Contents:
- Medical Video: 21 Amazing Vitamin E Uses & Benefits For Hair Growth, Skin & Face
- What are the consequences if the child lacks vitamin E?
- How much vitamin E does my child need?
- List of food sources of Vitamin E
Medical Video: 21 Amazing Vitamin E Uses & Benefits For Hair Growth, Skin & Face
Unlike other vitamins or minerals (eg calcium, iron, and vitamin D), most parents in general are not worried that their baby will not get enough vitamin E intake.
The reason is that children consume many food sources of vitamin E, such as vegetable oil, peanut butter, and breakfast cereals enriched by vitamin E.
What are the consequences if the child lacks vitamin E?
Vitamin E deficiency can result in cystic fibrosis, chronic liver cholestasis, abetalipoproteinemia, short-bowel syndrome, vitamin E deficiency syndrome, and other malabsorption syndromes which can lead to a number of nerve disorders. 1 milligram is equivalent to 1.5 international units (IU)
How much vitamin E does my child need?
- Ages 1-3 years: 6 milligrams (mg), or 9 IU of vitamin E every day
- Age 4 - 8 years: 7 mg, or 10.5 IU per day
Most children don't get enough vitamin E from food alone, but chronic vitamin E deficiency that causes health problems is usually quite rare. Getting vitamin E less than the recommended amount is a case that is common in children and adults.
You do not have to fill all the total RDA of vitamin E for your child in one day. Alternatively, you can pay attention to the fulfillment of your child's vitamin E intake to fit the average number of recommendations in a few days or per week.
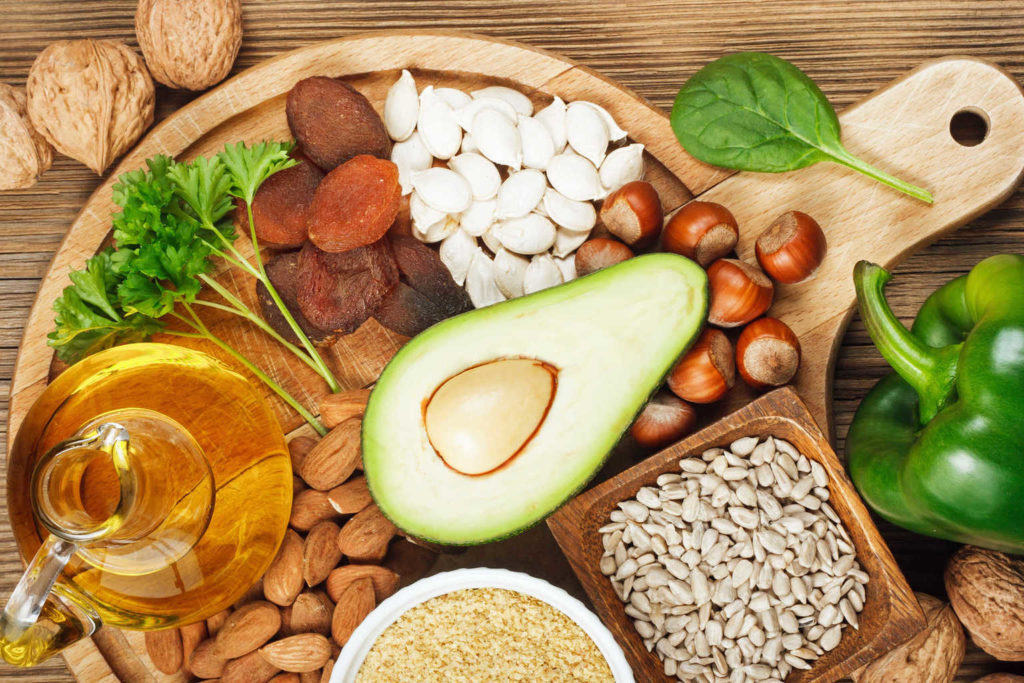
List of food sources of Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Some food sources rich in vitamin E are:
- 1 ounce of roasted almonds, without oil (28 g): 7 mg
- 1 teaspoon wheat germ oil (15 ml): 6 mg
- 1 ounce of sunflower seeds, roasted, without oil (28 g): 6 mg
- 1 tbsp almond butter (16 g): 4 mg
- 1 tbsp sunflower seed jam (16 g): 4 mg
- 1 tbsp peanut butter (16 g): 2 mg
- 1 ounce of roasted peanuts, without oil (28 g): 2 mg
- 1 teaspoon of sunflower oil (5 ml): 1.8 mg
- 1 teaspoon of safflower oil (5 ml): 1.5 mg
- 1/2 medium kiwi fruit, peeled (38 g): 1 mg
- 1 teaspoon of corn oil (5 ml): 0.6 mg
- 1/4 cup spinach, boiled / team (39 g): 0.8 mg
- 1/4 cup of broccoli, boiled / team (46 g): 0.6 mg
- 1 teaspoon of soybean oil (5 ml): 0.4 mg
- 1/4 cup of fresh mango (30 g): 0.9 mg
Vitamin E levels contained in foods will vary depending on the size of the vegetables or fruits, or the brand of the product chosen. Keep in mind that nuts and seeds can make small children choke and peanut butter should be given in a thin spread.
Your child may eat less or exceed the average amount of food mentioned above, judging by his age and appetite. Estimate the nutritional content according to your child's needs.
It is very possible for your child not to get enough of these important nutrients, because vitamin E works as an anticoagulant which increases the chance of the risk of bleeding problems.
Children aged 2 - 3 years cannot get more than 200 mg (300 IU) of vitamin E per day. Children aged 4 - 8 cannot get more than 300 mg (450 IU) of vitamin E per day.