Contents:
- Medical Video: Female Bladder Leakage: Solutions to Get Control | UCLA Obstetrics & Gynecology
- The difference is overactive bladder, urinary tract infections and urinary incontinence
- Different causes
- Different symptoms
- Different ways of treatment
Medical Video: Female Bladder Leakage: Solutions to Get Control | UCLA Obstetrics & Gynecology
Overactive bladder and urinary tract infections and urinary incontinence all disrupt urination habits that make you uncomfortable. Sometimes, the symptoms of the three can look similar, making it difficult to tell which ones are attacking you. To better understand the difference between an overactive bladder, urinary tract infection, and urinary incontinence, see the full review below.
The difference is overactive bladder, urinary tract infections and urinary incontinence
Although both attack the work of the bladder, it does not mean that these three diseases can be just interpreted. In fact, there are still differences that characterize overactive bladder disease, urinary tract infections and urinary incontinence:
Different causes
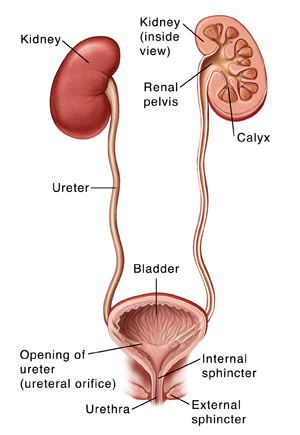
The cause of urinary tract infection (UTI) is the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli) which attacks the kidneys and urinary tract, bladder, to the urethra (opening of the urethra).
Meanwhile, the cause of urinary incontinence is a combination of weakening of the bladder muscle to control the flow of urine and the heavy pressure received by the stomach. Urinary incontinence is usually triggered by coughing, pregnancy, childbirth, or prostate gland problems. Natural aging and the condition of the bladder that is always full can also result in urinary output being difficult to control.
In contrast to urinary tract infections and urinary incontinence, the overactive bladder is caused by bladder function as the urine storage has decreased. This is also affected by a nervous system disorder in the bladder that sends false messages to the brain. As a result, you can feel like urinating on the lizard even though the bladder isn't actually fully filled.
Different symptoms
Urinary tract infection
Symptoms of UTI actually depend on which urinary tract is infected. If the target is aimed at the lower urinary tract, the urethra and bladder, the symptoms are:
- Burning or pain when urinating
- The frequency of urination increases
- The urine smells, bleeds, and has a thick color
- Pelvic pain in women
- Anal pain in men
While UTI in the upper urinary tract usually attacks the kidneys, with symptoms such as:
- Pain or pain in the upper and side back
- Cold hot body
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
Urinary incontinence
Signs of urinary incontinence can be divided into several types. In mild cases, urine can come out by itself when you cough, sneeze, laugh, or lift heavy objects.
In a moderate level, the urge to urinate is so large that the urine comes out on its own. In cases that are already severe, the urine comes out more often than usual even once an hour without being able to be controlled.
Overactive bladder
Note if you experience one or more of the following overactive bladder symptoms:
- The urge to urinate is difficult to hold
- Frequent incontinence (urine out without control)
- The frequency of urination more often than usual
- Waking up in the middle of the night to urinate
Different ways of treatment
Urinary tract infection
As with symptoms, UTI treatment is also based on the causes and which parts are affected. If UTI is caused by bacteria, antibiotics are the antidote. Antivirus is often chosen if the initial cause is a virus. Whereas if the cause is fungus, then antifungal is the right treatment.
The choice of medication will be adjusted according to your doctor's health condition, severity, and type of bacteria, virus, or fungus that causes your UTI
Urinary incontinence
Treatment for urinary incontinence is determined by the cause and severity of the condition. For example, by doing Kegel exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles, practice bladder function, consume drugs according to a doctor's prescription, to insert a special medical device into your urinary tract. If it is already considered severe, surgery procedures may be the last step to treat this condition.
Overactive bladder
Similar to urinary incontinence, the overactive bladder also requires prescription oral medications and Kegel exercises to help strengthen the muscles around the bladder and urethra. Only difference, people with overactive bladder must regulate the time of fluid intake into the body.
Botox injections and training nerve stimulation in the bladder also become an advanced treatment to improve overactive bladder work. Surgery is also needed if it can no longer be helped with a lighter treatment.













