Contents:
- Medical Video: PTSD, Psychological Trauma and Head Injuries
- Danger of heading the ball
- Memory is reduced
- Brain function is impaired
- Who are the most vulnerable to the danger of heading a ball?
- Can I head the ball while playing soccer?
Medical Video: PTSD, Psychological Trauma and Head Injuries
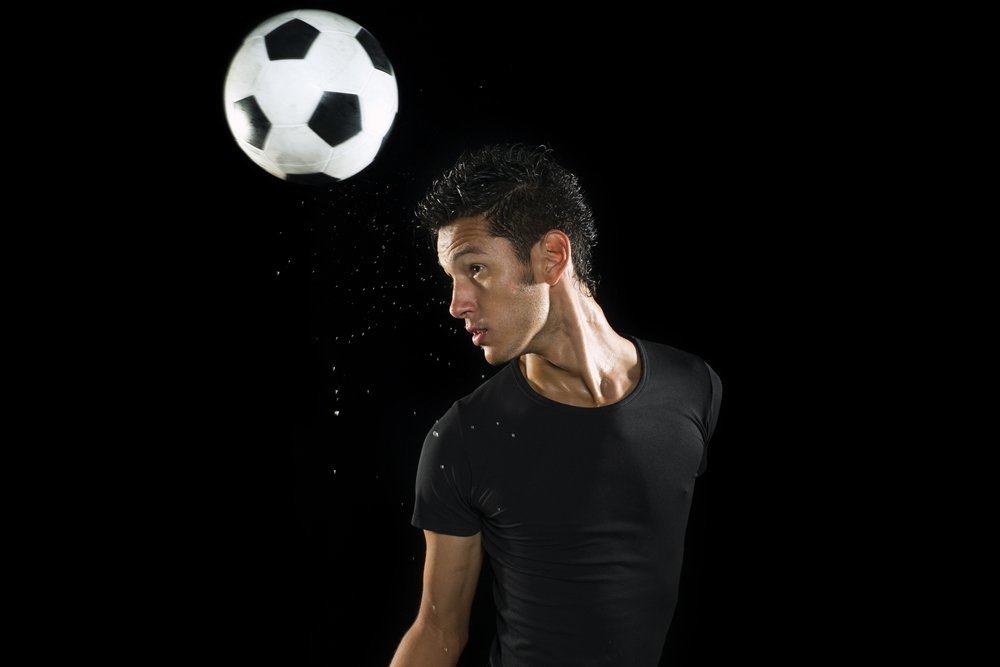
In the game of soccer, heading a ball is one skill that is quite complicated but effective in the field. Sometimes, this one technique can be a savior of a match for a particular team. So, it's no wonder that soccer players often head the ball as a defense or attack technique. However, did you know that behind the efficacy of heading the ball there is a danger that lurks football players? The danger in question is not only physical, such as injury or trauma to the head, you know. Heading the ball turned out to have a considerable impact on brain function. Do you often ball the ball? Read the explanation below to find out the dangers of heading the ball in your brain.
Danger of heading the ball
For a long time, studies carried out on ball head side effects have been limited to physical effects such as neck shock or injury. However, recently many researchers have begun to study the effects of this technique on how the brain works and activates. The results of these studies turned out to be quite surprising. Consider the following conclusions.
Memory is reduced
A study conducted by the University of Stirling in Scotland tried to see the effect of heading the ball on memory. In the study, the study participants were asked to head the ball 20 times. After the session ended, the participants then worked on a test to test their memory. As a result, the research participants' memory decreased by 41 to 67 percent. The impact was felt immediately after the training session headed the ball over. Fortunately the participants' memory returned to normal after 24 hours.
Brain function is impaired
Another study conducted by Harvard Medical School revealed that there was a significant difference between the brains of soccer players who often headed the ball with the swimmer's brain. Unlike soccer, swimming is usually not so vulnerable to collisions or head trauma. The difference highlighted by research in the Journal of the American Medical Association is the disruption or abnormality in the frontal, temporal, and occipital lobes in the brains of soccer players.
The parts of the brain that are disrupted are responsible for controlling alertness or attention, managing the visual process, and the ability to think complex. Impacts that may be felt directly are disorders of behavior patterns, mood swings or mood such as depression and anxiety, and difficulty sleeping.
Who are the most vulnerable to the danger of heading a ball?
Although the danger of heading the ball is already quite often voiced by health experts, soccer athletes or those who like to play soccer do not seem to be so affected by the warning of danger. This is because the impact that is generated on the functioning of your brain everyday is very disguised so it is difficult to distinguish whether certain disorders that you experience are generated by heading the ball or for other things, such as collisions with other players. Concussion or trauma to the head that has been experienced is also at risk of causing cognitive impairment. So, people who have had a concussion become more susceptible to the danger of heading the ball.
Children and adolescents are also more susceptible to brain dysfunction due to heading the ball. In children and adolescents under the age of 14 whose bodies are still developing, the brain has not been completely veiled by myelin. Myelin sheath serves to protect nerves and emit signals in the brain. So, the child's brain is more sensitive to shocks or collisions.
In addition, children over the age of 5 years will grow to 90% of an adult's head. Meanwhile, their necks were not yet strong enough to support such a big head. If children head the ball, the pressure received becomes much stronger so that the impact on the brain is also greater.
Can I head the ball while playing soccer?
Children under the age of 14 should avoid training or practice heading the ball with leather balls. If a child or teenager wants to practice a good ball heading technique, it is best to do it with plastic balls first until their head and brain develop perfectly.
The danger of heading balls for the brains of adults still needs further investigation. Because, it is not yet known the danger of heading a ball that will continue to haunt you in the long run. If you are worried, you should reduce the frequency of heading balls when practicing or competing in football. You are also advised to master the technique of heading the ball correctly and safely first, for example by closing the jaw and teeth tightly before the head touches the ball. Thus, you can minimize the risks that might be caused to the head and brain.
READ ALSO:
- 4 Exercising Errors That Often Cause Cracks
- The 10 Most Common Types of Sports Injuries
- Recognize Brain Concussion Symptoms in Children