Contents:
- Medical Video: All the Signs That You’re Not Drinking Enough Water
- What is the water requirement for the elderly?
- What are the consequences if the elderly drink too much water?
Drinking plenty of water is good for preventing dehydration. However, drinking too much water is also not good for the elderly.
The elderly kidneys are no longer functioning as effectively as the kidneys of young adults to process fluids. Therefore, too much intake over reasonable limits can rinse large amounts of electrolyte salt in the body. The condition of lack of salt (sodium) is also called hyponatremia.
In mild cases, low sodium levels in the body tend to cause a decline in cognitive cognitive functions - such as confusion, daze, and drowsiness. Nausea and lethargy (including weakness or muscle cramps) can also be a sign of the body's sodium in the body has fallen far from normal.
If hyponatremia continues to a dangerous level, lack of sodium in the body can cause severe headaches due to fluid buildup in brain tissue. Headaches are the main sign that this condition has developed very seriously. Serious hyponatremia due to the elderly who mostly drink water later can also cause the bones to be prone to breakage.
Seizures can occur due to the nerves of the brain that are very deficient in sodium intake. In severe cases, the elderly can experience respiratory failure even to coma. This is caused by brain swelling due to very low sodium levels.
In addition to the effects of drinking lots of water, disruption of body fluid balance can also be affected by the side effects of the drugs they use, such as diuretics, antidepressants, painkillers, or other drug use.
How to avoid hyponatremia in the elderly?
Medical Video: All the Signs That You’re Not Drinking Enough Water
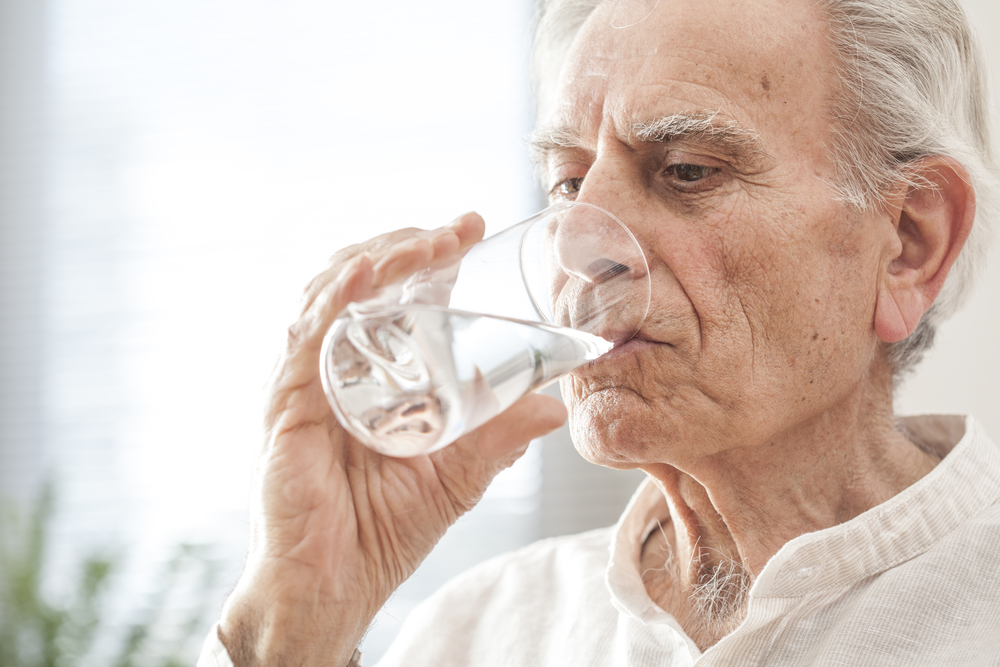
We are always stressed to drink lots of water to maintain body fluids. Lack of body fluids does make you prone to dehydration. This is also the most vulnerable experienced by the elderly. However, be careful. Elderly people should not drink lots of water. This can endanger his health. Why is that?
What is the water requirement for the elderly?
In general, drinking 8 glasses of water a day (about 2 liters) can meet the water needs of many people. However, actual water requirements vary between individuals. To make it easier for you to measure it, the recommendation is equivalent to drinking four to six glasses of size 250 ml (standard size of glass mineral water) per day.
Well, this calculation is different for the elderly. In general, the elderly need more water because they are prone to dehydration. This change in the amount of water requirements is influenced by many things, including body weight, increased body fat mass levels, and decreased kidney function due to aging.
In general, water needs for the elderly at least 1.5 liters a day. However, according to the recommendations of the Indonesian Ministry of Health, the elderly Indonesian fluid needs are as follows:
Woman:
- 60-64 th 2.3 liters
- 65-80 th 1.6 liters
- > 80 years: 1, 5 liters
Man:
- 60-64 years: 2.6 liters
- 65-80 years old: 1.9 liters
- > 80 years: 1.6 liters
Although it does require more fluid intake, don't let the elderly drink the most water. Excess body fluid will affect his health.
What are the consequences if the elderly drink too much water?
Drinking plenty of water is good for preventing dehydration. However, drinking too much water is also not good for the elderly.
The elderly kidneys are no longer functioning as effectively as the kidneys of young adults to process fluids. Therefore, too much intake over reasonable limits can rinse large amounts of electrolyte salt in the body. The condition of lack of salt (sodium) is also called hyponatremia.
In mild cases, low sodium levels in the body tend to cause a decline in cognitive cognitive functions - such as confusion, daze, and drowsiness. Nausea and lethargy (including weakness or muscle cramps) can also be a sign of the body's sodium in the body has fallen far from normal.
If hyponatremia continues to a dangerous level, lack of sodium in the body can cause severe headaches due to fluid buildup in brain tissue. Headaches are the main sign that this condition has developed very seriously. Serious hyponatremia due to the elderly who mostly drink water later can also cause the bones to be prone to breakage.
Seizures can occur due to the nerves of the brain that are very deficient in sodium intake. In severe cases, the elderly can experience respiratory failure even to coma. This is caused by brain swelling due to very low sodium levels.
In addition to the effects of drinking lots of water, disruption of body fluid balance can also be affected by the side effects of the drugs they use, such as diuretics, antidepressants, painkillers, or other drug use.
How to avoid hyponatremia in the elderly?
Not that you have to limit the fluid intake of the elderly because this can actually lead to dehydration which is also equally harmful to his health. However, the elderly fluid needs must always be closely monitored. Moreover, the recommendation for fluid intake above does not consider the water content of other foods and beverages, such as fruit and vegetables, soup / soup, porridge, sweet drinks, and so on.
Also, be more careful when inviting the elderly to physical activity that requires high intensity so as not to become dehydrated. If the activity is indeed high, it's okay to allow the elderly to drink more water.
Be careful of signs and symptoms of low sodium levels. Always consult with your doctor about the risks of the drugs used. Routine health checks can also be a way to find out the possibility of disease occurring.