Contents:
- Medical Video: 5 Common Signs of Heart Disease
- How can sleep patterns affect heart health?
- Risk factors for heart disease that occur due to lack of sleep
- 1. Obesity
- 2. Hyperglycemia and risk of diabetes
- 3. Increased cholesterol
- 4. High blood pressure
- The impact of sleeping too long on heart health
Medical Video: 5 Common Signs of Heart Disease
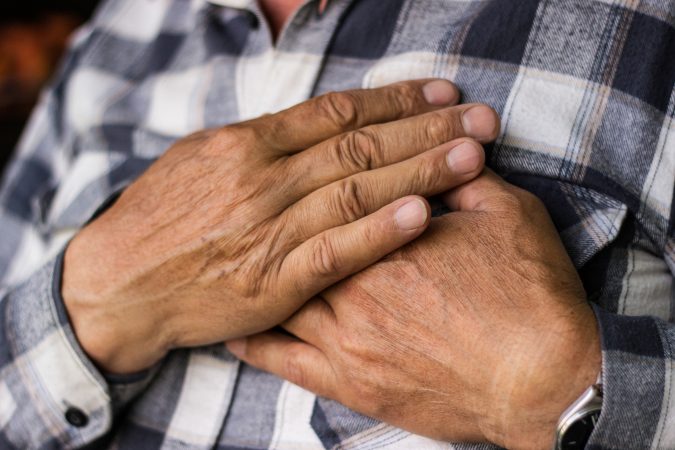
Some processes of body repair, especially in the heart, occur when a person sleeps. However, the repair process is determined by the quality of sleep which is characterized by adequate sleep. Not too long or too long. Both lack of sleep and sleep for too long have their own ways to have an impact on heart health.
How can sleep patterns affect heart health?
Either sleeping too long or too long is thought to be a risk factor for heart disease. This is also common, with around 44% of patients with coronary heart disease also known to experience sleep disorders. Researchers believe that irregular sleep has an impact on heart health in two ways, namely:
- Direct effects on physical health - through the impact of lack of energy, metabolic disorders, increased appetite, secretion of stress hormone cortisol and inflammation of the vessels due to increased blood pressure and heart rate.
- Indirect effects through behavior - Sleep patterns trigger unhealthy lifestyles caused by mood disorders, fatigue and lazy moves and cognitive disorders such as decreased ability to manage stress and negative effects on decision making to adopt a healthy lifestyle.
Experiencing changes in sleep patterns for some time, such as when caring for a child or family member or experiencing stress insomnia, is a natural thing and is a sleep pattern disorder that can be easily overcome. But chronic sleep pattern disorders such as those that last for a long time in a row can have a serious impact on heart health.
Risk factors for heart disease that occur due to lack of sleep
Some of the causes of heart disease can occur when a person has a sleep disorder, including:
1. Obesity
Obesity is known as a trigger for damage to the heart and blood vessels because it can significantly increase blood pressure and cholesterol. Weight gain due to lack of sleep is a form of impaired metabolic function.
In this case, obesity can be triggered by two things, namely the process of burning fat and hormones that affect appetite. When lack of sleep, the body does not produce energy from food or fat deposits optimally. In addition, lack of sleep also causes us to have less physical activity and use energy from food stores.
Sleep deprivation also tends to make us even more hungry because the process of satiety hormone secretion which acts to restrain hunger is that leptin tends to be less when it is lacking in sleep.
2. Hyperglycemia and risk of diabetes
As a metabolic syndrome, diabetes has a disease feature that can damage blood vessel function, which is increased blood sugar levels or hyperglycemia. This can occur because lack of time affects the body's function in carrying out glucose metabolism and increasing blood sugar levels. As a result, hyperglycemia can accelerate the accumulation of fat in blood vessels which results in the onset of atherosclerosis, which is an early sign of coronary heart disease.
3. Increased cholesterol
Cholesterol is an important nutrient obtained from food, but requires an optimal metabolic process, so there is no buildup in the bloodstream. When a person lacks sleep, their body has difficulty metabolizing the type of bad cholesterol or low-density lipoprotein (LDL). As a result if it occurs for a long time, cholesterol levels in the blood will increase and can trigger damage in the blood vessels and heart.
4. High blood pressure
Increased blood pressure and heart rate are the effects of the shortest sleep deprivation. Some studies have shown that lack of nighttime sleep will increase blood pressure the next day. If it occurs continuously, then an increase in blood pressure can become primary hypertension which is a risk factor for various cardiovascular diseases.
The impact of sleeping too long on heart health
The average adequacy of quality sleep generally only requires 7 to 9 hours per day. Excessive sleep that occurs continuously can have an impact on the overall health of the body and the effects caused are not much different from lack of sleep.
The simplest impact of lack of sleep is a reduction in the portion of time for physical activity, making it easier to experience obesity. Being overweight and lacking in sleep can also trigger chronic inflammation in blood vessels due to abnormal cytokine protein expression when a person sleeps too long. Inflammation of blood vessels is a risk factor for stroke heart disease.
Excess sleep also triggers metabolic problems such as glucose intolerance, because the body does not respond to glucose normally to be absorbed and used as an energy ingredient. This will risk triggering hyperglycemia which can cause diabetes and heart disease.