Contents:
- Medical Video: Medical Animation: Testicular Cancer
- How do you do the testis yourself?
- What if you find something different in your testicles?
Medical Video: Medical Animation: Testicular Cancer
Most testicular cancers can be found at an early stage. In some men, early testicular cancer causes symptoms that make them need medical help. Usually a lump in the testis is the first symptom. Sometimes the testicle swells or enlarges from its normal size without a lump. But some men do not realize that something is wrong until the cancer has enlarged and / or has spread.
Most doctors agree that examining the male testicles is part of the overall physical examination. The American Cancer Society recommends examining the testes by a doctor as a routine examination related to cancer.
You need to be aware of testicular cancer and see a doctor immediately if they find a lump in the testis. Routine examination of the testes themselves has not been adequately studied to show whether they reduce the risk of death from this cancer. This is why routine testicular examination is not recommended for all men. But, some doctors recommend that all men check their testicles monthly after puberty.
Men with risk factors, such as testes that do not go down, have a history of previous testicular cancer, or family members who have had this cancer, should seriously consider this self-examination every month. If you have risk factors, talk to your doctor. Every man must decide for himself whether he needs to do a testicular examination every month.
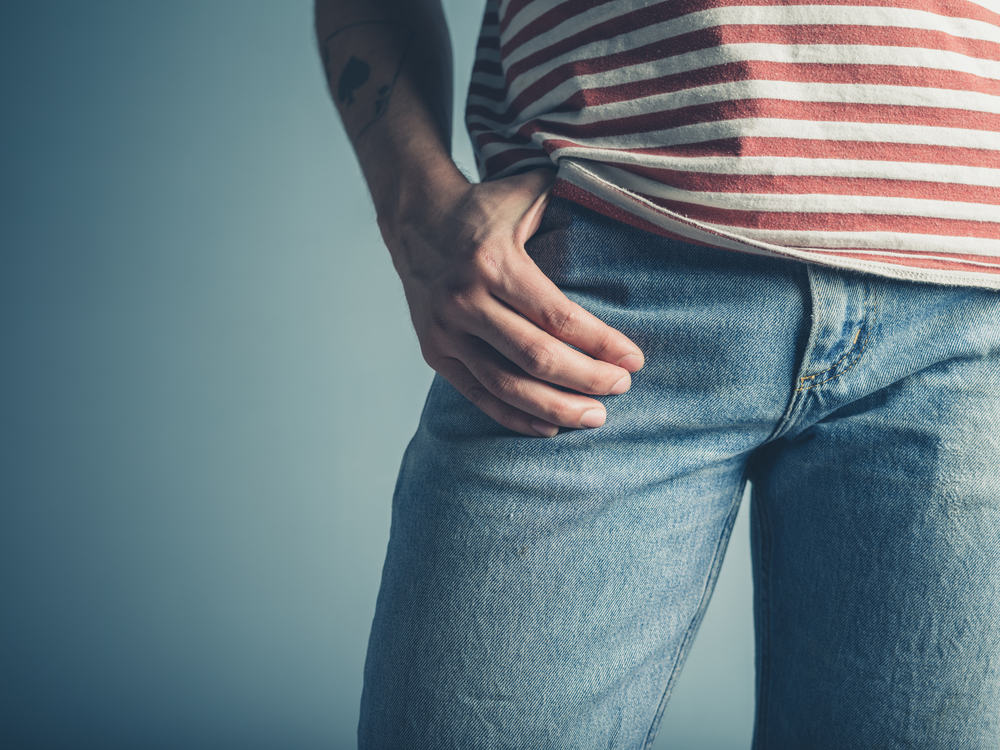
How do you do the testis yourself?
It is better to examine the testicles themselves during or just after bathing with hot water. The scrotum (the skin covering the testicles) is most relaxed at this time, and makes it easier to examine the testicles
- Check one testicle at a time. Use both hands gently to rotate the testicles (with a little pressure) between your fingers. Place your thumb over your testis, with your index finger and middle finger behind the testes, and then rotate between your fingers.
- You should be able to feel the epididymis (sperm tube carrier), which feels soft, like a rope, and is slightly soft when pressed, and is located at the top of the back of each testicle. This is a normal lump
- Remember that one testis (usually the right) is slightly larger than the other in most men. This is also normal.
- When examining each testis, feel whether there are lumps along the front or sides. Lumps may be small like a rice or peanut.
- If you notice any swelling, lumps, or changes in the size or color of the testicles, or if you have pain in the groin, tell your doctor immediately.
Lumps or swelling may not be cancer, but they should be examined by your doctor as soon as possible. Testicular cancer can almost always be cured if treated early.
What if you find something different in your testicles?
If you find something unusual or something you are unsure of, either during a self-examination or at other times, immediately consult a doctor.
The doctor will ask if you experience symptoms (such as pain) and how long you suffer from this. During a physical examination, your doctor will feel your testicles for swelling or pain and the size and location of each lump. Your doctor may also examine your stomach, groin area, and other parts of your body, looking for signs of possible spread of cancer.
If something abnormal is found, the doctor may use ultrasound to look at the scrotum and testicles. This is an easy and painless way to find out if there is a tumor or other problem. Other checks may also be carried out.