Contents:
- Medical Video: 6 SIGNS THAT YOU MAY HAVE HIGH CHOLESTEROL
- What is dyslipidemia?
- Factors that affect blood fat levels
- 1. Genetic
- 2. Age
- 3. Lifestyle
- 4. Anti-cholesterol drugs
- Symptoms of dyslipidemia
- How to overcome dyslipidemia?
- 1. Regulate dietary intake or diet
- 2. Increase physical activity
- 3. Weight loss
- 4. STOP smoking
Medical Video: 6 SIGNS THAT YOU MAY HAVE HIGH CHOLESTEROL
Obesity or obesity is a scourge for us. In addition to less attractive appearance factors, obesity is a risk factor for many diseases. Obesity is always associated with a lot of fat, but do you know that high fat levels not only attack fat people? People who are in an ideal posture also can suffer from this one disease. People call it high cholesterol, even though what happens is an imbalance between good cholesterol and bad cholesterol. This disease is called dyslipidemia.
What is dyslipidemia?
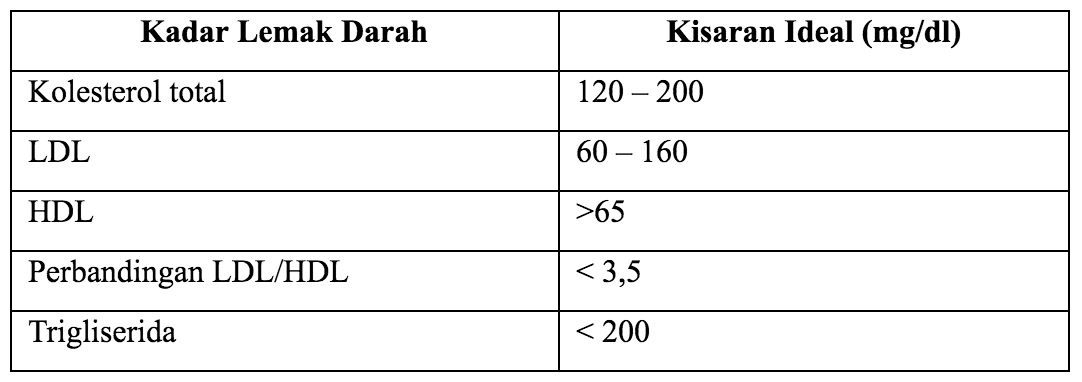
Before we talk about dyslipidemia, we must recognize the types of fat in our body, namely LDL (low-density lipoprotein or bad cholesterol), HDL (high-density lipoprotein or good cholesterol), triglycerides (the result of excess consumption of carbohydrates that are converted to fat), and total cholesterol (accumulation of all three types of cholesterol). Dyslipidemia is a disorder of fat metabolism characterized by an increase or decrease in the type of fat in blood plasma.
The main types of fat abnormalities were increased total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides, and decreased HDL cholesterol levels. So, these 3 things must be fulfilled when a person has dyslipidemia, not just high cholesterol. Normal fat levels must be maintained, but what is the normal level to be achieved?
Fat levels can be known through blood tests. Usually someone is advised to fast before doing this examination. The duration of fasting is 10-12 hours.
Factors that affect blood fat levels
1. Genetic
This factor has the most important role in determining a person's total cholesterol level. A person's cholesterol level can be low or high according to his genetic condition. These genetic conditions are very numerous, including familial hypercholesterolemia, familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency, and hepatic lipase deficiency.
2. Age
Increasing age, organ function will decline as well. Decreasing organ function will affect one's cholesterol metabolism process.
3. Lifestyle
Physical activity, high-fat diet, smoking, and alcohol consumption are examples of behaviors that significantly affect one's cholesterol level. The more often you do this, the cholesterol levels can also increase sharply.
4. Anti-cholesterol drugs
The use of anti-cholesterol drugs such as simvastatin will certainly affect one's blood cholesterol level. Simvastatin lowers cholesterol levels through inhibition in the synthesis or production of cholesterol.
Symptoms of dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia usually does not show symptoms, especially if the person's posture looks thin or ideal. However, there are some symptoms that, although not so typical, are often found in people with dyslipidemia, namely:
- Abdominal pain
- Dizzy
- Chest pain
- Hard to breathe
- Headache, especially at the nape of the neck
- Drastic reduction or weight gain
- Calf pain when walking
How to overcome dyslipidemia?
If you already have blood fat levels above normal, don't be discouraged. Apart from consuming anti-cholesterol drugs, there are a number of things you can do to achieve ideal fat levels.
1. Regulate dietary intake or diet
- Limit your intake of trans fats such as fried foods, crackers, cookies, bread and donuts.
- Limit consumption of carbohydrates to less than 60% of the daily menu. Foods like rice, noodles and pasta can increase triglycerides, because excess sugar will be converted into this type of fat.
- Increase consumption of omega 3 and omega 6 from fish or fish oil. Consumption of these foods can increase HDL (good cholesterol) and reduce triglycerides.
- Diets high in fiber such as nuts, fruits, vegetables and whole-grain cereals that have a hypocholesterolemic effect.
2. Increase physical activity
Effect of physical activity, especially the decrease in triglycerides and increase in HDL cholesterol. Aerobic exercise can reduce triglyceride concentrations by up to 20% and increase HDL cholesterol concentrations to 10%. However, without a diet and weight loss, physical activity has no effect on total cholesterol and LDL. The recommended physical activity is measurable activities such as brisk walking 30 minutes per day for 5 days per week or other activities equivalent to 4-7 kcal / minute.
Some of the activities you can do are:
- Sweep the page for 30 minutes
- Run fast (4.8-6.4 km per hour) for 30-40 minutes
- Swim - for 20 minutes
- Cycling for pleasure or transportation, a distance of 8 km in 30 minutes
- Play volleyball for 45 minutes
- Using a lawn mower that is pushed for 30 minutes
- Cleaning the house (on a large scale)
- Play basketball for 15 to 20 minutes
3. Weight loss
Normal waist circumference for Asia is a maximum of 90 cm for men and a maximum of 80 cm for women. Every 10 kg decrease in body weight is associated with a decrease in LDL cholesterol of 8 mg / dL. Every 1 kg decrease in body weight is associated with an increase in HDL cholesterol of 4 mg / dL and a decrease in TG concentration of 1.3 mg / dL.
4. STOP smoking
Stopping smoking can increase the concentration of HDL cholesterol by 5-10%. Smoking is also associated with an increase in the concentration of triglycerides, so if you stop smoking, it will also be beneficial for changes in triglyceride levels.