from a blood donor?
Not. You cannot contract HIV or other infectious diseases through legal blood donations.
Blood donation procedures monitored by PMI and the government are guaranteed security. Health workers will use sterile and disposable equipment for each donor, whose seal will be removed and disposed of with your knowledge.
What will PMI do to donor blood?
Donor blood collected will be sent to the laboratory for processing - divided as needed, for example red blood cells, plasma, blood platelets and / or cryoprecipitates. Donor blood is then ready to be distributed to various hospitals in Indonesia.
Blood donation is one simple thing you can do, but it can make a big difference in other people's lives. Each donated bag of blood donors can save three people in need.