Contents:
Medical Video: Sudden Blurred Vision Medical Course
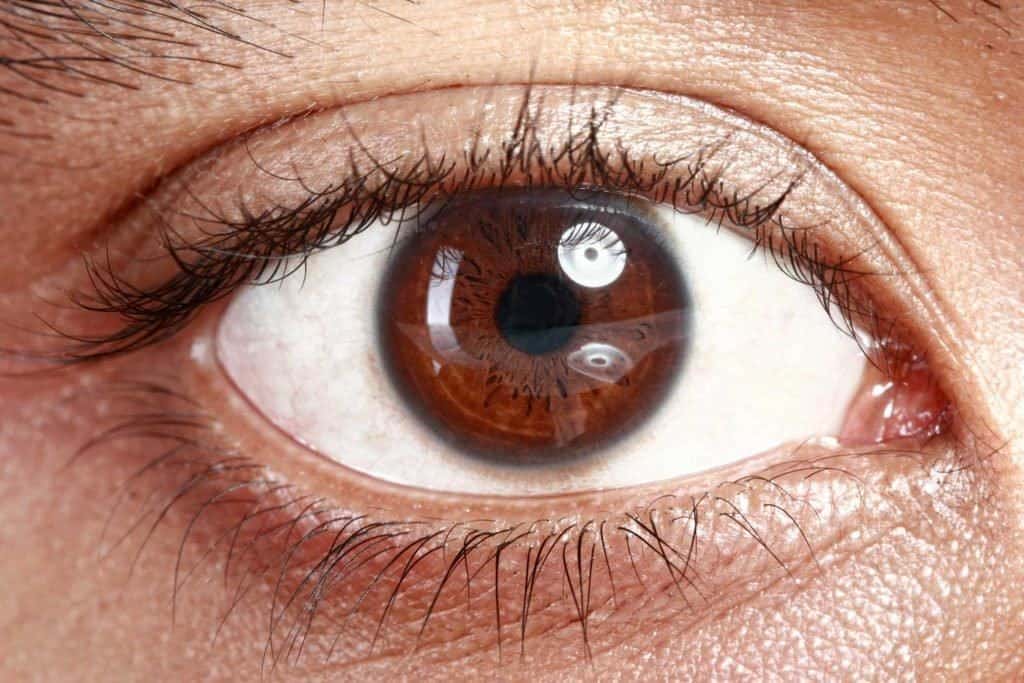
There are certain types of strokes called 'eye strokes', namely strokes in the retinal arteries that occur suddenly and can cause blindness if not treated immediately. If you or a loved one has a retinal artery stroke or retinal artery infarction, you may have questions about the disease.
What is meant by retinal artery infarction?
Retinal arteries are blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the eye.
Retinal artery infarction is caused by a blocked retinal artery which is a disruption of blood flow in the retinal artery. Blockage of blood flow to the eye through the retinal artery causes retinal arterial ischemia. Disruption of blood flow causes damage to the eye due to a process called retinal artery infarction, which is an eye injury that occurs due to chemical changes during and after ischemia. Furthermore, the eye will lose some of its function.
Often, retinal artery strokes cause partial or total blindness, depending on the size of the blockage in the retinal artery.
How do you recognize a retinal artery stroke?
Sudden vision loss is an emergency. This can be a sign of stroke, acute brain injury, heart disease, or other medical problems such as retinal artery strokes. Retinal artery infarction usually only affects one eye and does not cause eye pain.
Can my vision be normal again?
Some people who have a stroke in the retinal artery can get their eyesight again. However, retinal artery strokes can cause permanent blindness on one or more visual sides. The visual side describes the area above, below, right, or left in vision.
You have a better chance of recovery if you immediately get medical help.
What are the important facts about retinal artery infarction?
Retinal artery stroke is associated with stroke risk factors in general, such as heart disease and hypertension. In this case, blood clots move in the body (usually from the heart) and can clog the right or left retinal artery.
However, there are still other causes. Disease or narrowing of one of the carotid arteries in the neck is a trigger factor for stroke, but must be evaluated more thoroughly every time a blockage occurs in the retinal artery because the carotid artery is the main source of blockage.
A condition that is quite rare is called giant arteritis cells caused by inflammation of the blood vessels. Inflammation tends to attack blood vessels in the area of the forehead. This condition is associated with a retinal artery stroke, but is usually not related to brain stroke.
A detailed examination of the eyes is needed to get an evaluation of vision loss and identify retinal artery strokes. After obtaining a diagnosis of retinal artery stroke, a subsequent stroke and its causes will be investigated through a visual examination, determining the part of the retinal arteries that are blocked, imaging studies, blood tests or sometimes biopsies.
After an eye stroke, can I have a bigger stroke in the brain?
Because of several risk factors for brain stroke and retinal artery strokes overlapping, the doctor will evaluate and begin the steps needed. You also need to evaluate yourself if you have had a stroke that does not show symptoms.
Even so, many sufferers of occlusion (blockage) of the retinal arteries do not experience brain strokes. The health team can explain whether you are at risk of a stroke or not, and determine the best countermeasures.