Contents:
- Medical Video: 8 Serious Diseases Signaled by Our Skin
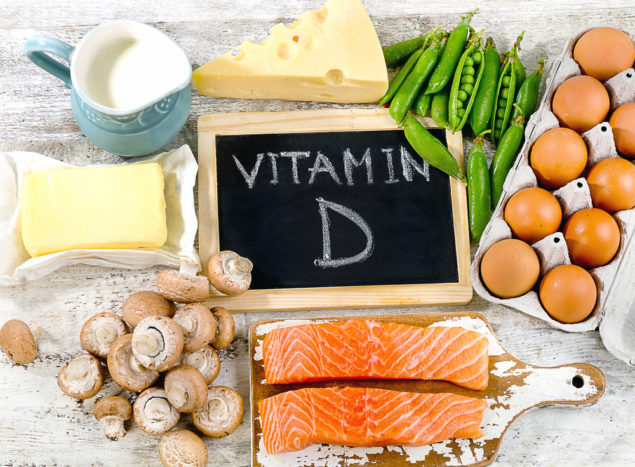
- What is the relationship between vitamin D and thyroid disease?
- Why don't the body get vitamin D deficiency?
- What causes a person to lack vitamin D?
Medical Video: 8 Serious Diseases Signaled by Our Skin
Thyroid disease occurs when hormone levels in your body are not balanced; can be excessive and can also lack production. A study published in the journal Cellular and Molecular Immunology says that there is a connection between vitamin D deficiency and thyroid disease. Is it true that thyroid disease is caused by lack of vitamin D in the body? Read on the reviews here.
What is the relationship between vitamin D and thyroid disease?
Studies have found a link between vitamin D deficiency and autoimmune thyroid disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and Graves' disease.
Vitamin D deficiency is also more common in patients with thyroid disease compared to people who are healthy and do not suffer from autoimmune diseases.
This is also supported by research from Turkey which states that vitamin D deficiency can trigger the development of autoimmune thyroid disease. The study showed that the antibodies of people with autoimmune thyroid disease could decline quite dramatically after taking a dose of 1,000 IU (25 mcg) per day in a month.
The decrease in special antibodies marking thyroid disease means the condition of the patient's thyroid and body has improved. Experts also believe this progress is one of them due to the administration of 1,000 D IU of vitamin D per day.
In essence, vitamin D is thought to have a role in maintaining thyroid health, but there is a direct relationship between lack of vitamin D in the body and the development or development of thyroid disease is still uncertain.
Why don't the body get vitamin D deficiency?
The main role of vitamin D is to regulate bone growth, calcium levels, and phosphorus in the body. So it's not surprising that a lot of research and advice links vitamin D to keeping your bones strong and healthy.
Vitamin D is also very necessary for mothers who are pregnant. Why? If pregnant women lack vitamin D, this will have an impact on the health of the fetal bone in the womb. Pregnant women must have enough vitamin D at the time of delivery to ensure their babies have adequate levels of vitamin D for the first 4-6 months of life. Because the vitamin D status in infants is completely dependent on mothers as a source of vitamin D.
What causes a person to lack vitamin D?
There are several things that can cause the body to lack vitamin D. The first cause is because the body is less exposed to sunlight. Then, use sunblock or a veil with SPF that is too large can also cause the skin to absorb sunlight less as a source of vitamin D in the body.
Lack of eating foods that contain vitamin D can also make the body deficient in vitamin D. In addition, there are some things that make vitamin D in your body less:
- Celiac disease or Crohn's disease can cause impaired absorption of vitamin D
- If you have a disease with symptoms of seizures, the anticonvulsant drugs you take can reduce vitamin D in the body
- Liver or kidney disease can cause a disruption in the production of the active form of vitamin D
- People with dark skin absorb less vitamin D
- Obesity can make vitamin D in the body less absorbed optimally
Since there are not many foods that contain vitamin D, most people take vitamin D supplements. However, most multivitamins do not contain enough vitamin D, because generally one capsule contains only about 400 IU of vitamin D. While the recommended daily intake of vitamin D is around 600 IU adults and 800 IU for elderly people (over 70 years).
Important to note, too much vitamin D content in the body is also not necessarily good. Excess vitamin D can make someone experience symptoms of high calcium levels or called hypercalcemia. Hypercalcemia shows symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, constipation, nausea and vomiting, and becomes dazed. Cardiac arrhythmias and kidney problems can also be caused by vitamin D poisoning.