Contents:
- Medical Video: 6 Things You Should Never Do After Eating
- Outdoor exercise habits that are not good for health, but you may often do
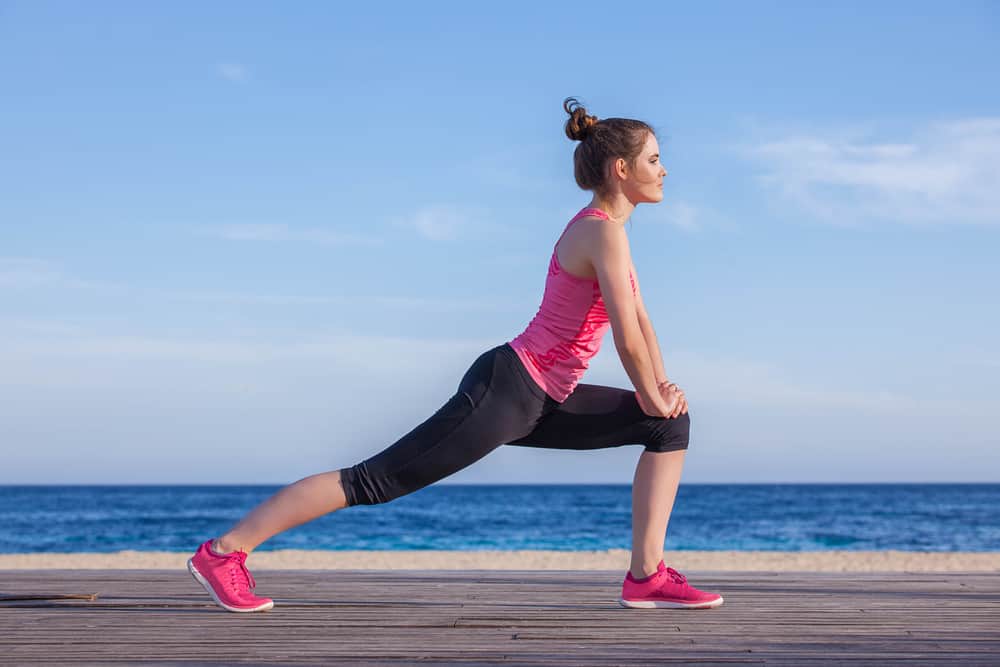
- 1. Stretching before exercise
- 2. Run on a soft surface
- 3. Increase the intensity of exercise at random to sweat more
- 4. rarely drink
Medical Video: 6 Things You Should Never Do After Eating
Although the gym offers a variety of facilities that can support the success of sports programs, some people still prefer to exercise outdoors. Sports in the city park can not only repel boredom with that sight, but also make the body and mind more relaxed. But some of the habits that you might do when exercising outdoors might turn your back on you. Are you sure, you are free from the habits below?
Outdoor exercise habits that are not good for health, but you may often do
1. Stretching before exercise
Many people believe that stretching before exercise can reduce the risk of injury while exercising. In fact, this is only a myth. A study by the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons found that stretching before running completely did notI have an impact on injury. Other studies published in the Millitary Medical Journal also state something similar.
Static stretching is the most common form of stretching that you often find when you work out in school. For example, turning your head to the right and left for 10 counts, holding your knees, stretching your arms to the right and left, and so on.
Instead of doing a static stretch set,the researchers actually suggest that you warm up by brisk walking or jogging with a slow tempo before exercising. This type of warming will be useful for your next training session.
2. Run on a soft surface
When deciding to exercise outdoors, especially running, surely most people will choose a running track that is softer than hard. The reason is, people consider that soft paths are better for joints. The fact is, until now there is not enough evidence related to this one habit.
Hirofumi Tanaka, PhD, a sports program director from the University of Texas, who was quoted from the Women Health Megazine website warned runners to be more careful when running on soft surfaces. Because the soft surface tends to be more unstable than if you run on a paved road. This can actually increase the risk of falls and sprained ankles or sprains.
3. Increase the intensity of exercise at random to sweat more
How much sweat you spend during exercise does not necessarily mean the body has burned a lot of calories.In fact, the calories burned when you run 5 km when the weather is 60 degrees will be the same as when you run 5 km when the heat is 85 degrees.
Each person produces different amounts of sweat. For example, women have more numbers of sweat glands than men, but male sweat glands tend to work more actively. That is, men naturally sweat faster and more than women even though the number of activated sweat glands is equal and the intensity of temperature and physical activity are equally equal.
Similarly, when comparing the amount of sweat from people who are actively exercising and those who are not. People who are fit can sweat faster during exercise because their body temperature is lower than those who are sedentary (less active). But the amount of sweat will be more in people who rarely exercise or never exercise, because their bodies heat up faster.
There is a good idea to avoid exercising during broad daylight, when the weather is hot. Not only at risk of being affected heatstroke, doing physical activity at high temperatures will also increase the risk of skin cancer. Try scheduling sports or other physical activities when the air temperature has started to be slightly lower, for example in the morning or evening.
4. rarely drink
Water intake when doing outdoor sports is important. But, this all depends on how long the training session you are doing. If you are going to run 5 km, you will automatically need water. But, for more strenuous activities, such as triathlon or other long-distance running Olympics in the summer, water alone is not enough to replace the fluid lost during your activity.
Actually when your body is very sweaty, you lose salt and electrolytes in the body. The bad thing is, when you fill your body fluids just by drinking water, it actually dilutes the salt and electrolyte levels which can cause hyponatremia (low sodium levels that cause cells to swell).
Instead, you need an isotonic drink. Isotonic drinks are drinks intended for athletes, to replace fluids, electrolytes, and sugar in athletes quickly. This type of drink can be quickly absorbed by the body because it has the same osmotic concentration and pressure as the liquid in the body.