Contents:
Medical Video: Diabetes A1c Test
Definition
What is glycohemoglobin?
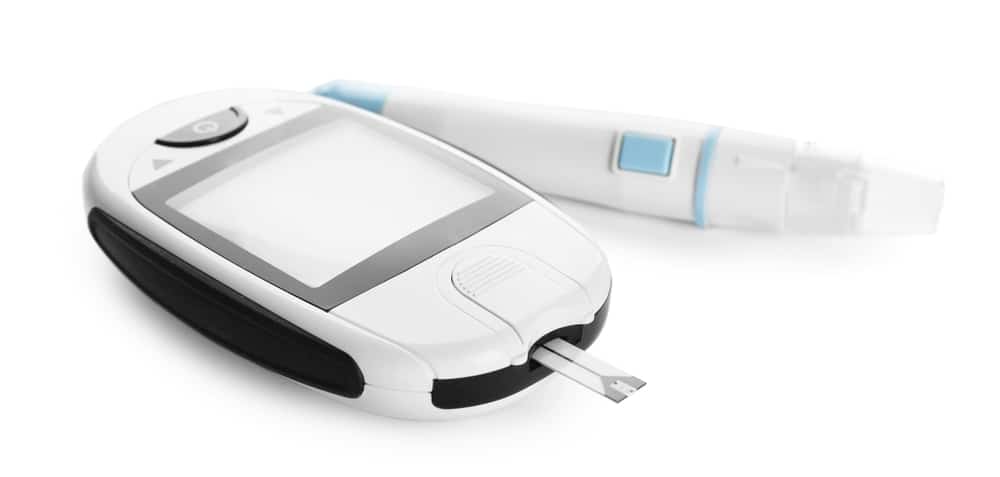
The glycohemoglobin test or hemoglobin A1c is a test that serves to determine the amount of glucose in red blood cells. When hemoglobin and glucose unite, a layer of sugar is formed in the hemoglobin. If the layer gets thicker, then the amount of sugar in the blood will increase. This A1c test serves to check the thickness of the sugar layer in the blood for the last 3 months (the same as the age of red blood cells). People who have diabetes or other diseases with problems with glucose will have more hemoglobin than normal people.
The home tests carried out to measure blood glucose levels can only be done temporarily because glucose levels in the blood can change for several days due to several factors, such as medication, diet, exercise, and the amount of insulin in the blood.
This test is useful for diabetics to control blood sugar over a long period of time. The A1c test results will not change due to changes in diet, exercise, or medication.
Glucose binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells under normal conditions. Because the age of red blood cells in the body is only about 3 to 4 months, this A1c test will show how much glucose is present in blood plasma. This test will show how successful you have been in controlling your diabetes for 2 to 3 months and whether your diabetes treatment needs to be replaced.
The A1c test also helps doctors determine how much side effects your diabetes can cause, such as kidney failure, vision problems, or foot numbness. Maintaining your A1 test results in good conditions can reduce the occurrence of side effects.
When do I have to undergo glikohemoglobin?
This test is usually done 2 to 4 times a year, depending on the type of diabetes you suffer, how well you control it, and advice from your doctor.
If this test is done to diagnose diabetes, before the test is done you should recognize the following symptoms of prediabetes:
- feeling thirsty fast
- frequent urination
- easily tired
- blurred vision
- old infection healed
Prevention & warning
What should I know before undergoing glycohemoglobin?
The A1c test will not show a temporary and acute increase or decrease in blood glucose, nor will blood sugar control be achieved for 3-4 weeks. A change in a diabetes brittle patient's glucose level will also not be demonstrated by this test.
If a person has varying hemoglobin, for example hemoglobin sickle cell (hemoglobin S or sickle cell), then the amount of hemoglobin A will decrease. This condition can limit the effectiveness of the A1c test in diagnosing or monitoring diabetes levels.
If someone has anemia, hemolysis, or severe bleeding, this A1c test will not work optimally. The same is true for people with iron-deficient (iron deficiency).
Process
What should I do before undergoing glycohemoglobin?
You don't need to fast before this test is done. This test can be done at any time even after eating.
How is the glycohemoglobin process?
The medical personnel who are in charge of taking your blood will take the following steps:
- wrap an elastic belt around your upper arm to stop the blood flow. This makes the blood vessels under the bond enlarge making it easier to inject needles into the vessels
- clean the part to be injected with alcohol
- inject a needle into a vein. More than one needle may be needed.
- attach the tube to the syringe to fill it with blood
- remove the ties from your arms when taking blood is enough
- attach gauze or cotton to the injected part, after the injection is finished
- put pressure on the part and then put on a bandage
What should I do after undergoing glycohemoglobin?
Elastic ties are wrapped around your upper arm and will feel tight. You may not feel anything when injected, or you may feel like being stung or pinched.
You may release plaster and cotton in the injection area after 20 to 30 minutes. Then you will be informed about the results of the test. Make sure you follow the directions from the doctor.
Explanation of Test Results
What do the test results mean?
The diagnosis of diabetes can be obtained by testing the same blood sample again or doing another test the next day. Normal test results known as "reference range" only function as a guide. This reference range is usually different in each laboratory. Your test results will usually follow a reference range guide from the laboratory in question.
| Hemoglobin A1c | |
| Normal | Less than 5.7% |
| Prediabetes (risk of diabetes) | 5.7%–6.4% |
| Diabetes | 6.5% or higher |
The results of the A1c diabetes test in non-pregnant adults (types 1 and 2) are usually less than 7%.
The A1c test results in children (type 2), usually at a rate of 7%.
You should consult your doctor to achieve maximum treatment results.
| A1c% | Average glucose estimation in blood plasma | Average glucose estimation in blood plasma |
| 6% | 126 mg / dL | 7.0 mmol / L |
| 7% | 154 mg / dL | 8.6 mmol / L |
| 8% | 183 mg / dL | 10.2 mmol / L |
| 9% | 212 mg / dL | 11.8 mmol / L |
| 10% | 240 mg / dL | 13.4 mmol / L |
| 11% | 269 mg / dL | 14.9 mmol / L |
| 12% | 298 mg / dL | 16.5 mmol / L |
| Reference to A1c table in children with type 1 diabetes | |
| Age | A1c% |
| Less than 6 years | Less than 8.5% |
| 6-12 years | Less than 8% |
| 13-19 years old | Less than 7.5% |
High yield
Some other health conditions can increase A1c levels, but the results will probably be the same. These health conditions include Cushing's syndrome, pheochromocytoa, and polycystic oravy syndrome (PCOS).
Hello Health Group does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.