Contents:
- Medical Video: Peripheral Neuropathy
- How does leprosy damage the peripheral nerves and skin?
- If leprosy damages the peripheral nerves it can attack the eyes
Medical Video: Peripheral Neuropathy
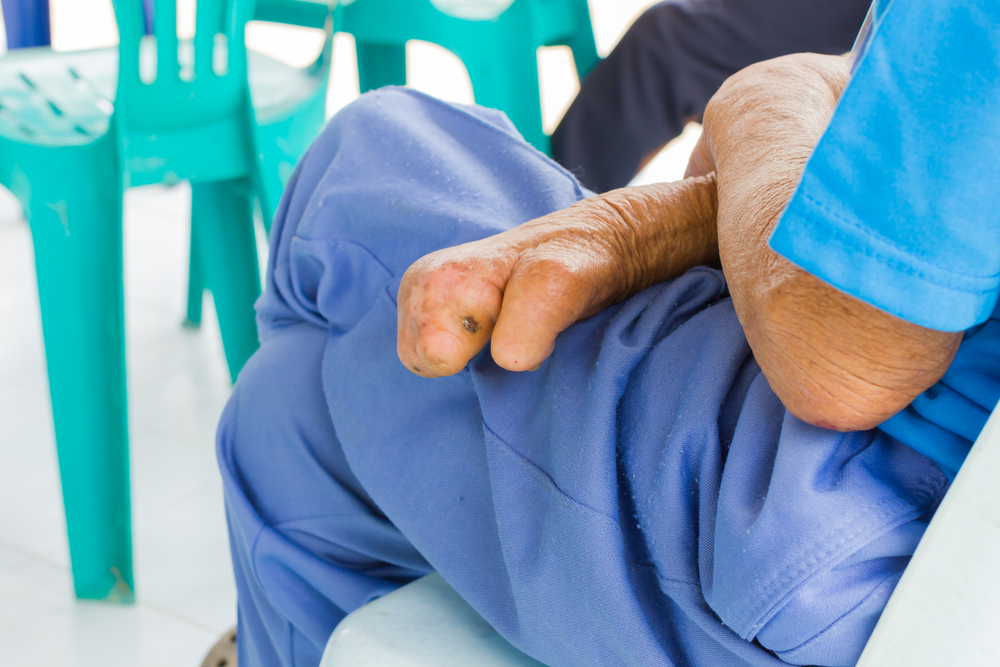
Leprosy is a disease that attacks the peripheral nerves, skin, eyes and bones if not treated immediately. Actually leprosy can be cured if the patient immediately does treatment and routinely undergoes treatment thoroughly. If not, it will most likely result in an incurable disability. How does leprosy damage the body of the sufferer? Consider the following review.
How does leprosy damage the peripheral nerves and skin?
Reporting from the International Book of Leprosy, M. Leprosy is the only bacterium that infects the peripheral nervous system. Most leprosy germs are in Schwann cells for leprosy to survive, divide themselves, and sow seeds in Schwann cells.
These germs choose regions where the temperature is colder in the body to multiply and related inflammatory cells around the nerve trunk near the skin. As a result, the skin becomes numb or loses touch function.
In addition, other signs of inflammation appear, namely lesions. Lesions are changes in skin color to be brighter than the surrounding area. These lesions have a slightly reddish color, swell, and feel soft.
Other signs of inflammation in the peripheral nerves are loss of muscle function (muscle paralysis) and anhidrosis, which is the body's inability to sweat normally, causing thin cracks in the epidermis or epithelium. This can also make the nose dry because there is no fluid (runny nose) that serves to moisturize.
The place where nerve damage occurs in leprosy is usually in the hands, feet, and eyes, precisely in the following nerves.
- Facial, attacks the eyelid nerves so that the eyes cannot close
- Auricular magnus, attacks the area behind the ear and jaw so that it is numb
- Ulnaris, attacks the little finger and ring finger so that it loses its ability to move
- Median, attacks the thumb, index finger and middle finger so that it loses its ability to move
- Radialis, attacks the wrist so that it loses its ability to move
- Peroneus communis, attacks the ankle so that it loses its ability to move
- Posterior tibialis, attacks the toe nerves so it loses the ability to move
After attacking the nerves, the bones will also be infected, causing disability or deformation in the bone, such as the nose saddle. Wounds and edema (swelling) which is an open wound that may be difficult to heal can increase the risk of amputation in parts of the body that have been damaged by injury.
If leprosy damages the peripheral nerves it can attack the eyes
The course of eye disease in leprosy patients occurs in two types of leprosy, namely tuberculoid and lepromatous. Tuberculoid leprosy is characterized by the appearance of large and numb lesions, while lepromatous leprosy (the most severe leprosy) is characterized by the appearance of many lesions.
Eye abnormalities in leprosy can cause changes in the eyelids due to disorders of the eyelid nerves and muscles, lacrimal glands, abnormalities in the cornea, and damage to the iris.
Leprosy occurs when macrophages (white blood cells) weaken and are unable to destroy leprosy germs so that germs can divide and eventually damage tissue. The formation of many leprosy germs on tissues is also influenced by the ability of germs to adapt to body temperature, virulence (germ ferocity), and the proliferation of leprosy germs.
There are four ways leprosy causes damage to the eye, namely:
- Leprosy germs infiltrate and directly attack the eyes or eyelids (infiltration)
- Direct infection of leprosy germs in the trigeminal nerve and facial nerve (exposure)
- Secondary inflammation of the eye due to infiltration
- Secondary complications due to bacterial infections around the eyes
Eye complaints in leprosy patients vary. For example, excessive watering of the eyes at first, but it will dry out (keratitis), the eyes feel sore when they wake up in the morning, and the eyes cannot be closed (lagoftlamus). Leprosy can also cause iritis (inflammation of the iris), glaucoma, cataracts, eyebrows and eyelashes fall out, and end in blindness.