Contents:
- Medical Video: Gout and Pseudogout
- Difference between gout and pseudogout
- Symptoms
- Cause
- The trigger factor
- Treatment and prevention
Medical Video: Gout and Pseudogout
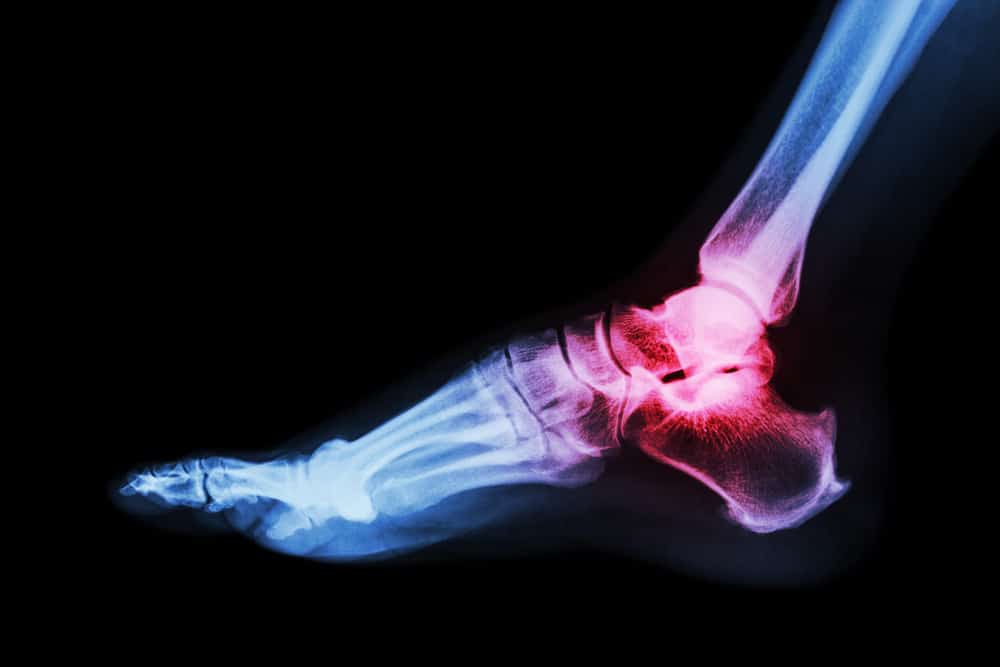
Your joints - for example on the wrist or leg - suddenly feel painful and swollen? Be careful, don't blame gout. You may be affected by pseudogout. Pseudogout, also known as fake gout, is indeed less commonly known than gout (gout) However, both have fundamental differences that you need to understand. Here is the easiest way to differentiate gout and pseudogout.
Difference between gout and pseudogout
Both gout and pseudogout (fake gout) both attack joints and are included in the group of arthritis. Both also often attack people who are elderly.
However, gout and pseudogout are caused by different things. So the symptoms, treatment, and ways to prevent the appearance of two joint diseases are certainly not the same. The best way to find out which disease is attacking you is to immediately see a doctor. Avoid self-diagnosis, or even undergo treatment without the supervision of your doctor.
But as an illustration, please see what are the basic differences between gout and the following pseudogout.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gout and pseudogout that are similar are both equally cause extraordinary pain in one of your joints. Joint pain may be followed by swelling and redness of the skin color. The attack usually occurs suddenly.
The difference in symptoms lies in the joint being attacked. Gout usually attacks the toes, heels, fingertips, and wrists or feet. While pseudogout often attacks larger joints such as knees, shoulders, elbows, hips, and back.
In addition, symptoms of gout often attack at night. Even to make you wake up from sleep.
Cause
These two joint diseases are caused by clumping of certain substances in the body, especially in joints. However, substances that cause clots (crystals) are different.
Uric acid occurs when there is a buildup (crystallization) of uric acid, which is a residual substance produced by the body after breaking down purine. So the more you eat high purine foods, the more uric acid production in the body.
While pseudogout is caused by calcium pyrophosphate crystallization in the joint. Unfortunately, until now it has not been known exactly how calcium pyrophosphate can crystallize to trigger arthritis. However, calcium pyrophosphate crystals are known to accumulate as you age.
The trigger factor
Gout usually starts to show symptoms in middle age, namely when you enter the age of 30 or 50 years. While those who are more at risk of developing pseudogout are elderly people, that is, over the age of 60 years.
However, according to experts, the second biggest risk factor for this joint disease is heredity. Your chances of getting gout or pseudogout are greater if you have a history of two diseases in your family.
Treatment and prevention
The treatment step for these two diseases generally focuses on relieving the symptoms that arise, especially joint pain. You may be asked by your doctor to put cold compresses on the affected joint area and take painkillers. Usually you are also advised to rest first until conditions improve.
Gout can be prevented by reducing consumption of high purine foods. However, until now it has not been concluded how or whether there is a special diet to prevent pseudogout disease.
However, just in case of gout and pseudogout, you should start living a healthy lifestyle and diet. For example, by diligently exercising and increasing consumption of various types of vegetables and fruits. Make sure you also continue taking medication following the doctor's advice.