Contents:
If asked who is at risk of contracting HIV / AIDS, then our answer might be for commercial sex workers, those who often have free sex and multiple partners, or it could be those who make tattoos or piercings in places that are not sterile. But did you know that there are other groups who have the risk of contracting HIV just like those who are vulnerable to HIV?
Housewife
Surprisingly, there are currently not a few numbers of housewives who have HIV. As quoted from the Jakarta Globe, Emi Yuliana from the Surabaya AIDS Prevention Commission stated that there was an increase in cases or trends of housewives affected by HIV / AIDS.
Compared to the CSW group, the number of housewives with HIV / AIDS experienced a more drastic increase. This is probably due to a lack of interventions to prevent the spread of HIV / AIDS in housewives. Unlike the prevention of HIV / AIDS in commercial sex workers which is more encouraged. According to the Head of the Bogor Regional AIDS Agency, in 2016 around 60% of people with HIV / AIDS in the city of Bogor were housewives.
Prevention of the spread of HIV in housewives has problems because most pregnant women or those who want to run pregnant programs refuse to undergo HIV / AIDS tests. This rejection occurs usually because you feel embarrassed, taboo, or feel that both he and his partner have never had sexual relations with other people. Only less than 10% are willing to take an HIV test after marriage.
If doing an HIV test is considered taboo, then housewives can try to use a scorecard that contains questions related to work and sexual activity both individual and work sexual activity and partner sexual activity. For example, if your spouse works as a cross-province driver and rarely returns home, then you are in a risk group and further testing is needed including a blood test if needed.
Health workers
Those who work in the health sector, such as doctors, nurses, laboratory officers, and health facility waste cleaning officers also have the potential to contract HIV from patients. Blood from HIV-positive patients can transmit HIV to these health workers through open wounds. For example, workers who have open wounds then take blood from patients who are HIV positive, so it is not impossible that syringes or other sharp objects can become intermediaries and transfer HIV. There are several ways HIV can be transmitted to health workers, namely:
- If a syringe that has been used by an HIV positive patient is accidentally plugged into a health worker (also called needle-stick injury)
- If blood contaminated with HIV affects mucous membranes such as the eyes, nose and mouth.
- If blood contaminated with HIV affects open wounds.
HIV transmission to health workers can be prevented by:
- Use personal protection such as masks, hospital-specific clothes, goggle or special glasses, and gloves.
- Always cover open wounds with tape or bandages.
- Always be careful when handling sharp objects.
- Dispose of hospital waste that has the potential to transfer HIV (such as a syringe for example) to a solid or hard trash, not just in plastic because the tip of a sharp syringe can come out.
- Clean spilled blood as soon as possible.
- Always wash your hands using cleaning fluid after making contact with patients, especially if they are exposed to the patient's blood.
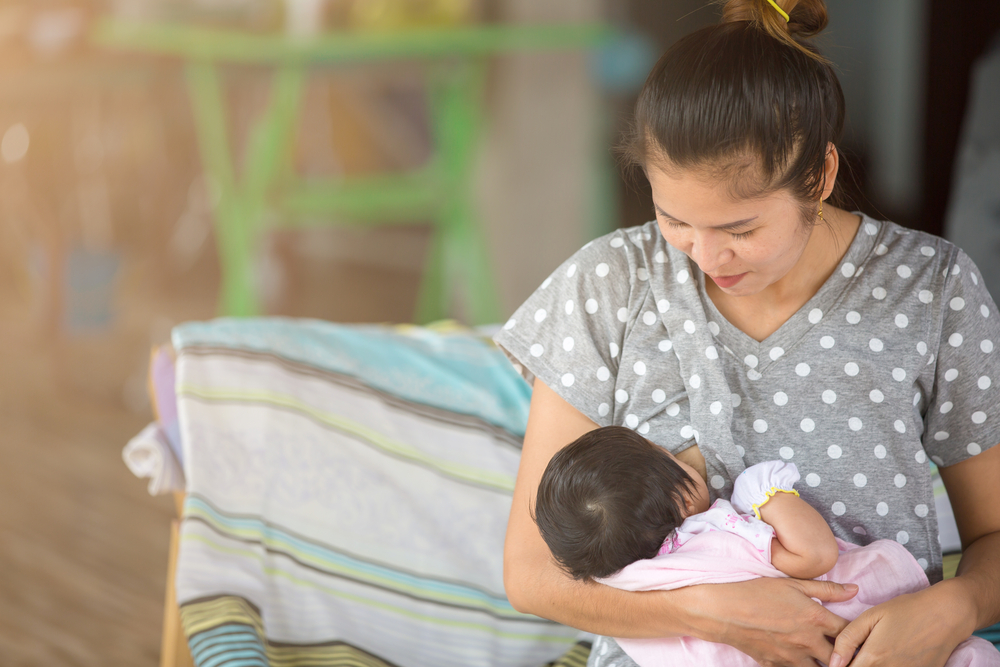
Baby
This may not be too foreign to you. Pregnant women who suffer from HIV can transmit the virus to their babies. This transmission can occur when the baby is still in the fetus, during the birth process, and when breastfeeding. This transmission from mother to baby is the most frequent cause of why children get HIV / AIDS.
HIV transmission from mother to baby can be prevented, if:
- Women who have HIV get HIV treatment during pregnancy and during childbirth or specifically schedule births by caesarean section. Caesarean section minimizes the possibility of maternal body fluids infecting the baby during the birth process.
- Babies born to HIV-infected mothers are then given HIV drugs for 6 weeks after birth and not breastfed. In the United States, mothers who suffer from HIV are advised not to breastfeed their babies and replace breast milk with formula milk as an option to meet the nutritional needs of babies.
HIV drugs reduce the amount of HIV virus in the body. Reducing the number of these viruses can directly reduce the likelihood of HIV transmission to the baby both during the womb and during the birth process.
A small dose of the drug can also be passed on to the baby through the placenta. This can protect babies from HIV infection, especially during the normal birth process because the birth process through the vaginal route exposes the baby to the mother's body fluids that carry the HIV virus.
READ ALSO:
- Detect Early Symptoms of HIV and AIDS
- Can HIV be infected through dialysis?
- 10 Wrong Myths About HIV / AIDS