Contents:
Medical Video: Breast Cancer in Pregnancy | Gina's Story
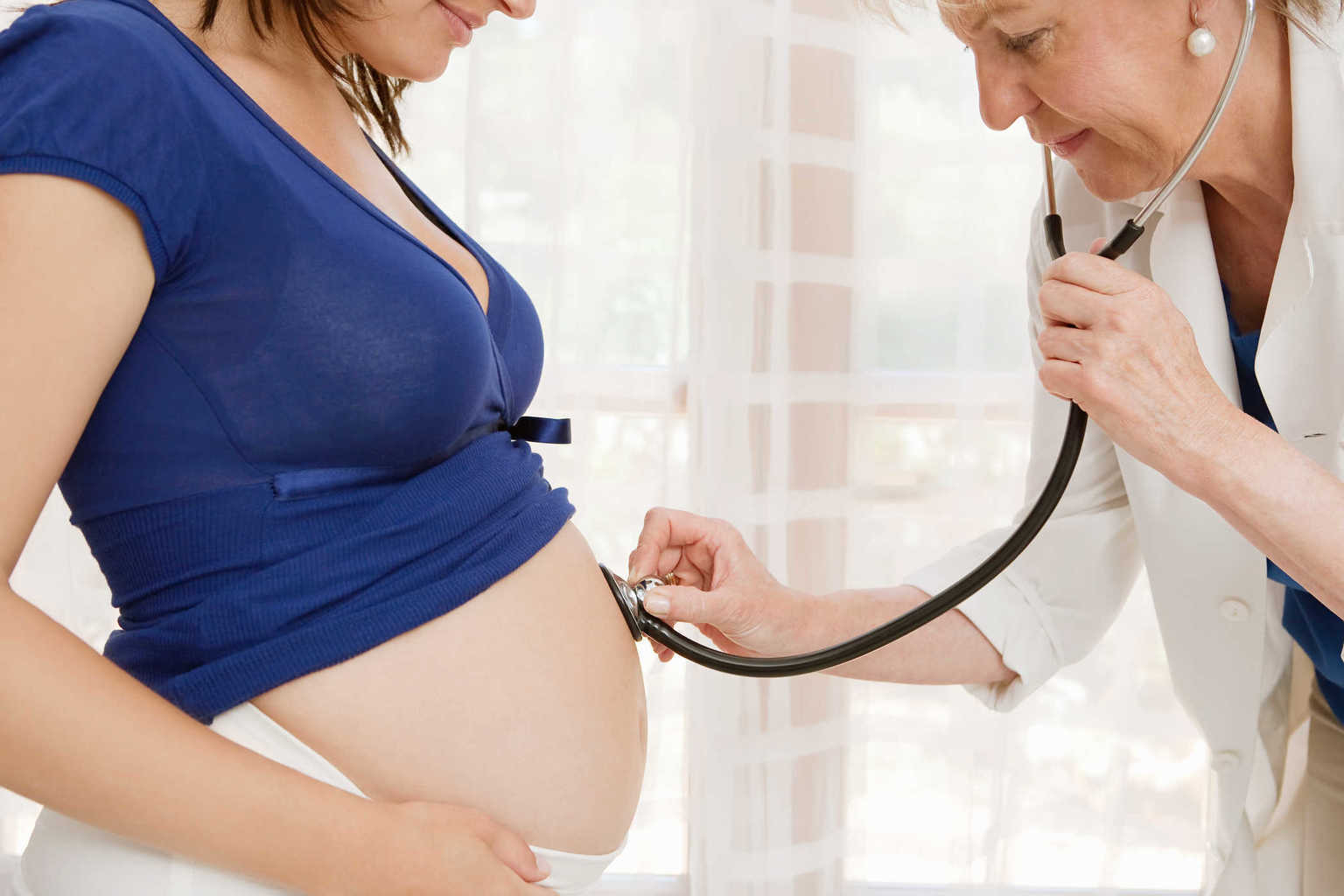
Treatment of breast cancer during pregnancy depends on the trimester of pregnancy and the time of delivery. For those of you who are about to give birth soon, the doctor can delay treatment until the delivery process is over. For those of you who are breastfeeding, the doctor will recommend to stop temporarily before receiving any treatment.
Operation
Surgery can be carried out safely during pregnancy. Many breast cancer sufferers are given the choice between mastectomy and breast conservation surgery. Mastectomy is the surgical removal of all breast tissue including the nipple area, while breast conservation surgery (or commonly called a lumpectomy) is surgical removal of the cancer along with the periphery of the normal breast tissue.
During pregnancy, you may be advised to undergo a mastectomy because not all women need radiotherapy. Unlike a mastectomy, breast conservation surgery needs to undergo radiotherapy.
Radiotherapy is generally not recommended for pregnant women during pregnancy. However, if breast conservation surgery is to be taken, this surgery may be possible during the third trimester and radiotherapy can be given after the baby is born. Because the shape of the breast changes during pregnancy, breast reconstruction generally will not be done in conjunction with a mastectomy. This is also done to avoid taking too long under the influence of anesthesia.
For those of you who are diagnosed in the second trimester and will undergo chemotherapy after surgery, you may also be allowed to take breast conservation surgery rather than a mastectomy. Because the radiotherapy will be given after the chemotherapy treatment is completed and the baby is born.
The specialist will examine the lymph nodes under your arm (you may have had a lymph node biopsy at the time of diagnosis). If the pre-operative test shows a positive result in the presence of cancer cells in the lymph nodes, surgery for total lymph node removal will be recommended. If not, you might be offered a sentinel lymph node biopsy to detect cancer cells in the lymph nodes (or nodes). If a biopsy shows one or more damaged lymph nodes, you may be advised to undergo surgery to remove part or all of the remaining lymph nodes.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy uses very small amounts of radioactive material (radioisotopes) that do not affect pregnancy. However, blue dyes used with radioisotopes to identify sentinel nodes are generally not recommended during pregnancy.
Whatever type of surgery you undergo will still involve general anesthesia. Although the use of anesthesia is safe for pregnant women, the risk of miscarriage in early pregnancy still exists even though it is very rare.
Chemotherapy
A series of chemotherapy treatments can be given during pregnancy. The antimual and steroid treatments needed to control the side effects of chemotherapy are safe for pregnant women. Generally, chemotherapy should be avoided before gestational age reaches the second and third trimesters. Because, chemotherapy carried out in the first trimester can harm the baby and can trigger a miscarriage. Women who undergo chemotherapy during pregnancy can still have healthy babies, although there is some evidence that shows the risk of premature babies and low body weight. As a precautionary measure, you are advised to stop chemotherapy for three to four weeks before the due date to avoid complications such as infection during or after labor. Chemotherapy can be resumed after your baby is born.
During chemotherapy, you are not allowed to breastfeed for a while because some chemotherapy drugs pass through the bloodstream and enter the milk.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is usually not recommended for pregnant women. The reason is that very low doses can still bring risks to your baby. If you are diagnosed in the second trimester and will undergo chemotherapy, you may be able to undergo radiotherapy after delivery. If you have been diagnosed in the third trimester of pregnancy and will undergo breast conservation surgery, radiotherapy may be delayed until delivery and after chemotherapy is complete.
Endocrine hormone therapy
If your breast cancer contains estrogen positive receptors (which means the hormone estrogen stimulates the growth of breast cancer cells), you might be advised to undergo hormone therapy. It is less likely for pregnant women with breast cancer to have positive estrogen receptors when compared to non-pregnant women. The most commonly prescribed hormone therapy for young women diagnosed with breast cancer is tamoxifen and goserelin (Zoladex). Both of these drugs cannot be given during pregnancy or breastfeeding. We have a booklet about these two drugs.
Targeted cancer therapy (sometimes called biological therapy)
As the name implies, this therapy specifically targets cancer cells and inhibits the growth process. The most widely used target therapy is trastuzumab (Herceptin), which is used to treat HER2 breast cancer (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) positive. Generally, targeted therapy is not recommended during the pregnancy period. In addition, breastfeeding activities should be suspended while undergoing trastuzumab or within six months of the last dose.
READ ALSO:
- Can I get pregnant after breast cancer treatment?
- How to diagnose breast cancer while pregnant
- Underwent a pregnancy with breast cancer