Contents:
- Medical Video: What You Need To Know About Infectious Disease
- Various ways bacteria can spread
- Through touch between skin and objects containing bacteria
- By air
- Food cross-contamination
- Other ways
- How can bacteria cause disease?
- How to avoid bacterial infections?
Medical Video: What You Need To Know About Infectious Disease
Bacteria are one-celled orgasms, one of the most life forms on Earth. These microorganisms are everywhere. They live in land, water, air, in the body of every human and animal. Most bacteria are harmless, even beneficial for health. Just look at the bacterial colonies in the intestines and vagina of women, which are in charge of maintaining the functions of the two organs that continue to run optimally. But beyond that, some bacteria are the culprit that causes disease. Bacterial infections can be mild to severe causing death. For example, such as tuberculosis and cholera. Do you know how bacteria can spread and cause disease, and what can be done to prevent it? Check out this article.
Various ways bacteria can spread
In general, the way to spread bacteria is through the following four main ways:
Through touch between skin and objects containing bacteria
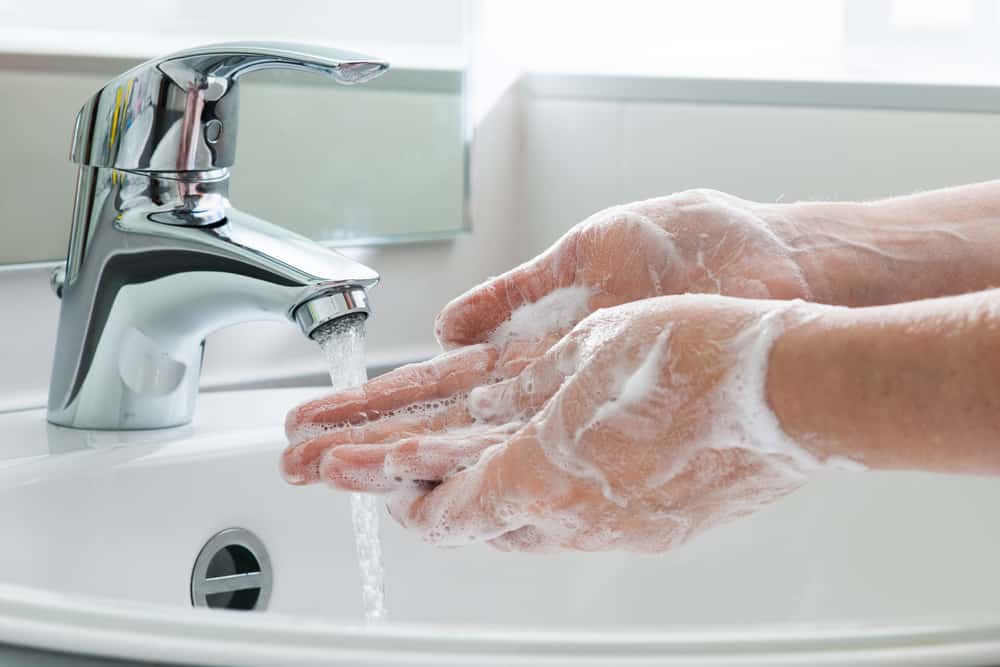
One of the most comfortable homes for bacteria is the human hand. About 5,000 bacteria inhabit your hands every time. Therefore, touching the hands, both directly with the skin of other people and holding objects, can be a medium for spreading bacteria.
Do not wash your hands after holding your nose / mouth while coughing / sneezing, holding animals, urinating, touching raw food, preparing food, changing children's diapers, and others can trigger the spread of bacteria from your body to others. Touching the skin of an infected person can also cause you to contract the disease.
The example is this: You are experiencing a red eye infection (conjunctivitis), and then you rub your eyes, don't wash your hands first, and then shake hands with other people. After that the person rubbed his eyes or ate with his hands without washing hands. The person can experience the same eye infection or infection in another part due to the transfer of bacteria from you through touch.
The principle of spreading the same bacteria also happens if you like borrowing and borrowing personal items or touching items that are used by sick people. For example, used tissue to sneeze or bath towels for people who have diarrhea.
By air
Another way of spreading bacteria is through moisture dew particles that come out when you cough or sneeze. Air particles that contain bacteria and viruses can be inhaled by other people and infect their bodies, so they contract the cough and flu you have. Even worse, bacteria are not visible to the naked eye, so you will never know who is sick and sneezing / coughing near you.
Therefore, you are recommended to use a mask when you are sick. Or if it is not available, you must always adhere to the ethics when coughing and sneezing, for example closing your mouth when coughing and sneezing, to prevent transmission of diseases through the air, such as tuberculosis.
Food cross-contamination
If you do not pay attention to cleanliness, cooking activities can often be a source of transmission of diseases caused by bacteria. The unclean cooking process, such as not washing hands after touching raw food, preparing food, and using the toilet before cooking can spread bacteria to others. Eating foods contaminated with bacteria can cause diarrhea, botulism, and food poisoning, for example.
Other ways
Beyond that, bacteria can also spread in different ways, such as through:
- Drink or use contaminated water (cholera and typhoid fever)
- Sexual contact (syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia)
- Contact with animals (anthrax, paint scratch disease)
- The transfer of bacteria from one part of the body, which is the real habitat, leads to another part, where bacteria cause disease (such as when E coli moves from the intestine to the urinary tract causing urinary tract infections).
How can bacteria cause disease?
Bacteria can cause disease in several ways. Some bad bacteria can multiply so much that they interfere with their natural ecosystem, such as bacterial vaginosis. Some destroy the network directly. Others produce toxins (poisons) that kill cells.
When bacteria infect, they will stay long in the body. They "devour" the body's nutrients and energy, and can produce poisons or toxins. The toxin can eventually cause symptoms of common infections, such as fever, wheezing, rash, coughing, vomiting, and diarrhea.
To find out how bacteria cause disease, usually, the doctor will see blood samples, urine, and other fluids under a microscope or send these samples to the laboratory to get more tests. Through this method the doctor can know which germs live in your body and how they can cause you pain.
How to avoid bacterial infections?
There are various ways to prevent bacterial infections, namely:
- Wash your hands with soap and running water after your hands hold your nose / mouth when coughing / sneezing, holding animals, urinating / urinating, touching raw food, preparing food, before eating, changing children's diapers, and so on. Washing your hands can prevent as many as 200 diseases.
- Don't touch the eyes, nose and mouth too often
- Food must be cooked or cooled as quickly as possible
- Vegetables and meat must be stored separately and prepared on separate cutting boards
- Meat should be processed well and cooked until cooked
- Using a condom during sexual intercourse reduces the possibility of the spread of sexually transmitted diseases
Bacterial infections can be cured by prescription antibiotics.