Contents:
- Medical Video: How do you treat a patient with gas gangrene ? | My Health
- What is gangrene gas?
- Characteristics and symptoms of gangrene gas
- Causes of gangrene gas
- How to treat gangrene gas?
- Complications due to gangrene gas
- How to prevent gangrene gas?
Medical Video: How do you treat a patient with gas gangrene ? | My Health
When you get hurt, what do you do to treat the wound? Do you wash your wounds clean? Close it tightly? Handling good wounds is very important to prevent more serious and even life-threatening complications such as gangrene gas.
What is gangrene gas?
Gangrene gas is an infection of tissue, cells, and blood vessels caused by bacteria. These infecting bacteria will then release gas and release toxins that cause tissue death. Although it is a rare condition, gangrene gas can spread quickly and can be life threatening if left unchecked.
Most gangrene infections occur due to trauma that causes open sores or places of operation that are exposed to bacteria. In more rare cases, gangrene can also occur due to disruption of blood flow to certain body tissues and that part is infected by bacteria. This condition is at risk for sufferers atherosclerosis or diabetes mellitus.
Characteristics and symptoms of gangrene gas
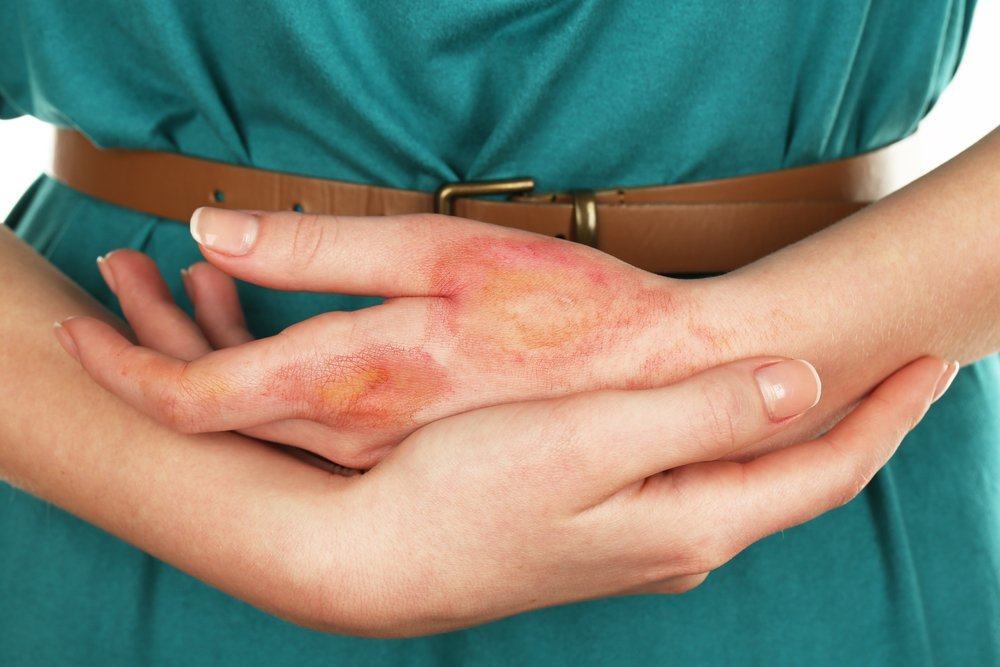
Gangrene gas can occur anywhere on the body, but is most often found on the feet and hands. Symptoms of gangrene gas can be:
- fever
- air under the skin
- pain and swelling around the wound
- pale skin that quickly turns into magic, dark red, purple, or black
- resilient with smelling liquid
- excessive sweating
- fast pulse
- gag
- yellow skin (jaundice) in further cases
The above symptoms mostly appear approximately 6 to 48 hours after the infection and can spread quickly. Immediately contact a medical officer or take the patient to the hospital to get quick treatment.
Causes of gangrene gas
Gangrene gas is mostly caused by bacteria known as names Clostridium perferingens. In some cases, this condition can also be caused by bacteria from the group Streptococcus. Infections that occur usually last suddenly and can spread quickly.
Gangrene gas usually appears at a new surgical site or in a new wound area. In very rare cases, gangrene can also appear spontaneously without a clear trigger.
Some wounds have a high risk of developing gangrene:
- injury to the muscle
- severe tissue damage
- very deep wound
- wounds contaminated by feces, especially those obtained from livestock
You will also be more at risk of experiencing gangrene gas if you have conditions such as:
- diabetes
- arterial disease
- colon cancer
- frostbite(frostbite)
- open fracture
- use contaminated needles to inject certain substances into your body
How to treat gangrene gas?
After being diagnosed, gangrene gas must be treated immediately. Usually the doctor will give antibiotics that are inserted through an IV so that it can go directly into your blood vessels. Tissues that have died or become infected must be removed surgically immediately. Your doctor may also need to repair blood vessels so that blood flow to the infected site can return smoothly.
Repairing damaged tissue can be done by technique skin graft. Through this method, the doctor will take healthy skin from the uninfected place and plant it on the injured site after of course removing infected skin cells. In cases of severe gangrene, doctors can only suggest one limb amputation to save other parts of the body from spreading the infection.
Some doctors also use the method of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to help speed healing of gangrene gas. In this therapy, you will be asked to breathe oxygen gas in a special pressure room. The goal is to increase oxygen levels in your blood, so that it can help damaged tissue to heal faster.
Complications due to gangrene gas
The faster the gangrene gas is handled, the better the results of the treatment. Some complications that can occur if this condition is left are:
- permanent tissue damage
- jaundice or yellow
- liver damage
- kidney failure
- in shock
- spread infection
- coma
- Dead
How to prevent gangrene gas?
The best way to prevent the formation of gangrene gas is to keep the wound clean. Be sure to always wash the wound and cover it with a bandage. Call your doctor if you get signs of infection in the wound. These signs can be redness, swelling, pain, and discharge from the wound. If your doctor gives you antibiotics to drink, make sure you drink it according to the rules.
Changing lifestyle can also reduce the risk of developing gangrene, such as;
- Avoid all tobacco products.
- Treat your health problems correctly if there are, such as diabetes or arterial disease.
- Maintain weight by exercising regularly and eating healthy foods.