Contents:
- Medical Video: How Color Blind People See the World
- Ins and outs of the eyes, the window of the world
- Then, what causes color blindness?
- Different types of color blindness that is owned, also different what he saw
- 1. Blind green-red
- 2. Blind yellow blue
- 3. Total color blindness
- How do doctors diagnose this type of color blindness?
Medical Video: How Color Blind People See the World
Even though it's called color blindness, this visual impairment is not as simple as just being able to see black and white. There are many types of color blindness, ranging from partial to total. Then, what is seen by people who are color blind?
Ins and outs of the eyes, the window of the world
In the eye there is a retinal layer that has 2 kinds of cells to capture light, namely stem cells and cone cells. Stem cells are very sensitive to light so they are useful when you are in a dim room, while cone cells have better accuracy while having photopigments that are useful for distinguishing colors.
Cone cells have 3 types of photopigments that are useful for distinguishing 3 basic colors, namely red, blue, and green. Color besides the three basic colors is a combination of the three basic colors, such as yellow which is a combination of red and green.
Then, what causes color blindness?
Color blindness is most often caused by genetic abnormalities inherited from parents. In red green color blindness, the genes responsible for color blindness are on the X chromosome, so that men who only have 1 X chromosome suffer more color blindness than women who have two X chromosomes. While yellow blue color blindness is an autosomal disorder.
Different types of color blindness that is owned, also different what he saw
Color blindness is not as simple as black and white, but there are several types of color blindness based on the type of cone cell abnormality and the type of cone cells involved. There are three types of color blindness, namely
- Blind red green
- Blind yellow blue
- Total color blindness
1. Blind green-red
Blind red or green red-green color blindness is the most common type of color blindness. This condition is caused by loss or limited function of red (protan) or green (deutran) cones. There are several types of green color blindness, namely:
- Protanomaly: red cone abnormal cell photopigmen. Red, orange and yellow colors look greener.
- Protanopia: cone red photopigmen are not fully functional. The red color will look black. Some colors like orange, yellow and green look like yellow.
- Deuteranomaly: abnormal green cell cone fotopigmen. Green and yellow appear redder, and it is difficult to distinguish between purple and blue.
- Deuteranopia: cone cell green photopigmen are not fully functional. The red color looks brownish yellow and green as pale brown (beige).
2. Blind yellow blue
Yellow or blue color blind blue-yellow color blindness less often than red green color blindness. Caused by blue photopigmen (tritan) not functioning or only functioning partially. There are 2 types of yellow blue color blindness, namely:
- Tritanomaly: limited blue cone cell function. The blue color looks greener and it is difficult to distinguish between yellow and red with pink. This type of color blindness is very rare.
- Tritanopia: limited number of blue cone cells or less. The blue color looks green and yellow looks like purple. Color blindness is also very rare.
3. Total color blindness
Type or total color blindness monochromacy making patients totally unable to see their color and visual acuity can also be affected. There are two types, namely:
- Conical monochromation: This type of color blindness occurs due to a malfunction of 2 types of cone cells. To be able to see colors, at least 2 types of cone cells are needed so that the brain can compare two different types of signals. If only 1 type of cone cell works, the comparison process does not work so the color is not visible. There are 3 types of monochromation depending on cone cells that still work, namely monochromation of red cone cells, monochromation of green cones, and monochromation of blue cone cells.
- Stem monochromation: This is the most rare and hardest type of color blindness. In this color blindness, there are no cone cells at all. There are only stem cells that work so the world really looks like black and white and gray. Patients with monochromated stems tend to be uncomfortable when in brightly lit environments.
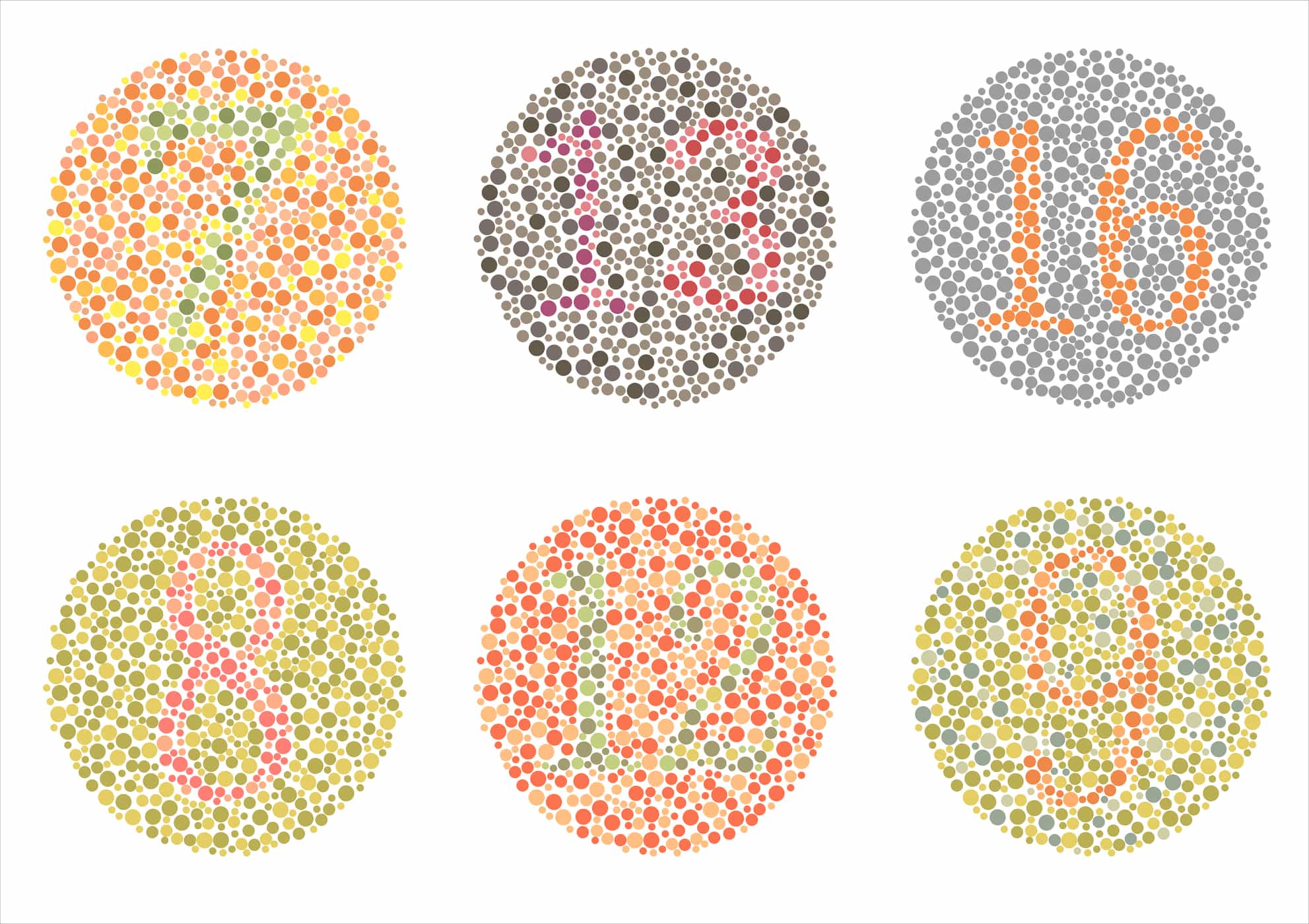
How do doctors diagnose this type of color blindness?
Many checks can be done to check for color blindness, but what is most common and easy to do is to use the Ishihara test. A book containing certain images and numbers will be shown to the patient and the patient will be asked to read the numbers in the picture. However, the color blindness test was developed by a Japanese doctor named Dr. This Shinobu Ishihara can only be used for red green color blind examination.