Contents:
- Medical Video: Do NOT crown your teeth! - Must watch before dental work!
- Unplug milk teeth, when to do it?
- 1. Jaw capacity is inadequate for new teeth growth
- 2. Milk teeth do not date
- 3. Infection
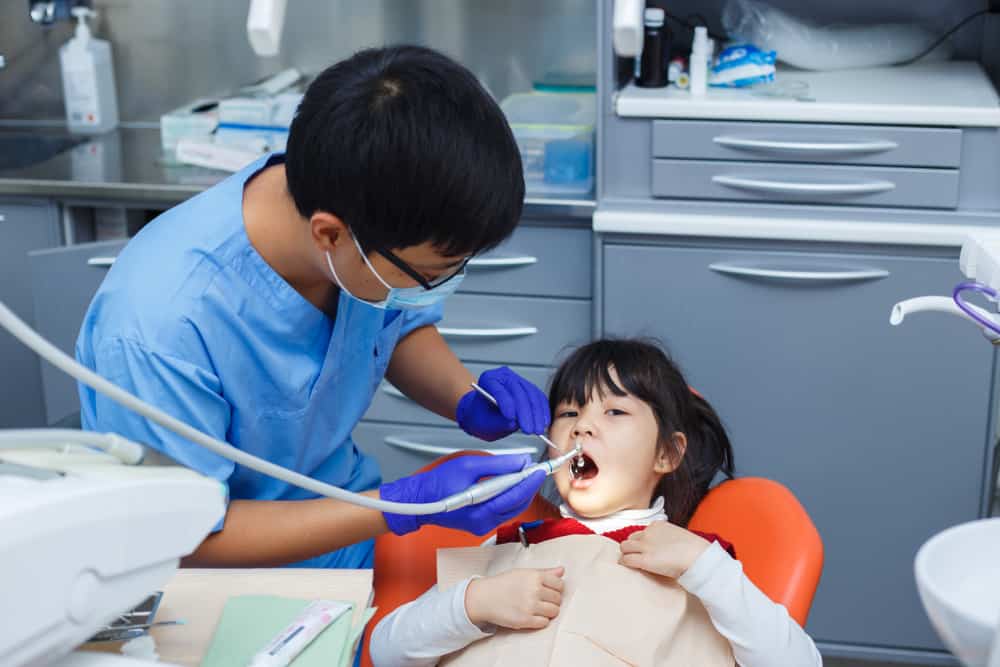
Medical Video: Do NOT crown your teeth! - Must watch before dental work!
Ideally, milk teeth will start one by one starting around the age of six to seven years. Entering the age of 15-17 years, usually all milk teeth have been replaced with adult teeth. However, sometimes the doctor will advise you to pull out the milk teeth as the best way to go when you feel something is wrong in changing the baby's teeth to permanent teeth. I wonder why? Check out the explanation below!
Unplug milk teeth, when to do it?
The process of removing the milk teeth inevitably must be done when there is a problem or problem in the oral cavity. Among them are:
1. Jaw capacity is inadequate for new teeth growth
The small size of the jaw is generally accompanied by the size of small milk teeth as well. In fact, the size of adult teeth that grow later can be much larger than the previous milk teeth. This inadequate supply of space will make the newly outgrown adult teeth pile up and seem uncluttered.
In fact, it is not uncommon for adult teeth to get out because they do not have enough space or are blocked by other teeth. The only option to improve this dental structure is by braces or commonly called stirrups.
Besides functioning to flatten the teeth that are not neat, the use of stirrups will also help increase the size of the jaw that is minimal.
2. Milk teeth do not date
Before the age of 17, all milk teeth should be dislodged and replaced with permanent teeth. Unfortunately, not all children get the date tooth phase according to the time. Indeed, in some cases sometimes the milk teeth appear so strong that they do not show any signs of dislodging at all.
That is why, pulling out milk teeth is usually the choice to replace it with adult teeth which is time to come out. Because if it is not removed, chances are that the milk teeth will still remain in the mouth without knowing when they will be dislodged and replaced by permanent teeth.
3. Infection
When the milk teeth are severely damaged by infection, they will usually extend to the pulp. In dental anatomy, the pulp is the innermost layer after enamel and dentine. Pulp can also be called the center or core of a tooth composed of blood vessels, nerves, and other soft tissues.
Infection that has reached the pulp cannot be underestimated because it means that the bacteria will be easier to enter and stay in the pulp. If the administration of antibiotics is not able to cure the tooth infection, then extracting milk teeth can be the best choice.