Contents:
- Medical Video: Types of stem cell transplants: autologous vs. allogeneic
- What are blood transplants and marrow stem cells?
- Who needs a stem cell transplant?
- Types of transplants
- Collection process
- Is it safe for a transplant?
Medical Video: Types of stem cell transplants: autologous vs. allogeneic
What are blood transplants and marrow stem cells?
Blood transplantation and marrow stem cells can replace the abnormal stem cells of patients with healthy ones through donors. This procedure allows patients to get new stem cells that are able to work optimally.
Stem cells found in the bone marrow, spongy tissue in bone. Stem cells develop into three types of blood cells the body needs:
- Red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body
- White blood cells, which fight infection
- Platelets, which help with blood clots
A small number of stem cells are also found in the blood and the umbilical cord (the fetus connects to the mother's placenta).
Another type of stem cell (called embryonic stem cell) can develop into all types of cells in the body. These cells are not found in the bone marrow.
Who needs a stem cell transplant?
Doctors recommend stem cell transplantation to treat patients who have:
- Certain cancers, such as leukemia. High doses of chemotherapy and radiation used to treat certain types of cancer can actually be very damaging or destroying the bone marrow. Transplantation will replace damaged stem cells during cancer treatment.
- Severe blood disease, such as thalassemia, aplastic anemia, and sickle cell anemia. In this disease, the body does not make enough red blood cells or the body does not work properly.
- Some immune deficiency diseases prevent the body from producing several types of white blood cells. Without these cells, a person is susceptible to life-threatening infections. Stem cell transplantation will replace lost white blood cells.
Types of transplants
The two main types of stem cell transplants are autologous and allogeneic.
For autologous transplants, your stem cells will be collected and stored for future use. This is so that you have enough reserves of healthy stem cells, even if you are sick. If you have cancer, cancer cells are removed or destroyed from the cells collected.
For allogeneic transplants, you will get stem cells from a donor. Donors can be from a relationship (such as brothers or sisters) or people who have no blood relations. You can also get stem cells from cord blood donated by people who don't have blood relations.
To prevent complications, donor stem cells must suit you. The test to test the compatibility of donor cells with patients is called HLA tissue typing.
Collection process
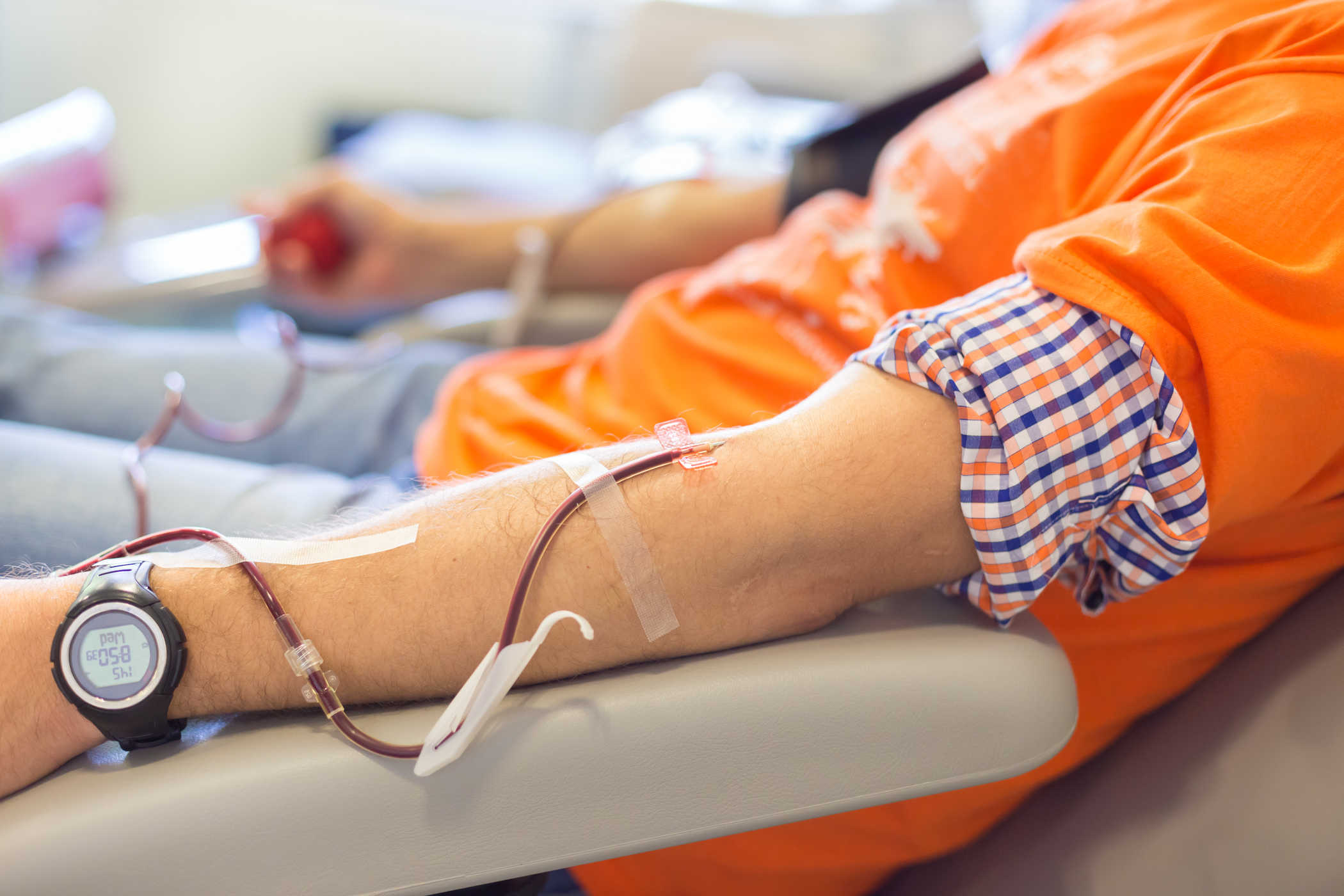
Stem cells used in transplants are collected from donors in several ways, for example through the apheresis procedure.
In this procedure, the needle is inserted into the donor's arm to draw blood. Then, blood will flow through a machine that separates stem cells from the blood. Remaining blood is returned to the donor.
Stem cells can be collected directly from the donor's pelvis. At present, the procedure is not used much anymore because it must be done in a hospital using local or general anesthesia. In this procedure, the hollow needle is inserted repeatedly into the pelvis and the marrow is sucked out of the bone.
Blood containing stem cells can be collected from the umbilical cord and placenta after the baby is born. The blood will be frozen and stored in the umbilical cord blood bank for future use.
Is it safe for a transplant?
Stem cell transplant has a serious risk. Some complications can threaten a patient's life. However, stem cell transplantation is the best hope for healing or extending the life span of some people.