Contents:
- Medical Video: How to Read a Nutrition Label
- 1. Amount of dish per package
- 2. Total calories per serving
- 3. Figures for nutritional adequacy (AKG)
- 4. Nutritional content that must be limited
- 5. The nutritional content that must be fulfilled
- 6. Additional nutritional content
- 7. Note also the list of food compositions
- 8. Compare the nutritional value information label between two food products
Medical Video: How to Read a Nutrition Label
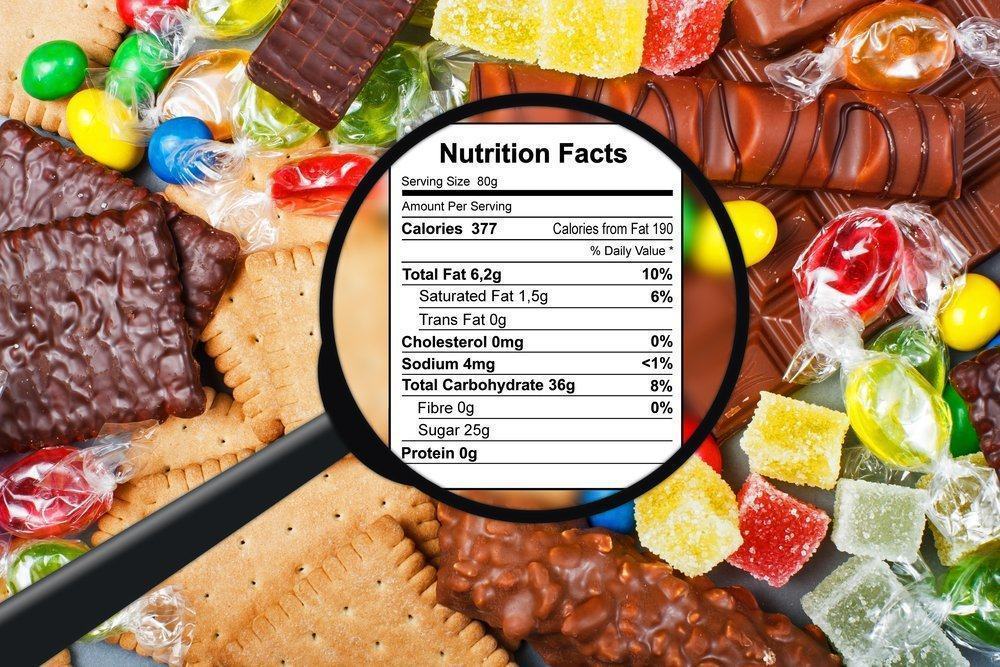
Information on alias nutritional value nutrition facts is a label that is usually on food packaging, containing information on the nutritional content of these foods. The nutritional value information label is useful as a consideration for you as a consumer to buy an item. The information included is very useful for someone with a certain medical condition or someone who is limiting the amount of calorie intake. This information is very necessary to find out the nutrition of the product you are going to buy and consume.
But if you are confused with all the information listed on the label, what are the most important things to consider in reading the nutrition label?
1. Amount of dish per package
One food package (one pack or one box) usually has more than one serving. The number of servings per package shows the number of serving items contained in one food package. For example, a pack of food has a statement of "8 servings per package", which means that every single package can be divided into 8 servings or can be consumed 8 times with each frequency consuming one serving.
Now, what you need to know is, every nutritional value information label represents the nutritional content for one dish, not one package. If you eat two packs of food that have a dose of one serving per packet, you will get twice the amount of nutrients from what is listed on the nutritional value information label. Therefore, you need to pay attention to how much nutrient content the packaged food is, and compare it to the amount you eat.
2. Total calories per serving
The total calories show how much energy you will get from each meal. The more servings you eat, the greater the number of calories you get. Writing calories is usually accompanied by calories from fat that is calculated separately, because it does not include total calories. For example, one pack of macaroni and cheese has a total calorie information of 250 servings per glass, and 110 calories from fat. So, if you eat two glasses, you will get 500 calories, plus 220 calories from fat.
Daily calories usually refer to the number of calories needed per day or as much as 2000 calories. The FDA classifies the calorie content in the packaging as follows:
- Low, if the calorie level is close to or around 40
- Medium, if the calorie level is close to or around 100
- High, if the calorie level is close to or around 400
3. Figures for nutritional adequacy (AKG)
AKG, or sometimes written Daily Values (DV), refers to the average daily energy requirement of 2000 calories. AKG shows the amount of nutrient levels both in heavy units such as milligram (mg) or gram (gr), as well as presentation in percentage form (%) AKG. Each nutrient has a recommendation for the amount of each daily consumption, while the percentage of RDA is obtained based on the proportion of nutrient content in the dish, compared to the recommended amount of daily consumption. Daily nutritional requirements are said to be fulfilled if% of the RDA from these nutrients reaches 100%.
4. Nutritional content that must be limited
Some of the ingredients that must be limited from consumption of packaged foods are saturated fat and trans fat, added sugar, and salt (sodium / sodium). This nutrient content is usually easily fulfilled from various types of food. If excessive, it will increase the risk of various chronic diseases such as heart disease, hypertension, and cancer. Therefore, look for packaged foods with less than 5% AKG. Keep in mind, some nutrients such as saturated fat or trans fat do not have% AKG, so limit intake to less than 20 grams per day.
5. The nutritional content that must be fulfilled
Some nutrients such as vitamins, proteins, minerals, and fiber are needed to maintain nutrient balance every day, prevent various diseases and health problems. For example, fulfilling the adequacy of RDA from calcium can prevent bone loss, iron can prevent anemia, and vitamin C is needed to strengthen the body's immunity. Therefore, to meet these nutritional needs, choose packaged foods / drinks labeled with adequate nutrition of around 20% or more.
6. Additional nutritional content
Carbohydrates and sugar fructose and sucrose are additional nutrients and are not needed in too much because the body can easily meet the daily needs of these nutrients. For example, carbohydrates can be met from sugar, fibrous vegetables, whole grains, and rice, while fructose and sucrose can be obtained from the consumption of fruits.
7. Note also the list of food compositions
Foods made from more than one food usually have a list of compositions, and in general the list of compositions is sorted from the highest number to the least. Content levels also usually include food ingredients that have their own nutritional content. For example, if you want to reduce sugar consumption, avoid foods that use artificial sweeteners or added sugars such as aspartame and corn syrup.
8. Compare the nutritional value information label between two food products
If you are confused about choosing between two packaged foods, both the type and the brand, you can compare the nutritional content of the food label. This aims to identify differences in the level of nutrient intake for a product, which is higher or lower. For example, a food may have the same levels and% of RDA of minerals, but has different fat and calorie content. By comparing it, you can find out the number of calories that are more suitable for you.
READ ALSO:
- Pros of Cons MSG: Is It Really Bad for Health?
- 5 Steps Reduce Eating Sugar
- 7 Unexpected Foods Can Contain Chemicals and Dyes