Contents:
- Medical Video: Prenatal Genetic Testing with Dr. Gayatri Chhatre, OB/GYN
- What are chromosomal abnormalities?
- How to detect chromosomal abnormalities?
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Medical Video: Prenatal Genetic Testing with Dr. Gayatri Chhatre, OB/GYN
Mother must have taken care of her pregnancy so that her baby would be born healthy. However, sometimes some babies can be born with chromosomal abnormalities that are not known to be the cause. Actually, there are ways to find out whether the baby in the womb has chromosomal abnormalities or not, which is done before the baby is born.
What are chromosomal abnormalities?
Before discussing how to detect it, what must be done to find out if the baby has chromosomes or not, we should first know what chromosomal abnormalities are.
Chromosomal abnormalities occur when there are defects in the chromosome or in the genetic makeup on the chromosomes in the womb. This chromosomal abnormality can be in the form of additional material that may be attached to the chromosome or the presence of part or all of the missing chromosomes, or defective chromosomes.
Any addition or decrease in chromosome material can interfere with normal development and function in the baby's body. So there are many different types caused by this chromosomal abnormality. For example, Down syndrome has three chromosomes number 21 or Edward syndrome has an additional chromosome number 18, and many more.
How to detect chromosomal abnormalities?
Some tests can be done to detect chromosomal abnormalities during pregnancy, including:
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a test performed to diagnose chromosomal abnormalities and neural tube defects, such as spina bifida. Amniocentesis is done by taking samples from the amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus.
Amniocentesis is usually done by pregnant women who are at high risk of having a chromosomal abnormality at 15-20 weeks gestation (second trimester), but can be done at any time during pregnancy. Pregnant women who have a high risk of having chromosomal abnormalities, among others, are those who will give birth over the age of 35 years or who have performed a maternal serum abnormality screening test.
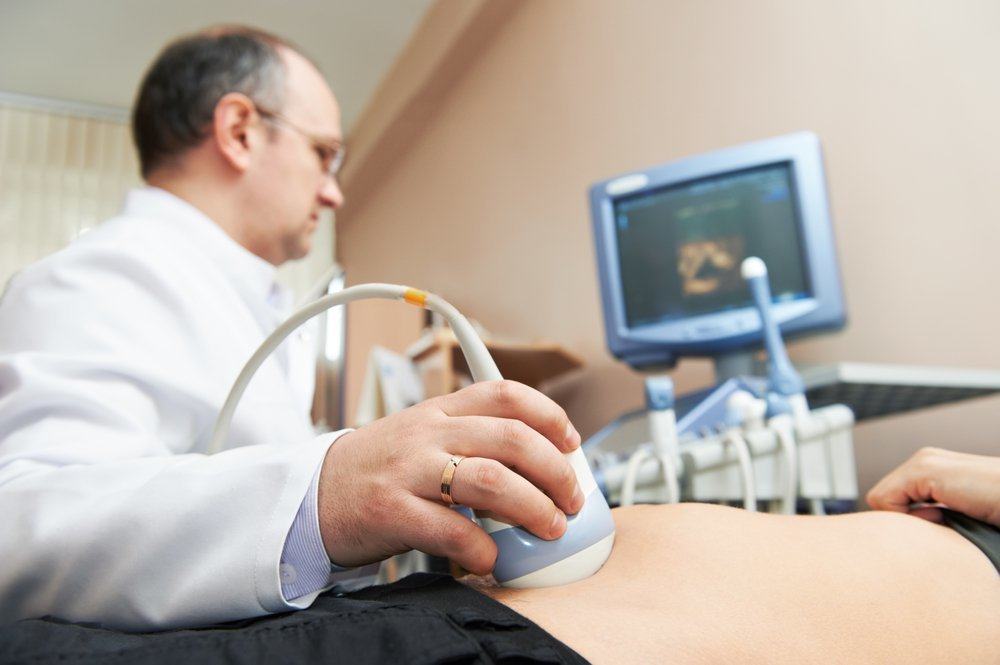
Amniocentesis is done by inserting a needle through the mother's stomach into the baby's amniotic sac in the uterus to get a sample of the baby's amniotic fluid. Help ultrasound needed to guide the insertion and discharge of needles. About three tablespoons of amniotic fluid are then removed through a needle. The cells of the amniotic fluid are then used for genetic testing in the laboratory. The results will usually come out around 10 days to 2 weeks, depending on each laboratory. The risk of miscarriage after amniocentesis is 1/500 to 1/1000 of pregnancy.
Women who are pregnant with twins need to be sampled from each baby's amniotic fluid to study each baby. This depends on the position of the baby and placenta, the amount of fluid, and the anatomy of the woman, because sometimes amniocentesis cannot be done. Keep in mind that amniotic fluid contains baby cells that contain genetic information.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
If amniocentesis involves taking a sample of amniotic fluid, CVS involves taking samples from placental tissue. Tissue in the placenta has the same genetic material as that in the fetus, so this tissue can be tested for chromosomal abnormalities and some other genetic problems. However, CVS cannot test open neural tube defects. Therefore, pregnant women who have had a CVS test may also need a blood test in the second trimester to determine the risk of neural tube defects because CVS cannot provide the test results.
CVS is usually done in pregnant women who have a risk of chromosomal abnormalities or who have a history of genetic defects. CVS can be done at gestational age between 10-13 weeks (first trimester). However, CVS can trigger a risk of miscarriage of around 1/250 to 1/300.
CVS is done by inserting a small tube (catheter) through the vagina or cervix (choose one) into the placenta. The entry and expenditure of these small tubes are also guided by ultrasound. A small piece of placental tissue is then taken and sent to the laboratory for genetic testing. Results from CVS usually come out around 10 days to 2 weeks, depending on each laboratory.
Pregnant women twins usually require samples from each placenta, but this cannot always be done because of the difficulty of the procedure and the position of the placenta. Some pregnant women are prohibited from doing this procedure, such as in pregnant women with active vaginal infections (for example, herpes or gonorrhea). Pregnant women who do not get accurate results after undergoing this procedure may require amniocentesis as a follow-up. Incomplete or inconclusive results can occur because the doctor may take samples that do not have enough tissue to grow in the laboratory.
READ ALSO
- 10 Things You Must Do During the First Trimester of Pregnancy
- Various Things That Cause Women to be Susceptible to Miscarriage
- Factors That Trigger the Risk of Containing a Down Syndrome Baby