Contents:
- Medical Video: Average Blood Glucose Levels
- What is blood sugar?
- Blood glucose is the body's main energy source
- How good are blood sugar levels?
- Common abnormalities in blood sugar levels
- High blood sugar levels
- Low blood sugar levels
Medical Video: Average Blood Glucose Levels
Maybe most of you often hear that diabetes occurs due to high blood sugar levels. Yes, blood sugar or what is often called blood glucose you should control and pay attention to the levels every day. Because the blood glucose level is one of the determinants of health. Actually, what is sugar or blood glucose?
What is blood sugar?
Blood sugar is a sugar found in your blood that usually comes from the food you consume. Blood glucose is a fuel source for all body cells so they can function properly.
Actually, all the foods you eat, whether carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, can be processed into blood glucose. However, the main source of blood glucose is foods that contain carbohydrates.
If you eat carbohydrates, then the food will be easily processed by the body into blood glucose. Meanwhile, the content of other nutrients such as fat and protein requires a longer time to be converted into blood sugar.
Blood glucose is the body's main energy source
After the body manages to process food into blood sugar, this substance will be directly distributed to all parts of the body's cells through blood vessels. From brain cells, to the cells in your feet you will get blood glucose.
Therefore, blood sugar is a very important thing and must be kept normal. If blood glucose is too little, the cells will not get food and cannot function.
While if too much, there will be many symptoms and disorders that arise due to this condition.
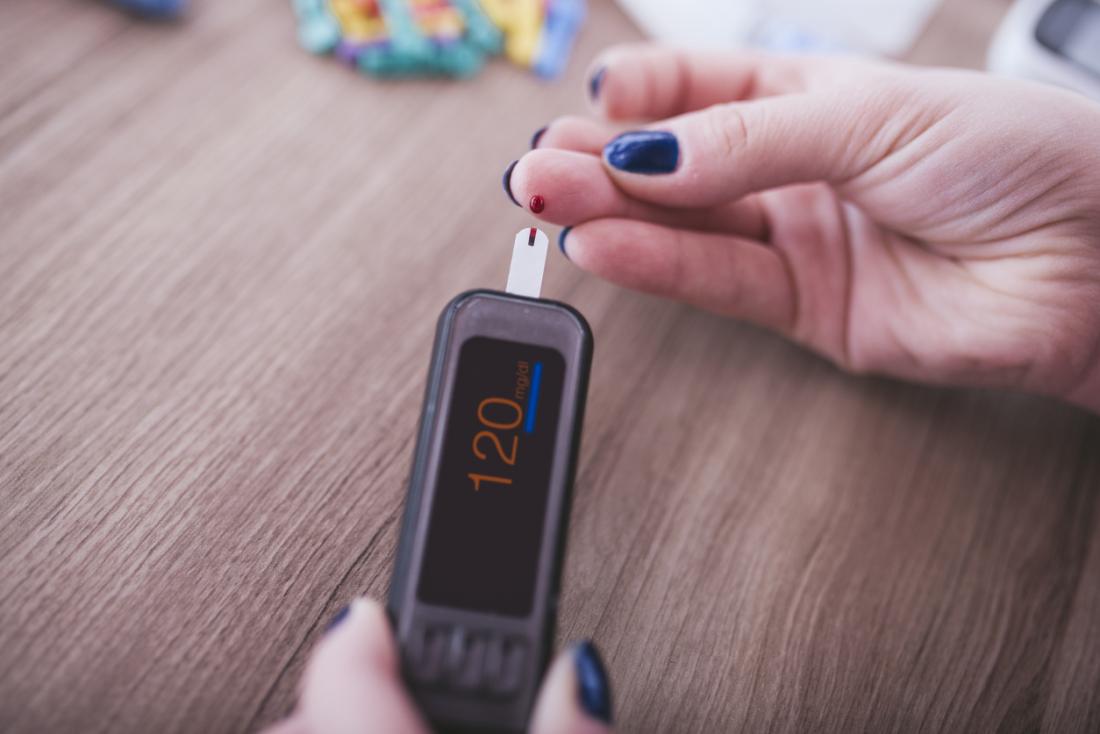
How good are blood sugar levels?
Normal blood sugar number:
- Fasting (for at least 8 hours): less than 100 mg / dL
- Before eating (lowest level in a day): around 70 to 80 mg / dL. Numbers can also vary between 60 and 90.
- After eating (2 hours after): less than 140 mg / dL.
Sugar levels that are higher or lower than normal numbers are classified as unhealthy, and indicate problems that arise in your body.
Common abnormalities in blood sugar levels
High blood sugar levels
High blood sugar is also known as hyperglycemia and has two main types:
- Fasting hyperglycemia. With this condition, the patient's blood sugar is higher than 130 mg / dL after fasting (not eating and drinking) for at least 8 hours.
- Postprandial hyperglycemia after meals. With this condition, the patient's blood sugar is higher than 180 mg / dL 2 hours after they eat. Normally, if a person does not have diabetes, blood sugar rarely reaches 140 mg / dL after eating, even when eating heavily.
The most common cause of hyperglycemia is diabetes. While symptoms of hyperglycemia include:
- Often feel thirsty
- Headache
- Reduced concentration
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- High blood sugar levels: more than 180 mg / dL
It is important to deal with symptoms of high blood sugar before the condition develops into other complications.
Frequent or long-term hyperglycemia can cause:
- Vaginal and skin infections
- Long healed wounds
- Reduced vision
- Nerve damage, accompanied by cold and sore or insensitive feet, hair loss in the hands and feet, or erectile dysfunction
- Disorders of the stomach or intestine (such as chronic constipation or diarrhea)
- Damage to the eyes, blood vessels or kidneys
Hyperglycemia can also cause other serious conditions. Patients with type 1 diabetes are more likely to experience ketoacidosis (a condition where acid builds up in the blood). Meanwhile, patients with type 2 diabetes are at risk of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS). This condition is potentially deadly, characterized by the inability of the body to process sugar.
Low blood sugar levels
Other conditions that can be caused by abnormal blood sugar levels are hypoglycemia or low blood sugar This condition occurs when the body does not get enough sugar for energy needs. People with diabetes usually have hypoglycemia.
Causes of hypoglycemia include diet, medication or certain medical conditions, and exercise.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia include:
- Daze
- Dizzy
- Feeling shaky
- Starving
- Headache
- Easily offended
- Irregular heartbeat (heart beat fast)
- Pale skin
- Sweating
- Trembling
- Fatigue
- Worry
Frequent or ongoing hypoglycemia can cause:
- Reduced coordination
- Reduced concentration
- Numbness in the mouth and tongue
- Fainted
- Nightmare
- Coma
Hello Health Group does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.