Contents:
- Medical Video: Genetics of hearing loss
- What are the causes of sudden deafness?
- 1. Iron deficiency anemia
- 2. Virus infection
- 3. The eardrum ruptures
- 4. Head trauma or acoustics
- 5. Tumor
- 6. Medicine
- 7. Multiple sclerosis (MS)
Medical Video: Genetics of hearing loss
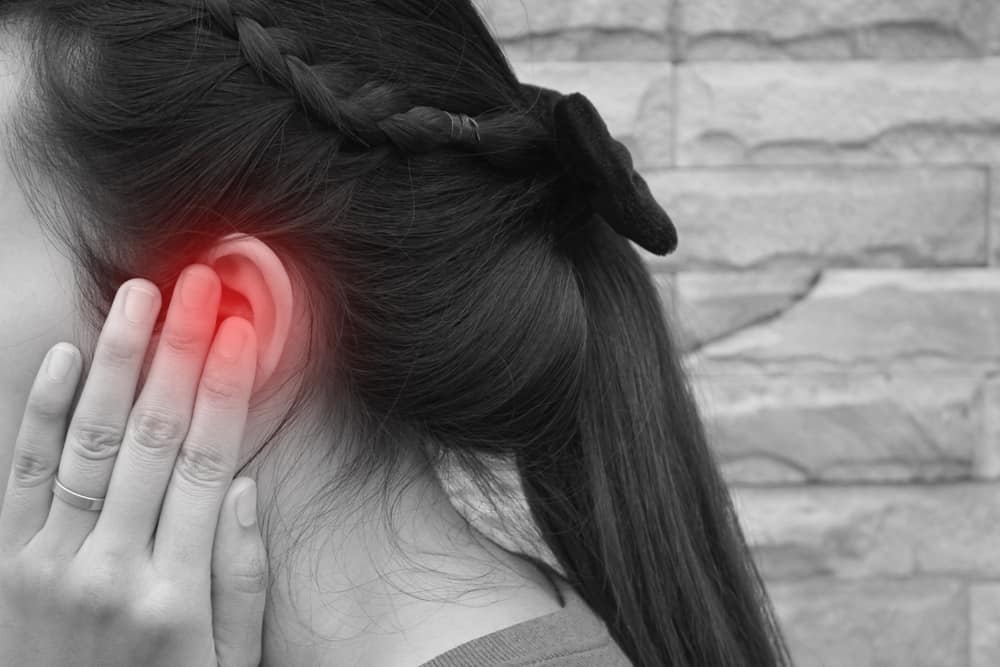
Some of you may have experienced sudden hearing loss at least once in life. When you experience sudden deafness, the sounds around you suddenly muffle as if heard from a distance. Usually this condition only affects one ear and can return to normal within a few days. However, sudden deafness should not be underestimated.There are several conditions that can cause the ear to become sudden deafness. Anything? Check out the answer here.
What are the causes of sudden deafness?
Sudden deafness or sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL) includes hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear hair cell or nerve pathway that leads from the inner ear to the brain.
Sometimes in addition to sudden deafness, there are several other symptoms that arise when a person experiences this, namely the ear feels light, and the ears ring.
In addition to water intrusion, here are some of the most common causes of sudden deaf ears:
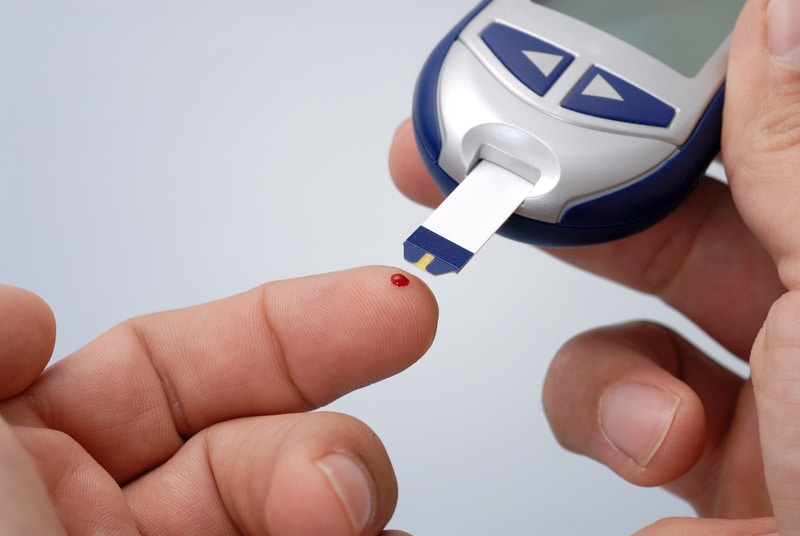
1. Iron deficiency anemia
Studies from Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine found that people who have iron-deficiency anemia are at twice the risk of experiencing this hearing loss than healthy people.
Researchers show that the inner ear is very sensitive to changes in blood supply. Iron is also clearly needed to keep the hearing system functioning normally. Too little blood and iron can eventually disrupt cell work and even kill it. This can cause hearing loss if damage or damage occurs to the hair cells in the inner ear.
So, maybe iron deficiency anemia can cause sudden deafness due to insufficient oxygenated blood flow to the inner ear. Sudden deaf ears caused by iron deficiency anemia usually develop within approximately 72 hours.
2. Virus infection
Viral infections are one of the most common causes of sudden deafness.Reporting from Hear-it, one in four people who experience sudden deafness are known to have an upper respiratory tract infection one month before the hearing loss occurs
Viruses associated with sudden deafness include goiter, measles, rubella, and meningitis, syphilis and AIDS.
3. The eardrum ruptures
The rupture of the eardrum is caused by the tearing of a thin membrane that separates the middle ear from the outer ear. This condition can result in sensorineural hearing loss.
4. Head trauma or acoustics
Damage to your inner ear can also be caused by an impact on the head or exposure to very loud sounds, such as an explosion.
5. Tumor
Tumors that grow on part of the brain which regulates hearing ability (parietal lobe), can cause hearing loss.
6. Medicine
There is certain drugs that can damage your ears and ultimately interfere with the ability to hear. Usually, the initial symptoms that are experienced are the appearance of a ringing sound, vertigo, and over time the ability to hear will be lost or deaf.
These drugs have a direct effect on the organs in the ear that function to receive and process sounds which will then be sent to the brain for translation.
According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, there are at least 200 types of over-the-counter and prescription drugs that can cause loss of hearing ability.
7. Multiple sclerosis (MS)
Nervous system disorders caused by multiple sclerosis (MS) can affect nerve cells in the brain and spine. The brain membrane (myelin) can also be affected and cause damage to nerve fibers at the base of the brain.Usually, people with this condition will show symptoms such as sudden hearing loss.