Contents:
- Medical Video: Rabies Infection: Treatment, Vaccines and Prevention
- Signs and symptoms of rabies
- During the incubation period
- Initial symptoms
- Advanced symptoms
- How can someone get rabies?
- How to treat rabies in humans?
- Treatment of local wounds
- PEP recommendations
Medical Video: Rabies Infection: Treatment, Vaccines and Prevention
Rabies is a contagious viral disease that is often fatal after the onset of clinical symptoms. In the case of humans, the rabies virus is transmitted by 90% by pet dogs. Viruses can affect wild animals and pets, and can spread to humans through saliva from bites or scratches.
Rabies is found in all continents except Antarctica, but more than 95% of human deaths from the virus occur in Asia and Africa. Especially, this occurs in remote rural communities, where children between the ages of 5-14 years are often victims.
Signs and symptoms of rabies
During the incubation period
The incubation period is the time needed for the appearance of symptoms after a person is infected with the virus. The incubation period of rabies usually occurs 2-12 weeks, although it can also occur for 4 days. The closer the infection area is, the shorter the incubation period. The length of the incubation period is very important, because it is the only period that can determine the success of treatment.
Initial symptoms
The initial symptoms of rabies often feel vague and we can easily mistake them for other diseases. The following are the initial symptoms of rabies:
- Fever
- Headache
- Feeling unwell
- Feeling scared or anxious
In addition, about half of sufferers also experience pain and tingling in the infected location.
Advanced symptoms
The initial symptoms will last for 2-10 days before more severe symptoms begin to develop. This usually includes aggressive behavior, hallucinations, agitation, and the production of a lot of saliva.
How can someone get rabies?
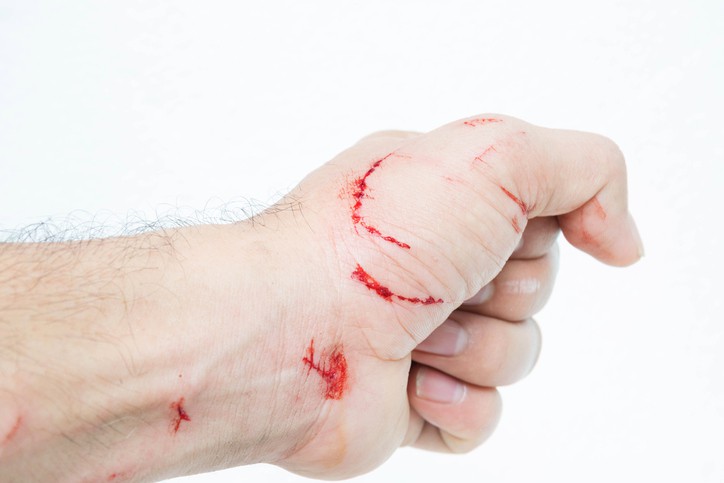
People are usually infected after deep bites or scratches by infected animals. Dogs are the main source as well as transmitters of this disease. Besides dogs, bats are also the largest source of human death in Australia and Western Europe. Meanwhile, deaths due to exposure to foxes, raccoons, skunks, civets, and other wild carnivorous species are very rare.
Transmission can also occur when an infectious material, usually saliva, comes in direct contact with the human mucosa or a wound that is still fresh on the skin. Human-to-human transmission by bite, theoretically might be possible, but it was never confirmed. In addition, consumption of raw meat or other tissues from infected animals is not proven to transmit rabies to humans.
How to treat rabies in humans?
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)is bite treatment that starts immediately after a person is exposed to rabies. This must be done so that the virus does not enter the central nervous system which will produce death in the short term. This PEP consists of:
- Local treatment of wounds starting as soon as possible after exposure.
- Providing a effective and effective rabies vaccine that meets WHO standards.
- Provision of rabies immunoglobulin (RIG), if needed.
Treatment of local wounds
This involves first aid from the wound which includes immediate and thorough rinsing by washing the wound for at least 15 minutes with soap and water, detergent, povidone iodine, or with other substances that can kill the virus.
PEP recommendations
Depending on the severity of human contact with animals suspected of being rabies animals, the provision of PEP is recommended as follows (see table):
All exposure categories II and III are considered as carriers of risk of developing rabies that requires PEP. This risk will increase if:
- Mammals that bite are a species known as a source or transmitting rabies.
- Animals look sick or show abnormal behavior.
- The wound or mucous membrane is contaminated by the animal.
- Unreasonable bite.
- Animals have not been vaccinated.
If you are in an area that is heavily infected by rabies, seek medical advice as soon as possible if you are bitten or scratched by animals, especially dogs.
READ ALSO:
- Can Asthma Patients Have Pets?
- Various Diseases That Can Be Transmitted by Pets
- Pet Bites