Contents:
- Medical Video: Why sitting is bad for you - Murat Dalkilinç
- The danger of sitting too long on brain health
- Indeed, what does it have to do with the health of the human brain?
- How to reduce the risk of danger if you really have to sit long?
- Apply upright sitting position
- Set time to rest
- Use a standing work desk
Medical Video: Why sitting is bad for you - Murat Dalkilinç
Do daily activities require you to always sit for a long time? Or the hobby of playing computer or watching television makes it difficult for you to move from your favorite chair? If so, from now on you should be careful because there is a danger of sitting too long which can lurk your health.
The danger of sitting too long on brain health
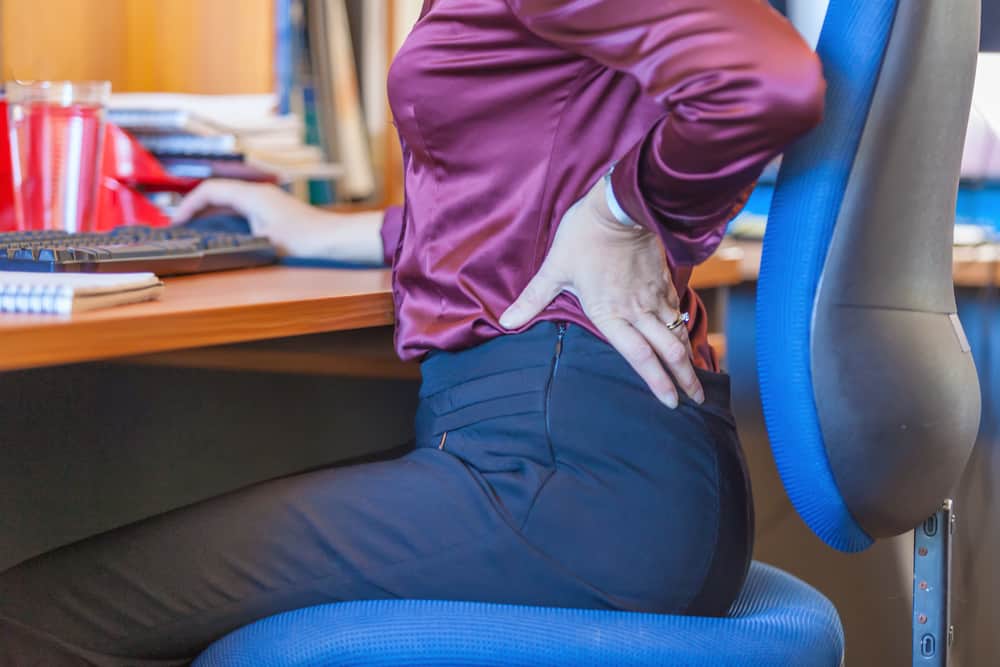
Having lots of activities does feel tiring, to overcome them you might occasionally look for a chair to sit and take a break. But it is different with office workers or those who spend their days sitting for hours. Even though it looks comfortable, in fact there is a danger of sitting too long which targets your body's health.
How can? Yes, this has been proven in research from the University of California (UCLA) and the University of Adelaide which conducted a study of 35 people aged 45 to 75 years. All participants were recorded and asked about daily physical activity, including the time spent sitting, walking, and doing moderate to strong physical activities every day.
Furthermore, each participant also underwent an MRI examination test (magnetic resonance imaging) to determine the health of their brain. The study focused on the relationship between sitting, level of activity, and thickness of brain composition.
The results found that the longer the time spent by someone to sit every day, the area that plays a role in forming a new memory (medial temporal lobe), also tends to thin out. Sadly, every hour you sit, this area will be depleted by as much as two percent, and so on.
In other words, someone who sits for 10 hours per day, tends to have a medial temperal lobe six percent thinner than someone who only sits about seven hours a day.
The medial temporal lobe is the part of the brain responsible for shaping long-term memory. Normally, it only starts to thin out when someone reaches old age. If this condition occurs at a young age or before old age, it will reduce your ability to remember something - usually it will lead to dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
Indeed, what does it have to do with the health of the human brain?
The brain is an important organ that is the center of command and the nervous system of humans. That is why, if something happens that affects the organs of the body such as disruption of the body's metabolism and blood circulation, it can have a negative impact on your brain. Likewise, vice versa, if there are problems in the brain, of course, it will inhibit the work of other organs.
Even so, further research is needed to find out more about how the danger of sitting too long has a long-term impact on the brain's work. It is important to remember, a person who experiences thinning of the medial temporal lobe of the brain is not always caused by too long sitting habits.
But it could be because the person is less active both physically and socially, has limited space, does routine work that does not stimulate body movements, or because of other conditions that can affect brain health.
How to reduce the risk of danger if you really have to sit long?
Basically, the body is not designed to continue to sit for a long time. Still there must be physical movement to support the work of bones, muscles, and body organs.
Therefore, if your daily activities require you to sit for a short time, you can do the following trick to reduce the risk of danger of sitting too long:
Apply upright sitting position
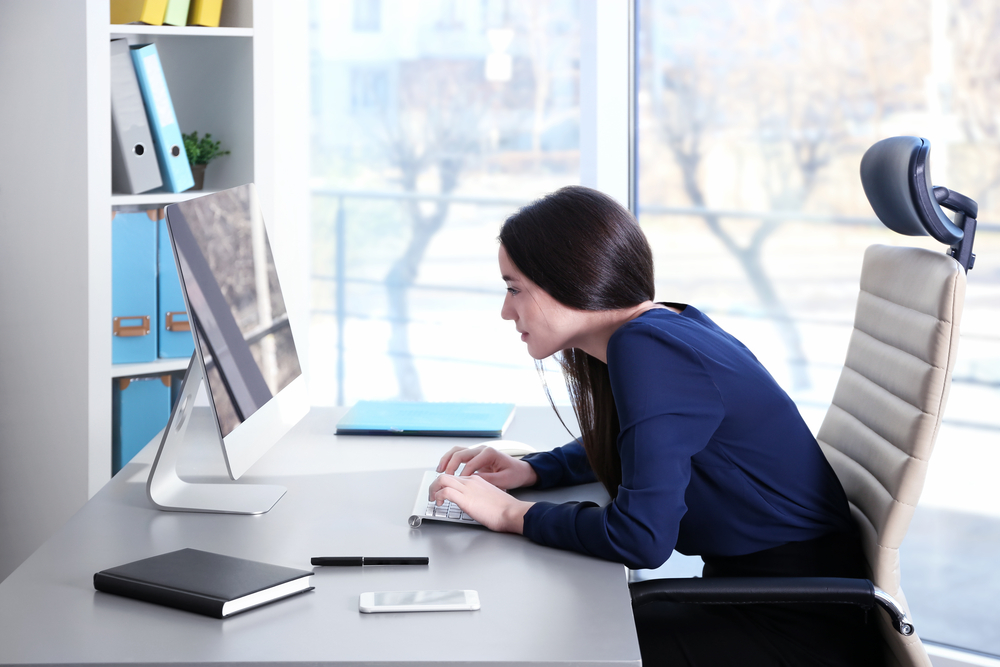
If you really have to sit for a long time - whether because of work or other things. It is best to avoid leaning and bending forward toward the table, if you are sitting at a table. Instead, sit with your body upright.
Set time to rest
According to a study published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, it is suggested that people spend a lot of time sitting every day, to spend time standing then walking and doing light stretches at least every two hours.
Use a standing work desk
If every day you always use a work desk equipped with a sitting chair, try occasionally to work on a standing work desk that will require you to do work in an upright state.
Alternatively, you can replace your favorite seat with exercise ball or gym ball. This way, you can sit upright and be accompanied by a body that keeps on moving.