Contents:
- Medical Video: Atherosclerosis (2009)
- Get to know lipoprotein
- Bad vs. good lipoprotein
- The process of forming plaques in blood vessels
- Conclusion
Medical Video: Atherosclerosis (2009)
To patients with high blood pressure, a doctor often gives advice to regulate the consumption of fatty foods, namely reducing bad fat and adding good fat. But what is good fat and fat? What's the difference? Then how can the process of fat we consume become a plaque in a blood vessel? Come on, let's see!
Get to know lipoprotein
Cholesterol is a fat that is not soluble in water, so that in the blood, fat will be bound by protein so that fat can dissolve in water. The protein is called lipoprotein. It is this fat that binds to lipoproteins that have a role in causing plaques in blood vessels.
Lipoproteins can be divided into "bad" and "good" ones. What is an evil lipoprotein is low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) which is more fat than protein. Conversely, which includes good lipoprotein is high-density lipoprotein (HDL) which has more protein content.
Bad vs. good lipoprotein
LDL and VLDL are called bad lipoproteins because they have a role in carrying cholesterol into the walls of blood vessels that trigger plaque. The higher the level of LDL and VLDL, the risk for blood vessel plaque will increase.
Conversely, HDL as a good lipoprotein removes cholesterol from the walls of blood vessels and brings it to the liver for later removal, thus protecting blood vessels from the formation of plaque. The higher the HDL level, the lower the risk of plaque. In addition, it turns out that HDL has an anti-inflammatory effect that further reduces the risk of plaque formation.
The process of forming plaques in blood vessels
The presence of injury to a blood vessel is the beginning of the formation of plaque. Some things that can cause injury to blood vessels are free radicals, high blood pressure, bacteria, and viruses. Injury to blood vessels triggers inflammation which if it occurs continuously over a long period of time will trigger the formation of plaque.
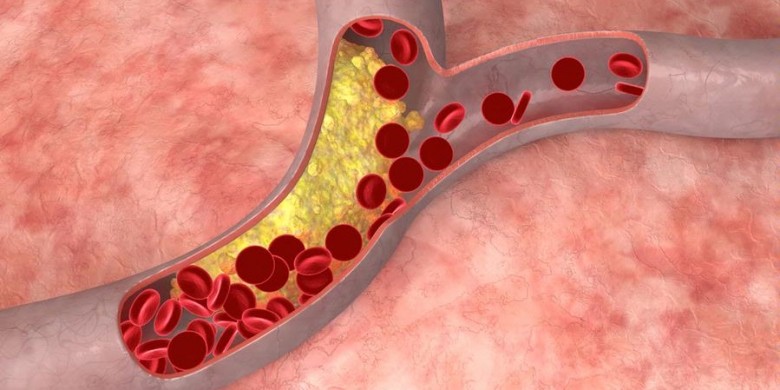
The process of forming blood vessel plaques begins with the accumulation of LDL cholesterol in the blood vessel walls. The more that accumulates, the LDL cholesterol will undergo an oxidation process by free radicals. This oxidized LDL turns out to cause irritation to the walls of blood vessels, which triggers an inflammatory response.
One of the inflammatory cells that plays a role is monocytes. Monocytes enter the walls of blood vessels and will turn into macrophages which have the function of "eating" oxidized LDL cholesterol. The macrophage will continue to "eat" LDL cholesterol and if viewed with a microscope, the macrophage will look like "foamy", therefore eventually macrophages will be referred to as foam cell.
Set foam cell this can be seen without a microscope shaped like a yellow mass attached to the walls of a blood vessel called as fatty streak. Fatty streak this is the initial picture of blood vessel plaque.
Foam cell will continue to form if the inflammatory process occurs repeatedly until someday foam cell will accumulate in the walls of blood vessels that trigger the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells will migrate from the tunica media towards the direction of the intima piled with the group foam cell.
In this new place, muscle cells undergo division and the number is increasing and the size is enlarged. Cholesterol piles and smooth muscles that cover them will form mature plaques. If the above process continues, mature plaques will accumulate and protrude towards the arteries and narrow the diameter of the arteries.
Blood vessels with thick plaque are also more susceptible to damage, besides it also becomes easier to accumulate calcium so that the blood vessels become hard and not elastic, which triggers high blood pressure.
Conclusion
Fat does have the impression that it is not good for our health, but that does not mean we should not consume it at all. We must adjust the proportion of fat consumption by increasing good fat and avoiding bad fats. Get to know what foods contain good fats and bad fats so that your blood vessels don't form blood vessel plaques quickly.