Contents:
- Medical Video: Checking Your Blood Glucose | Diabetes Discharge | Nucleus Health
- What is a blood sugar test?
- Know the connection between diabetes and blood sugar tests
- What is the preparation and how to do a blood sugar test?
- How do you do a blood sugar test in a clinic or hospital?
- How do you read the glucose test results?
Medical Video: Checking Your Blood Glucose | Diabetes Discharge | Nucleus Health
People with diabetes generally require a routine blood sugar test. This blood sugar test can be done at home to keep her blood sugar levels stable while controlling her diabetes. What should be known about blood sugar testing?
What is a blood sugar test?
A blood sugar test or blood glucose test is a test done to measure the amount of sugar in your blood. Blood sugar or glucose is the body's main energy source. Your body converts the carbohydrates you eat into glucose.
Glucose or blood sugar testing is done primarily to check the condition of type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Diabetes is a condition that causes blood sugar to increase.
In healthy people, glucose is processed in the body by a hormone called insulin. But if you have diabetes, your body doesn't produce enough insulin or insulin doesn't work well. This causes blood glucose to accumulate or increase.
If left untreated, high blood sugar can cause organ damage. Blood sugar tests can also be used (although it is rarely done) to test for hypoglycemia, which occurs when blood glucose levels are too low.
Know the connection between diabetes and blood sugar tests
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and adolescents whose bodies are unable to produce enough insulin. This is a chronic condition and requires lifelong care. Type 1 diabetes has also been recorded in some people aged 30-40 years.
Meanwhile, type 2 diabetes (diabetes or diabetes) is usually diagnosed in adults who are overweight and obesity. This condition occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin, or when the insulin produced does not work properly. The danger of type 2 diabetes can be reduced by losing weight.
Gestational diabetes occurs when a pregnant woman has diabetes. This type of diabetes usually disappears after a woman gives birth.
After getting a diagnosis of diabetes, people with diabetes may have to undergo a blood sugar test to determine if their condition is well controlled. High glucose levels in diabetics may indicate that diabetes is not treated properly.
However, there are other causes that can increase your blood sugar or glucose, which are:
- prediabetes (people are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes)
- hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
- kidney problems
- pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- pancreatic cancer
In rare cases, high blood sugar levels can be a sign acromegaly, symptoms of Cushing's syndrome, kidney failure, or adrenal tumor.
Low blood sugar levels or commonly referred to as hypoglycemia can also occur. This possibility is caused by the following:
- excessive body insulin
- starving
- hypopituitarism
- hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid)
- Addison's disease, alcohol abuse, liver disease, or insulinoma (in rare cases)
What is the preparation and how to do a blood sugar test?
There are three different types of blood sugar tests, namely tests for fasting blood sugar, a 2-hour blood sugar test and a blood sugar test when.
1. Fasting blood sugar test
If you undergo a fasting glucose test, you may not eat or drink for 8 hours before the test. You are only allowed to drink water. You can schedule a fasting glucose test in the morning, so you don't need to fast during the day.
2. 2 hour blood sugar test
While the 2-hour blood sugar test is a postpandrial (PP) blood sugar test. This is a continuation of the fasting blood sugar test. So, if you have taken a blood sample after a full 8 hour fast, you will be asked to eat as usual. Then 2 hours after eating, your blood sugar level will be checked again.
It's actually natural blood sugar levels jump after eating. This happens both in healthy people and diabetics. HoweverIn healthy people, blood sugar levels will return to normal after 2 hours of eating.
3. When or random blood sugar tests
You are allowed to eat and drink before this test. Severe stress can cause blood glucose to increase temporarily. This stress is usually due to surgery, trauma, stroke, or heart attack. Certain drugs can also affect blood glucose levels.
Always tell your doctor about the medications you are taking - including prescription drugs, over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Your doctor may ask you to stop taking several medications or decide to change the dose before you undergo a test or examination.
Medications that can affect blood glucose levels include:
- Acetaminophen
- Corticosteroids
- Steroids
- Diuretics
- Oral contraception (birth control pills)
- Hormone therapy
- Aspirin
- Atypical antipsychotics
- Lithium
- Epinephrine
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Phenytoin
- Sulfonylurea drug
How do you do a blood sugar test in a clinic or hospital?
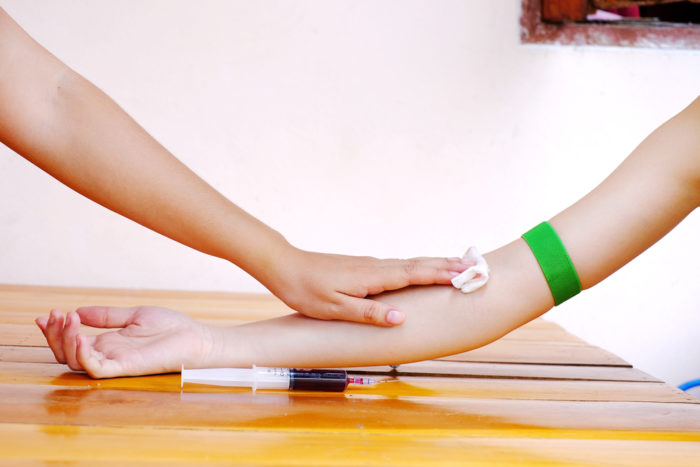
This glucose test generally only requires a small amount of blood sample.A nurse or will take blood from your vein or vein, usually from the inner elbow or on the back of your hand.
Before taking blood, the nurse will clean the blood collection area with an antiseptic to kill any germs. He will tie the elastic belt around your upper arm, to collect blood in the vein.
The nurse will then insert a sterile needle into your vein, then the blood will be pulled into the tube. You may feel a little pain, similar to needle puncture. You can reduce pain by trying to relax your arms.
When the nurse finishes taking blood, he releases the needle, puts pressure on the part that is injected and attaches the bandage. Followed by giving pressure for several minutes to prevent bruising. Your blood sample will then be sent to the laboratory for testing. Your doctor will follow up to discuss the results of the examination.
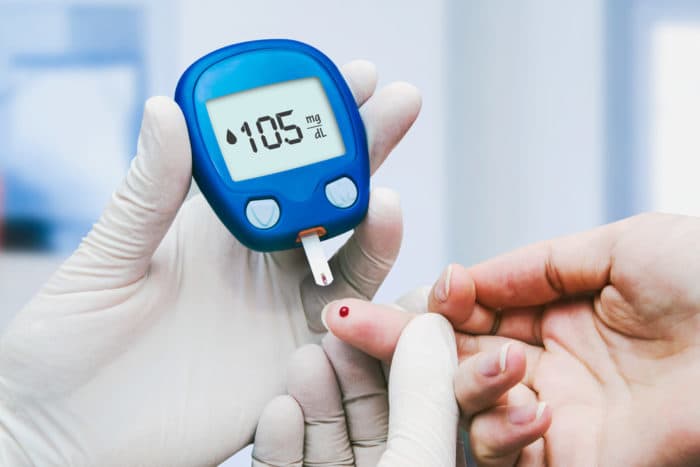
How do you read the glucose test results?
The World Health Organization or WHO defines the following glucose test results:
- Normal: 6.0 mmol / L or lower (below 110 mg / dl)
- Fasting glucose disorders: between 6.1 and 6.9 mmol / L (between 110 mg / dl and 125 mg / dl)
- Diabetes: 7.0 mmol / L (126 mg / dl) or more. Impaired fasting glucose is a form of prediabetes.