Contents:
- Medical Video: The Most BIZARRE Medical Conditions!!!
- What is werewolf syndrome (hypertrichosis)?
- Types of hypertrichosis
- Causes of hypertrichosis
- Symptoms of hypertrichosis
- Treatment for hypertrichosis
Medical Video: The Most BIZARRE Medical Conditions!!!
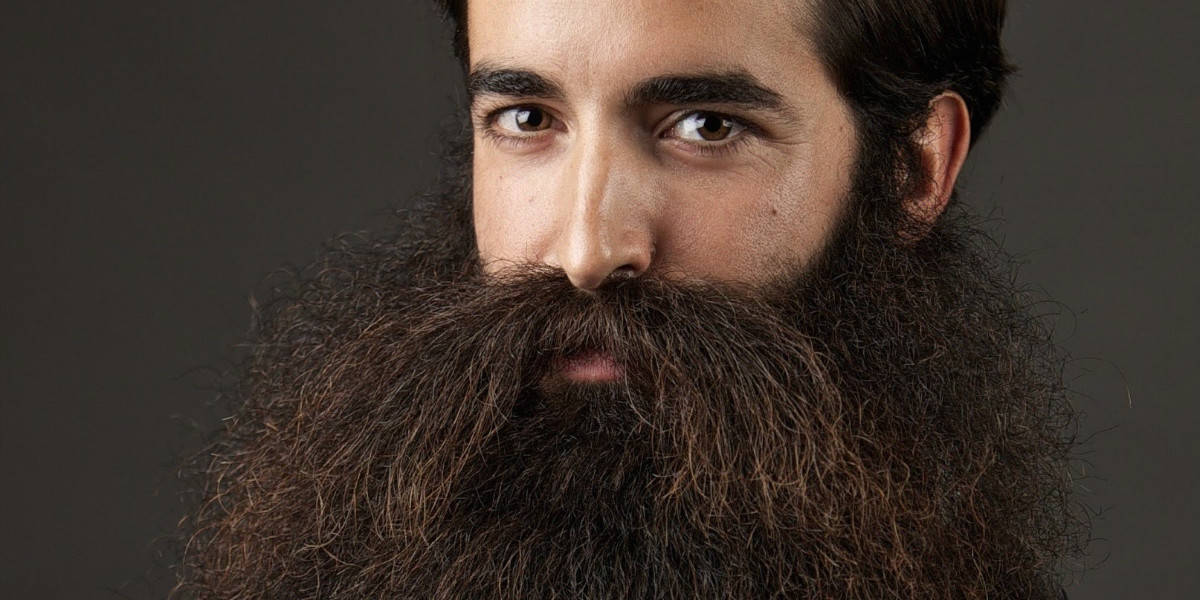
Having fine hair that grows all over the body is a natural thing. In general, feathers on the body cannot grow very long like hair on the head. However, what happens if fine hair grows very thick to make you look like a werewolf? This is not a mystical story. In the medical world, hair all over which grows thick beyond reasonable limits is a disorder named hypertrichosisor also called werewolf syndrome - only without fangs and creepy sharp claws.What causes it and how to solve it? Here's the explanation.
What is werewolf syndrome (hypertrichosis)?
Hypertrichosis (hypertrichosis) is a rare condition characterized by excessive and excessive hair growth throughout the body, even covering the face. Hypertrikosis can appear at birth or develop over time.
Both men and women can experience hypertrichosis.
Types of hypertrichosis
- Congenital hypertrichosis lanuginosa. First appears as fine hair that grows normally at birth. However, after weeks, this hair does not disappear, it continues to grow in various places in the baby's body.
- Congenital terminal hypertrichosis. Abnormal hair growth starts at birth and continues throughout a person's life. This hair is usually long and thick, covering the face and body.
- Nevoid hypertrichosis. Excessive hair growth in any form appears in the specified area. In some cases, more than one strand of hair.
- Hirsutism. This form of hypertrichosis only occurs in women, characterized by the growth of dark and thick hair on female body parts that usually do not have hair, such as the face, chest and back.
- Acquired hypertrichosis. This condition tends to develop later on. Excess dense hair can grow limited in a small area of the body or throughout the body.
Causes of hypertrichosis
Most cases of werewolf syndrome are caused by genetic mutations in carrier genes that stimulate hair growth. This genetic mutation makes cells that usually turn off hair growth in unusual areas such as the eyelids and forehead, remaining in the activated state.
In the case of female hirsutism, dense hair growth in the body is caused by a genetic inheritance that causes excess androgen production (male sex hormones). If your mother or sister has this condition, chances are that you will experience hirsutism.
Other causes include:
- Malnutrition.
- Poor diet or certain eating disorders, such as anorexia nervosa.
- Certain drugs, such as hair growth drugs, certain immunosuppressants, and androgenic steroids.
- Cancer and cell mutations.
- Autoimmune and contagious diseases that affect the skin.
Sometimes, skin conditions become very sensitive to UV light (porphyria cutanea tarda) can also trigger hypertrichosis.
If hypertrichosis occurs only in certain places in the body, it may be due to chronic skin conditions, such as lichen simplex, which are associated with recurrent rashes, itching, and certain skin scratches.
Increased blood supply in one particular area of the body can also cause this condition. Sometimes, symptoms of hypertrichosis appear in areas where a person uses plaster casts. This condition can also be caused by side effects of anti-bald drugs.
Several other cases occur without a known cause.
Symptoms of hypertrichosis
Hypertrikosis can occur at birth or develop later in life. Common symptoms of hypertrichosis are problems with your gums or teeth. Some teeth may be lost or your gums may be enlarged. Women with hirsutism develop stiff black hair like on the face, chest and back. Hypertrikosis usually produces one of three types of hair:
- Vellus: This type of hair is generally short (less than 0.2 cm long)) and not clearly visible. This hair type can be found in almost all parts of the body except the soles of the feet, back of the ears, lips, and palms, or in scar tissue.
- Lanugo: This type of hair is very soft and smooth, like the body of a newborn baby. It usually does not have pigments. Most babies lose lanugo in a few days or weeks after birth.
- Terminal: Long and thick hair, and usually very dark.
Treatment for hypertrichosis
You cannot do anything to prevent this form of congenital disease. The risk of certain forms of hypertrichosis can be reduced by avoiding certain drugs, such as minoxidil.Treating hypertrichosis is by removing hair through various short-term methods, including:
- Shave
- Waxing
- Revoke
- Hair bleaching
All of these methods are temporary solutions. This method also risks causing skin irritation that is painful or uncomfortable. In some parts of your body it may not be easy to do this method.
Long-term care includes electrolysis and laser surgery. Electrolysis is the destruction of hair follicles with a small electric charge. Laser surgery involves applying a special laser beam to several hairs at once. However, hair loss can often be permanent with this treatment.