Contents:
Medical Video: Owen Neck Boil (furuncle) Treat with Dr. Gonzo!
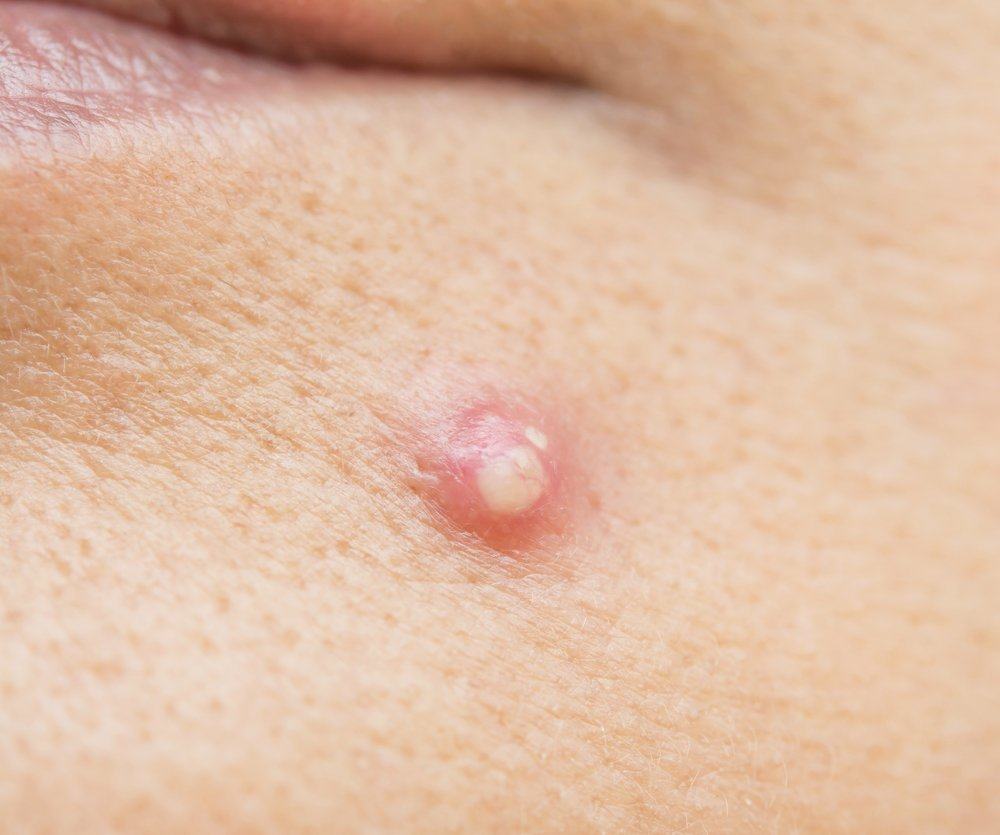
Boils are skin infections that attack hair follicles or oil glands under the skin. At first, the boil looks like a reddish rash on the skin that aches to the touch. Over time, redness on the skin will form a hard lump, filled with pus and softened again to the touch. Lumps can sometimes be as big as ping-pong balls.
Boils often appear on the body or back, neck, armpits, buttocks, or groin. But you can experience ulcers anywhere in all areas of hairy skin that are prone to sweating or experiencing friction.
What causes boils?
The main cause of boils is the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria that lives on the skin, inside the nose and throat. The skin is an important part of the human immune defense against foreign matter and disease-causing germs. Therefore, damaged skin, such as being scratched or punctured, can be a gateway for bacteria to enter the body and infect the surrounding skin.
Some boils can also be caused by infections from ingrown hair. Infected skin disrupts the body's immune system so that the location of the wound becomes festering.
Anyone can boil. However, people with certain diseases or who take certain drugs that weaken the immune system are more susceptible to suffering from ulcers. Diseases that weaken the immune system include diabetes or kidney failure. If you have a weak immune system, for example because of old age or HIV, you are also prone to ulcers.
READ ALSO: How HIV Affects Your Skin
A number of skin diseases that damage the protective layer of the skin, such as zits and eczema, make you more prone to boils. Boils can be transmitted through direct contact between healthy skin and pus if you live and / or borrow personal items with someone who has ulcers.
How to treat boils: don't squeeze it!
"Mature" boils can generally break apart in 1-2 weeks, marked by pus flowing out of the head of the boil. To speed up the process of healing boils, you can do the home remedies below:
- Compress warm water. Do it for 10 minutes, several times a day. Warm water compresses can reduce pain and provoke pus to rise to the surface. The boil can rupture itself after several routine compresses. After touching boils, always wash your hands with soap.
- Wash with antibacterial soap. When boils start to dry, wash with antibacterial soap until all pus is drained and wiped with alcohol. Apply an antibiotic ointment and cover the wound with a bandage. Routinely wash ulcers and replace the bandages two to three times a day.
READ ALSO: 4 Types of Vitamins that Are Good for Your Skin
Do not squeeze the boil. Squeezing boils can increase the risk of spreading infection. If already spread, boils can cause more serious complications. One example includes cellulitis, a type of serious bacterial infection on the skin. Infection can also enter the bloodstream and trigger blood poisoning (sepsis) which has the potential to cause infection in organs in the body, such as the heart (endocarditis) even to the bone (osteomyelitis).
When do boils need to be seen by a doctor?
Mules rarely require medical treatment by a doctor. But visit a doctor if more than one boil occurs at the same time, or if one or more of the following symptoms appear:
- Appears on the face
- There is fever and chills
- Diameter more than 5 cm
- Does not heal in two weeks (does not break after self-medication)
- Your lymph glands swell
- Embossed lines or redness in healthy skin around boils
- The pain is getting worse or very painful
- You have a heart murmur, diabetes, problems with the immune system, or use drugs that weaken the body's immune system (eg corticosteroids or chemotherapy) and boils appear on the skin
READ ALSO: 9 Causes of Boils and Lumps in the Vaginal Lips
If the infection has spread to deeper or wider tissue, pus samples can be taken to identify the type of bacteria that causes the infection more accurately. The results of pus samples can guide the doctor about the choice of antibiotics that can be used to treat your problem. Examples of drugs that have been used in the treatment of boils include clindamycin, mupirocin, and cephalexin ointments.