Contents:
- Medical Video: How To Check For Mouth For Cancer
- What is glossitis?
- Types of glossitis based on their appearance
- What are the causes of swollen tongue glossitis?
- How to deal with swollen tongue due to glossitis
Medical Video: How To Check For Mouth For Cancer
The oral cavity has two important organs, namely the teeth and tongue. If the teeth act to soften food, the tongue serves as a taster and swallow food. However, the function of the tongue can also experience interference, one of which is swollen and inflamed tongue, known as glossitis.
What is glossitis?
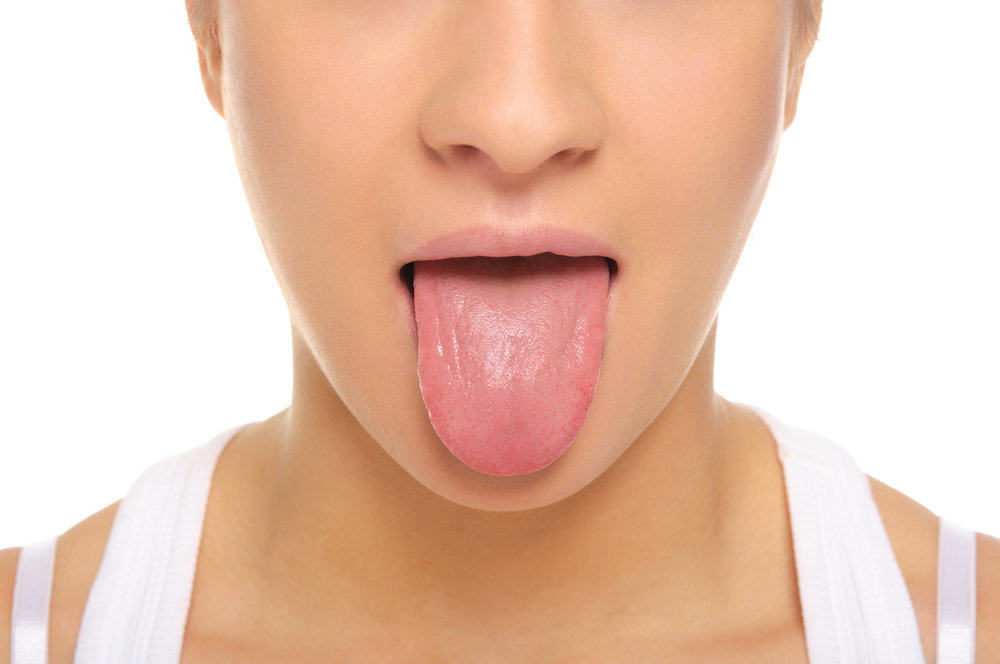
Glossitis is a disorder of the tongue caused by inflammation, causing a physical change in the tongue. This disease causes the tongue to swell and enlarge, change color, and there is a change in the structure of the upper surface of the tongue.
Inflammation due to glossitis usually occurs in the papilla, which is a group of nodules that give a texture over the surface of the tongue. The papilla is an important organ for tasting food, so it can cause changes in diet in people with glossitis. Inflammation in the upper part that causes pain can also affect the way you talk.
Symptoms of glossitis can occur on one part or almost the entire surface of the tongue. Inflammation of the tongue can also move around certain parts of the tongue. Episodes of glossitis tend to be short, but symptoms can recur and disappear for up to one year.
Types of glossitis based on their appearance
Glossitis has a development of non-specific diseases, because inflammation of the tongue can occur in several ways. The types of glossitis are distinguished as follows:
Acute glossitis - inflammation of the tongue appears suddenly and tends to be serious. This is usually due to an allergic reaction to the tongue.
Idiopathic glossitis - caused by inflammation of the tongue muscle and accompanied by loss of part of the papilla on the inflamed part of the tongue. The cause of this type of glossitis is unknown.
Chronic glossitis - type of glossitis that can be lost and recurred, usually caused by factors of malnutrition or other diseases.
Atrophic glossitis - a disease characterized by changes in the color and texture of the tongue due to the loss of almost all tongue papillae. Usually the tongue turns dark reddish.
What are the causes of swollen tongue glossitis?
The occurrence of glossitis can be influenced by genetic factors inherited in one family. But the appearance of inflammation in the tongue can be caused by several things, including:
- Allergic reactions - Hypersensitivity of the papilla and tongue muscles can be triggered by various irritants from food, diuretic drugs, diabetes medications, high blood pressure-lowering drugs and toothpastes.
- Infectious disease - the presence of inflammation can be triggered by streptococcus bacterial infection in the mouth, and indirectly herpes simplex disease can affect immunity and attack the muscles and papilla of the tongue causing inflammation and swelling.
- Dry mouth - lack of saliva produced by the salivary gland can cause the tongue to become inflamed, but this can be triggered by other diseases that attack the salivary gland or dehydration.
- Malnutrition - is a sign of iron, folate and vitamin B12 deficiency. Glossitis can also occur together with the condition of anemia in someone.
- Trauma to the mouth - pressure marks or open sores on the mouth often affect the tongue. The presence of rough surface friction such as those caused by braces can cause injury and trigger glossitis.
In general, glossitis can happen to anyone, but the risk of glossitis can increase if a person experiences a decrease in immunity, chronic inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis, and has a hole in the tongue (fissured tongue) Glossitis is also more common in people who often eat hot food, spicy food, and have smoking habits.
How to deal with swollen tongue due to glossitis
In general, pain and symptoms of glossitis can disappear on their own without specific treatment, along with the causes of glossitis such as anemia and the body's power begins to improve. Here are a few things you can do:
Take antibiotics - it may be needed if the infection-causing bacteria are present in the mouth and if the infection is caused by spread from other body parts.
Maintain oral health - done by maintaining cleanliness and handling holes or abscesses in the teeth and gums correctly. It is necessary to prevent repeated transmission and infection of the tongue.
Overcoming pain - in some cases, pain can be sustained so it needs to be dealt with by taking painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, applying corticosteroids to the tongue or by consuming zinc.
Avoid inflammatory triggers - Some substances can aggravate inflammation and inhibit inflammation healing, so when healing needs to avoid allergenic foods if there are, consumption of cigarettes, whitening agents on toothbrushes, hot foods and foods with a spicy, sour, salty and oily taste.