Contents:
- Medical Video: What's the difference between a heart attack and a cardiac arrest?
- Difference between cardiac arrest and heart attack
- What is cardiac arrest?
- What is a heart attack?
- What is the difference between cardiac arrest and heart attack?
- How can cardiac arrest and heart attack occur?
- Heart attacks can cause cardiac arrest
- What can be done?
Medical Video: What's the difference between a heart attack and a cardiac arrest?
Every symptom of a heart disorder that causes the heart to not work normally is a serious condition because it can lead to death. There are two types of fatal heart problems, namely cardiac arrest and heart attack.
Although often considered the same, both are not synonyms. Cardiac arrest and heart attack have different symptoms and causes.
Difference between cardiac arrest and heart attack
What is cardiac arrest?
Cardiac arrest (cardiac arrest) is a fatal condition in which the heart stops beating suddenly due to an electrical force disorder in the heart muscle, so that the heart cannot beat normally and trigger arrhythmia. This has an impact on the disruption of blood distribution throughout the body and death can occur within minutes because vital organs, especially the brain, do not receive enough blood.
What is a heart attack?
Meanwhile, a heart attack (heart attack) is a fatal condition that occurs when the heart does not receive enough oxygen from the bloodstream to the heart. This is due to atherosclerosis or blockage of arteries, so that the heart experiences a lack of intake of oxygen-containing blood.
The condition of a heart attack can occur in a duration of up to hours. During this time duration, the part of the heart that does not receive oxygen continues to suffer damage in the form of death of the heart muscle, if left untreated it can cause death. In contrast to cardiac arrest, the heart does not stop beating during an attack.
What is the difference between cardiac arrest and heart attack?
In terms of the process of occurrence, cardiac arrest occurs very quickly and is characterized by the following signs:
- Breath breaks or doesn't breathe at all
- Pupils enter the skull
- Squeeze suddenly
- Unconscious
- The skin color becomes pale bluish
- Pulse or heart rate cannot be found
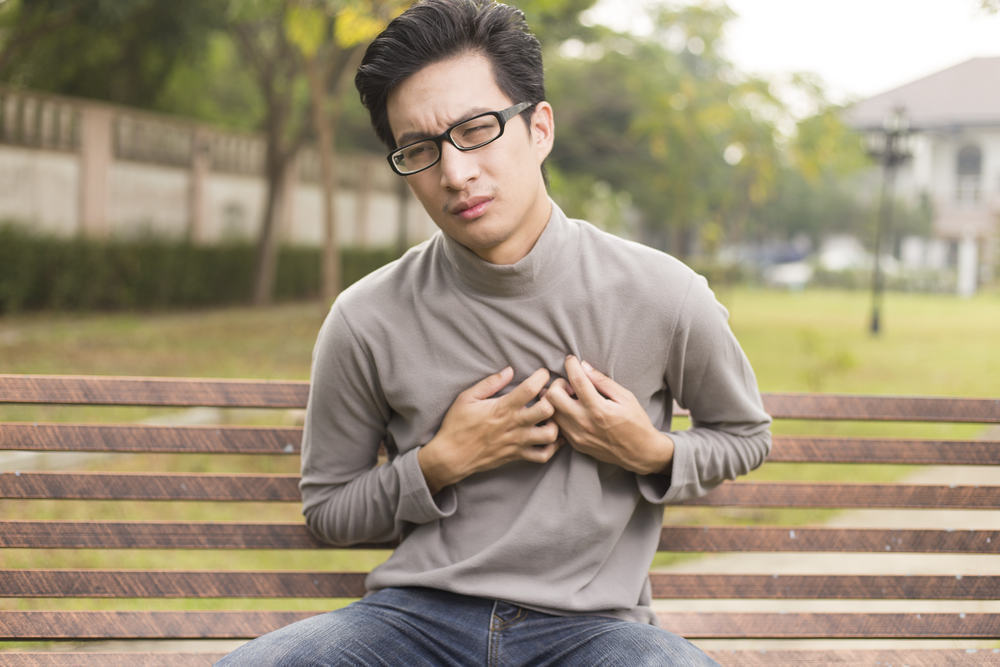
Whereas a heart attack occurs with a longer and slower duration, and can be accompanied by less specific symptoms, such as:
- Hard to breathe
- Abdominal pain that can be accompanied by nausea and vomiting
- Feel very weak
- A cold sweat
- Irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness or light head
- Contraction of muscles around the chest, neck and arms
- Pain in the upper abdomen (diaphragm), chest, hands, jaw or around the shoulder blades in the upper back.
How can cardiac arrest and heart attack occur?
Most cases of cardiac arrest are caused by arrhythmias originating from the chambers of the heart (ventricular fibrillation) due to disruption of the heart muscle electricity so that blood flow throughout the body and heart can stop. However arrhythmia disorders can also originate from the right heart of the heart (atrial fibrillation) which causes a disruption of the signal to pump blood to the heart chamber muscles and result in cardiac arrest.
Cardiac arrest is more likely to be experienced by someone who has an imperfect heart due to congenital abnormalities or who have suffered serious damage, such as those with coronary heart disease. Some incidents of trauma can also cause sudden cardiac arrest such as when electrocuted, drug overdose, excessive physical activity, loss of blood, blockages in the airways, accidents, drowning, and hypothermia.
While the occurrence of a heart attack is caused by a progressive blockage of the heart arteries due to cardiovascular disease. Blockages can come from blood fat or cholesterol blockage conditions can also increase blood pressure which erodes the walls of the vessels so that there is injury and buildup of frozen blood from inflammation. The risk of a heart attack is more likely due to an unhealthy lifestyle, a history of cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome in old age.
Heart attacks can cause cardiac arrest
Although different they are interrelated. Many cases of cardiac arrest in adults occur in someone with a history of heart disease. Cardiac arrest can occur after a person has a heart attack or even after the symptoms of a heart attack disappear. Most heart attacks do not have such an effect, this happens when a heart attack has caused serious damage and causes the heart to not beat normally due to heart muscle swelling or cardiomyopathy.
What can be done?
Cardiac arrest and heart attack is one of the main causes of death, but sufferers can be saved if they get the right help by professional staff since the first appearance of symptoms.
Heart attacks often appear with nonspecific signs but immediately contact a health worker if you suspect the patient has symptoms of a heart attack especially if he has a history of heart disease. The first treatment that can be done is to stop the patient from doing activities and rest in a sitting position to make it easier to breathe and immediately consume the medication that has been given by the doctor if available.
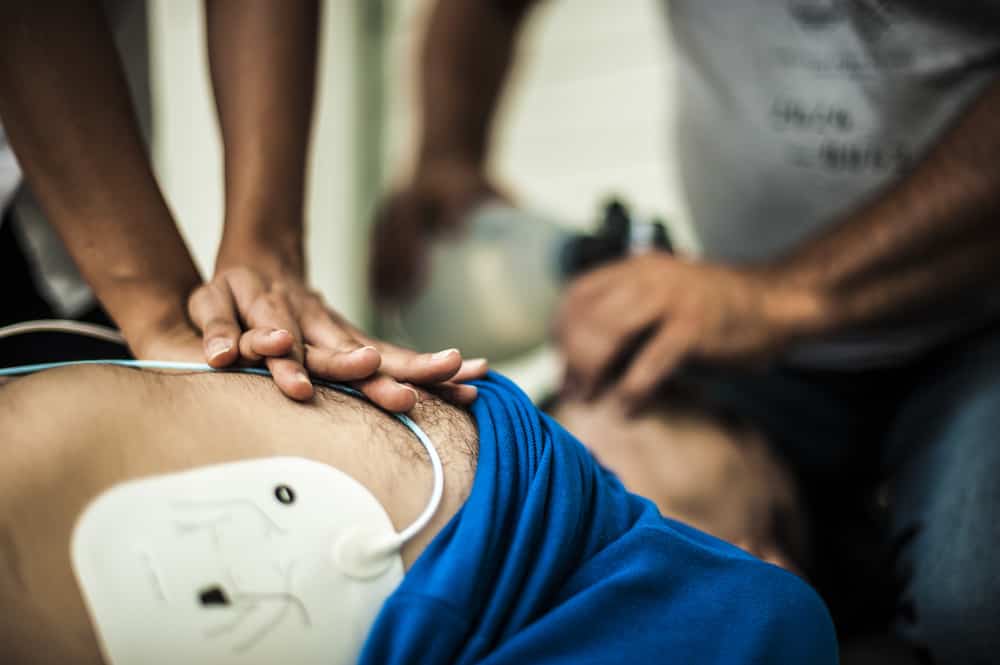
Whereas if there is a symptom of cardiac arrest, emergency treatment is needed and the handling of an external defibrillator or lung cardiac resuscitation in patients.