Contents:
- Medical Video: How Carbs Turn to Fat: Weight Loss Secret- Thomas DeLauer
- Carbohydrates are the main source of energy in the body
- How long does it take for carbohydrates to become energy in the body?
- How then can energy be in the body?
- In the muscle, glucose will be used to carry out activities
- Excess carbohydrates will actually become fat reserves
Medical Video: How Carbs Turn to Fat: Weight Loss Secret- Thomas DeLauer
Energy in the body is indeed produced from the food you eat. But can all foods be energy in the body? Yes, the energy you get to do physical activity every day is obtained from the food you eat, whether it's a source of carbohydrates, protein, and fat.
Even so, protein and fat will not be directly processed by the body into energy. It is different from carbohydrates which when it enters the body will be directly used as an energy source. Then how can carbohydrate food sources be the main energy source? How fast is carbohydrate converted into energy?
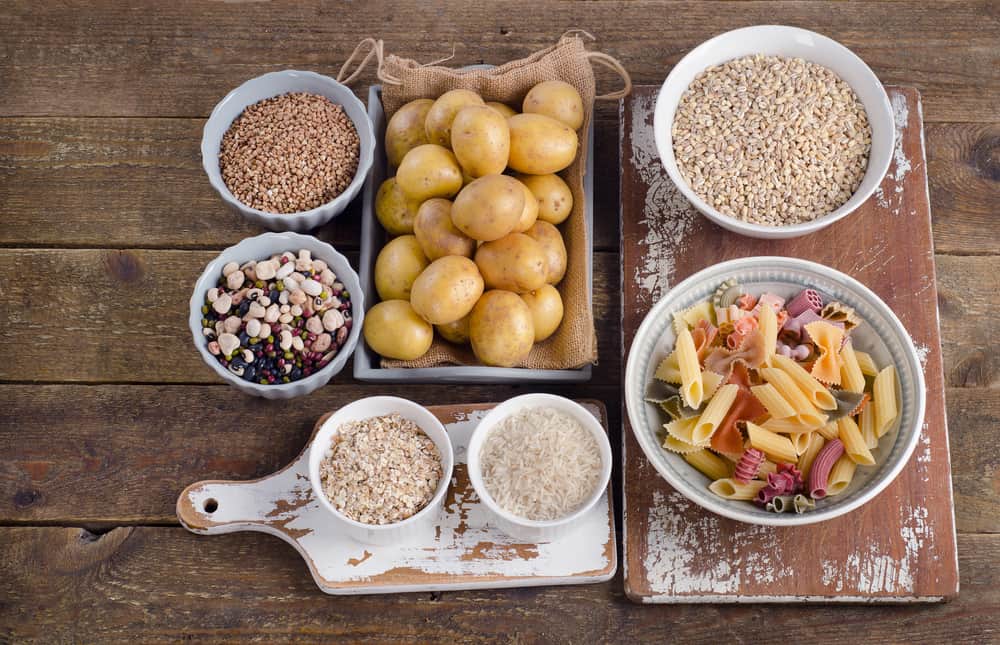
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy in the body
You can find carbohydrates in various types of food, such as vegetables, fruits, meat, tofu, and of course rice. However, the main source of carbohydrates is staple food, because it contains a considerable amount of carbohydrates when compared with other types of food. Foods that contain carbohydrates will be broken down into simpler forms in the mouth, stomach, and intestines. So that when it reaches the small intestine, the shape is very simple and is called monosaccharide.
This monosaccharide is then absorbed by the body into the bloodstream. When monosaccharides are in blood vessels, they are called blood sugar or glucose. The more food sources that contain carbohydrates you eat, the more glucose or blood sugar will be formed.
How long does it take for carbohydrates to become energy in the body?
Simple sources of carbohydrates such as sugar and sweet foods, will be very quickly broken down by the body because of its easy to digest form. This makes sugar the fastest to make glucose or blood sugar, which is less than 15 minutes.
Complex carbohydrates such as rice, corn, vermicelli, noodles, and others take longer to become glucose. Types of complex carbohydrate foods with a high glycemic index will take about 15 minutes to change the shape of blood glucose.
In contrast to the types of foods that contain a low glycemic index, the food process to be made into glucose takes as much as 15-30 minutes.
How then can energy be in the body?
Usually blood glucose levels will be high shortly after eating. At that time, the body will automatically send a signal to the pancreas gland - one of the digestive organs - to produce the hormone insulin.
The insulin hormone will enter the blood vessels and then tell the body cells that the main energy source (glucose) is available. Furthermore, the hormone insulin will open the door so that glucose from the blood can enter the cell. Glucose that enters the body's cells, will be converted into energy.
But not all body cells will use glucose as energy, the cells in the muscle and liver will store glucose as an energy reserve. The stored glucose will be used when there is no food that enters the body and the body experiences a lack of energy.
In the muscle, glucose will be used to carry out activities
Each cell will use the energy produced to carry out their respective functions. For example, cells in the digestive system will use the energy produced to digest and metabolize. It's different from heart cells, which use energy from glucose to pump blood. While for glucose that enters muscle cells, it will be used as an energy source for daily activities.
All of your body movements are from glucose which is processed into energy by muscle cells. In a state of rest, excessive glucose will be stored in muscle cells - called glycogen - to be used when there is no food intake.
Excess carbohydrates will actually become fat reserves
Just like muscle cells, cells in the liver also store glucose if there are too many. But this excessive amount of glucose will be stored in different forms. Liver organ converts too much glucose into triglycerides or commonly known as body fat reserves. Too much body fat or triglyceride reserves can cause a person to experience various degenerative diseases, such as heart disease and diabetes mellitus.