Contents:
- Medical Video: 10 Traits of Toxic Parents Who Ruin Their Children’s Lives
- Nutrition problems in Indonesia are under control
- 1. Lack of vitamin A (KVA)
- 2. IDD
- 3. Anemia
- Unresolved nutritional problems in Indonesia
- 1. Poor nutrition
- 2. Stunting
- What nutritional problems most threaten public health?
Medical Video: 10 Traits of Toxic Parents Who Ruin Their Children’s Lives
Nutritional problems are very complex and important things to overcome. Especially because Indonesia is one of the countries that has the most complete nutrition problems. Some studies say that nutritional problems in Indonesia tend to continue to increase, not comparable with some other ASEAN countries such as Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand.
Reporting from the page of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia, the development of nutritional problems in Indonesia can be grouped into three, namely controlled nutrition problems, unresolved problems (un-finished), and nutritional problems that have increased and threaten public health (emerging).
Nutrition problems in Indonesia are under control
1. Lack of vitamin A (KVA)
Vitamin A deficiency (KVA) is one of the nutritional problems in Indonesia that is commonly experienced by children and pregnant women. Even though this is a nutritional problem that can be controlled, vitamin A deficiency can be fatal if it is not immediately treated.
In children, vitamin A deficiency can cause visual disturbances to blindness and increase the development of diarrhea and measles. While for pregnant women who are deficient in vitamin A, there is a high risk of experiencing blindness or even death during labor.
Don't worry, vitamin A deficiency can be prevented by giving vitamin A capsules. Vitamin A capsules are given twice a year in February and August, from the age of six months. Red capsules (100,000 IU doses) are given for infants aged 6-11 months and blue capsules (dose of 200,000 IU) for children aged 12-59 months.
2. IDD
Your body needs iodine to make a chemical known as thyroid hormone. This thyroid hormone controls the metabolism and other important functions of the body. Iodine deficiency or IDD (Iodine Deficiency Disorders) is indeed not the only cause of low thyroid levels in the body. However, lack of iodine can cause an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, known as goiter.
To overcome this problem, the government has required that all the salts in circulation must contain iodine at least 30 ppm. How about you, have you used iodized salt?
3. Anemia
Anemia is a condition when the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to the body's tissues. This health problem is most commonly found in pregnant women with symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, pallor, irregular heartbeat, and headaches.
Based on data taken from Basic Health Research in 2013, more than 15 percent of children under five and 37 percent of pregnant women had anemia. Studies show that anemic pregnant women have a risk of dying in labor up to 3.6 times greater due to bleeding and or sepsis.
To prevent anemia, pregnant women are encouraged to consume at least 90 iron pills during their pregnancy. The iron in question is all iron consumption during pregnancy, including over-the-counter or multivitamin containing iron.
Unresolved nutritional problems in Indonesia
1. Poor nutrition
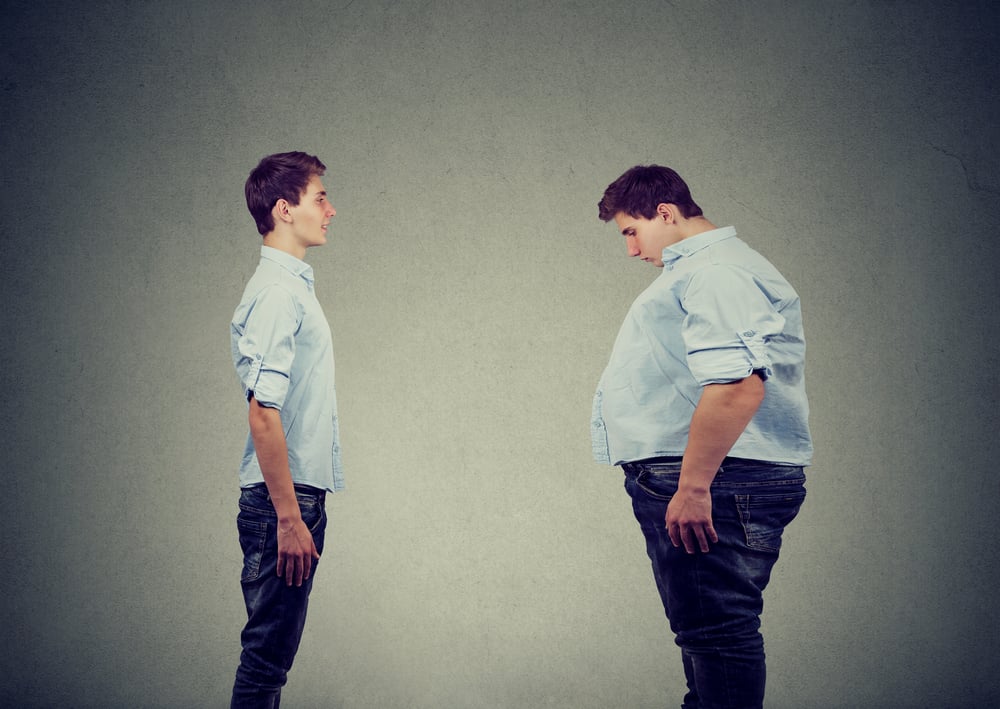
A thin body due to malnutrition is often judged to be better than a fat body due to over nutrition, when in fact it isn't. Just like obesity, children and adolescents with nutrition lack risks to their health. Well, you can measure your nutritional status category through this BMI calculator.
Babies born with low birth weight (LBW) generally will experience an unfavorable future life. Because the nutritional needs that are not fulfilled during the growth period of toddlers will increase their susceptibility to infectious diseases at the beginning of their lives and last until he grows up. Some of the risks of malnutrition include the following:
- Malnutrition, vitamin deficiency, or anemia
- Osteoporosis
- Decreased immune function
- Fertility problems caused by irregular menstrual cycles
- Problems of growth and development, especially in children and adolescents
2. Stunting
Stunting is a chronic malnutrition condition caused by long-term lack of nutrition, generally due to feeding which is not in accordance with nutritional needs. Stunting occurs from the womb and only seen when the child is two years old. Symptoms stunting including:
- Child's posture is shorter than that of his age
- The proportion of the body tends to be normal, but the child appears younger or smaller for his age
- Low weight for children his age
- Delayed bone growth
In 2013, as many as 37.2 percent of toddlers in Indonesia experienced stunting. This condition is often considered normal because of hereditary reasons. Even though, stunting can affect brain development, reduce a person's productivity at a young age, and increase the risk of developing non-communicable diseases in old age. Stunting also considered as one of the risk factors for diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and death from infection.
The best time to prevent stunting is to start from the beginning of pregnancy for the first two years of a child's life. Therefore, the nutritional needs of pregnant women must be fulfilled to optimize fetal development. In addition, exclusive breastfeeding and balanced nutrition for toddlers need special attention so that children do not grow short or stunting.
What nutritional problems most threaten public health?
Based on global nutrition reports or Global Nutrition Report in 2014, Indonesia was included in 17 countries which had 3 nutritional problems at once, namely stunting (short), wasting (thin), and overweight or over nutrition (obesity).
More nutrition, commonly known as obesity, is included in nutritional problems that threaten public health. More nutrition or obesity is an abnormal or excess fat condition that is serious in adipose tissue which can interfere with health. Come on, check your nutritional status category through this BMI calculator to find out if you include over nutrition or not.
The most basic causes of over nutrition are energy imbalances and calories consumed with the amount released. In both groups of children, adolescents and adults, the prevalence of over nutrition continues to increase by almost one percent every year. If since childhood the child has been obese, then they will be more susceptible to non-communicable diseases as adults, such as diabetes and heart disease.
To maintain a balanced and ideal body weight, you need to change your healthy lifestyle by limiting the consumption of foods high in fat and sugar, increasing consumption of fruits and vegetables, and regular physical activity.